A Comparative Look at Haiti and Cuba: Geography, History, and Culture
Related Articles: A Comparative Look at Haiti and Cuba: Geography, History, and Culture
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comparative Look at Haiti and Cuba: Geography, History, and Culture. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comparative Look at Haiti and Cuba: Geography, History, and Culture

The Caribbean islands of Haiti and Cuba, though geographically close, possess distinct histories, cultures, and landscapes. Understanding their unique characteristics requires a closer examination of their individual geographies, historical trajectories, and cultural expressions. This article explores the complexities of these neighboring islands through the lens of their geographical features, historical narratives, and cultural tapestry.
Geographical Comparisons: Island Landscapes and Natural Resources
Haiti:
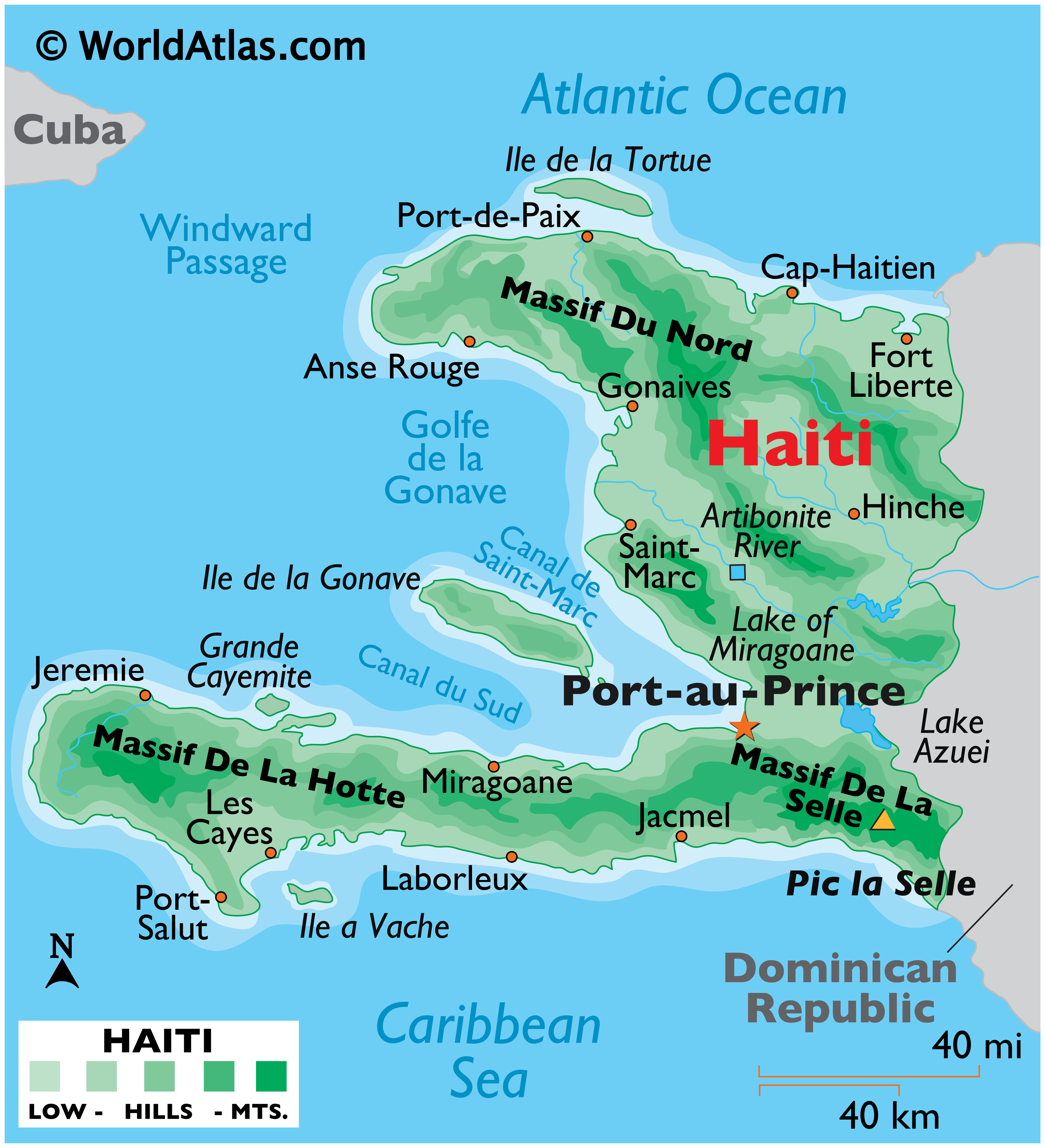
- Island Size: Haiti is the third-largest island in the Caribbean, with a total area of 27,750 square kilometers.
- Terrain: Haiti’s topography is characterized by rugged mountains, fertile valleys, and coastal plains. The Massif de la Hotte, a mountain range in the southwest, reaches elevations of over 2,300 meters.
- Natural Resources: Haiti possesses diverse natural resources, including bauxite, copper, gold, and limestone. However, deforestation and environmental degradation have significantly impacted its natural resource base.
- Climate: Haiti experiences a tropical climate with distinct wet and dry seasons. The island is susceptible to hurricanes and other natural disasters.
Cuba:
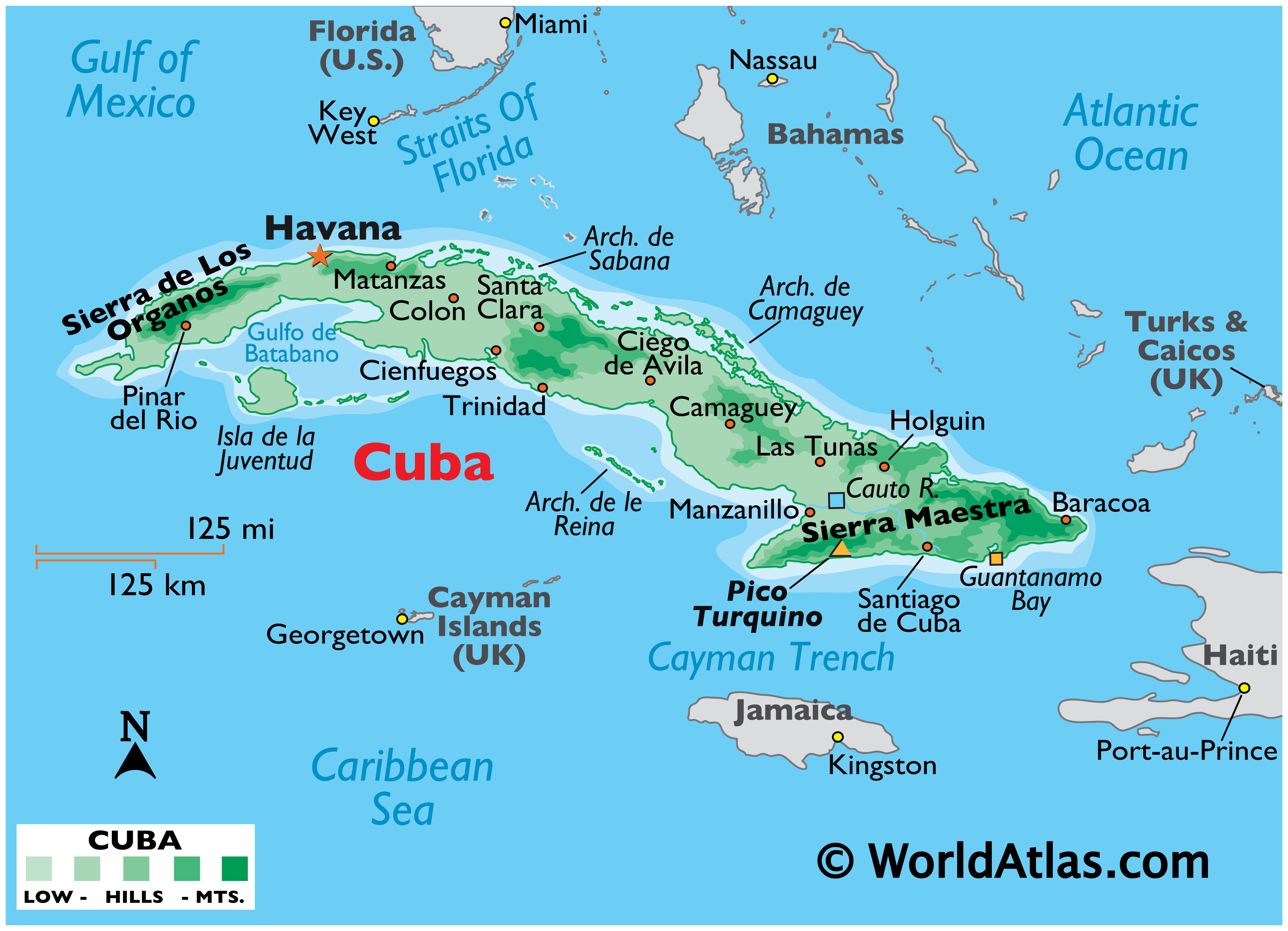
- Island Size: Cuba is the largest island in the Caribbean, with a total area of 110,860 square kilometers.
- Terrain: Cuba features a diverse landscape, ranging from rolling hills and fertile plains to mountainous regions and coastal areas. The Sierra Maestra mountain range, located in the southeast, is home to Cuba’s highest peak, Pico Turquino.
- Natural Resources: Cuba boasts significant natural resources, including nickel, cobalt, iron ore, and petroleum. The island also possesses abundant agricultural land, producing sugarcane, tobacco, and coffee.
- Climate: Cuba enjoys a tropical climate with warm temperatures year-round. The island experiences a distinct wet season from May to October.
Historical Parallels and Diverging Paths:
Shared Colonial Legacy: Both Haiti and Cuba were colonized by European powers, experiencing significant impacts on their societies and cultures. Haiti was a French colony, while Cuba was under Spanish rule. The transatlantic slave trade played a pivotal role in the economic and social development of both islands, leading to the establishment of a predominantly African-descended population.
Revolutionary Upheaval: Both islands witnessed revolutionary movements that sought to break free from colonial control. The Haitian Revolution (1791-1804) was the first successful slave revolt in history, leading to Haiti’s independence. Cuba’s struggle for independence spanned decades, culminating in the Cuban Revolution of 1959, which brought Fidel Castro to power.
Divergent Political Systems: Following their respective revolutions, Haiti and Cuba embarked on distinct political paths. Haiti, despite its early achievements in establishing a republic, has faced political instability and economic challenges throughout its history. Cuba, under communist rule, has implemented a centralized economic system and a one-party state.
Cultural Convergence and Distinctions:
Shared Roots: Both Haiti and Cuba share a rich musical heritage, influenced by African, European, and indigenous traditions. The vibrant rhythms of Haitian Kompa and Cuban Salsa reflect the islands’ shared history and cultural exchanges.
Cultural Divergences: Despite their shared roots, Haiti and Cuba have developed unique cultural expressions. Haitian Vodou, a syncretic religion that blends African beliefs with Catholicism, is a central aspect of Haitian culture. Cuban culture, shaped by its history of Spanish colonialism and communist rule, reflects a distinct blend of Latin American and socialist influences.
Exploring the Importance and Benefits of Understanding Haiti and Cuba:
Understanding the geographical, historical, and cultural nuances of Haiti and Cuba is essential for several reasons:
- Promoting Cultural Appreciation: Examining the unique cultural expressions of both islands fosters greater appreciation for the diversity and richness of Caribbean culture.
- Enhancing Global Understanding: Understanding the historical and political trajectories of Haiti and Cuba provides valuable insights into broader global trends and challenges.
- Fostering Intercultural Dialogue: Recognizing the complexities of these neighboring islands encourages open dialogue and exchange between their respective communities.
- Supporting Sustainable Development: Understanding the environmental challenges faced by Haiti and Cuba can contribute to the development of sustainable solutions for these island nations.
FAQs about Haiti and Cuba:
Q: What are the main differences between Haiti and Cuba in terms of geography?
A: Haiti is smaller than Cuba and features a more rugged terrain dominated by mountains and valleys. Cuba, on the other hand, boasts a more diverse landscape, including rolling hills, fertile plains, and mountainous regions.
Q: How do the historical experiences of Haiti and Cuba differ?
A: Haiti’s history is marked by its successful slave revolt and the establishment of the first black republic in the world. Cuba’s history is characterized by its long struggle for independence from Spain and its subsequent communist revolution.
Q: What are some of the key cultural differences between Haiti and Cuba?
A: Haitian culture is deeply rooted in Vodou, a syncretic religion that blends African beliefs with Catholicism. Cuban culture is a blend of Latin American and socialist influences, with a strong emphasis on music, dance, and literature.
Q: What are some of the challenges facing Haiti and Cuba?
A: Haiti faces significant challenges, including political instability, poverty, and environmental degradation. Cuba, despite its economic achievements, faces challenges related to its centralized economic system and limited political freedoms.
Tips for Learning More about Haiti and Cuba:
- Explore Travel Resources: Travel guides and websites can provide valuable information about the geography, history, and culture of both islands.
- Engage with Local Communities: Connect with Haitian and Cuban communities in your area to gain firsthand insights into their experiences and perspectives.
- Seek Out Educational Resources: Universities, libraries, and museums offer a wealth of resources on the history, culture, and politics of Haiti and Cuba.
- Support Sustainable Tourism: Choose responsible travel options that benefit local communities and promote environmental sustainability.
Conclusion:
Haiti and Cuba, though geographically close, represent distinct island nations with rich histories, diverse cultures, and unique challenges. Understanding their individual characteristics is crucial for fostering global understanding, promoting cultural appreciation, and supporting sustainable development. By engaging with the complexities of these neighboring islands, we can gain a deeper understanding of the Caribbean region and its place in the world.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comparative Look at Haiti and Cuba: Geography, History, and Culture. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!