A Historical Journey Through Asia: Understanding the Map of Colonization
Related Articles: A Historical Journey Through Asia: Understanding the Map of Colonization
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Historical Journey Through Asia: Understanding the Map of Colonization. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Historical Journey Through Asia: Understanding the Map of Colonization

The intricate tapestry of Asian history is woven with threads of both indigenous cultures and external influences, the latter often manifested through colonization. Understanding the map of Asian colonization is crucial for comprehending the continent’s diverse political landscapes, economic development, and social structures. This map, a visual representation of historical power dynamics, reveals a complex narrative of imperial ambitions, resistance movements, and the enduring legacy of colonialism.
A Glimpse into the Past:
The map of Asian colonization is a testament to the global ambitions of European powers, particularly during the Age of Exploration and the subsequent centuries. Driven by economic motives, desire for new markets, and a thirst for raw materials, European nations established vast colonial empires across Asia.
Key Players and Their Impact:
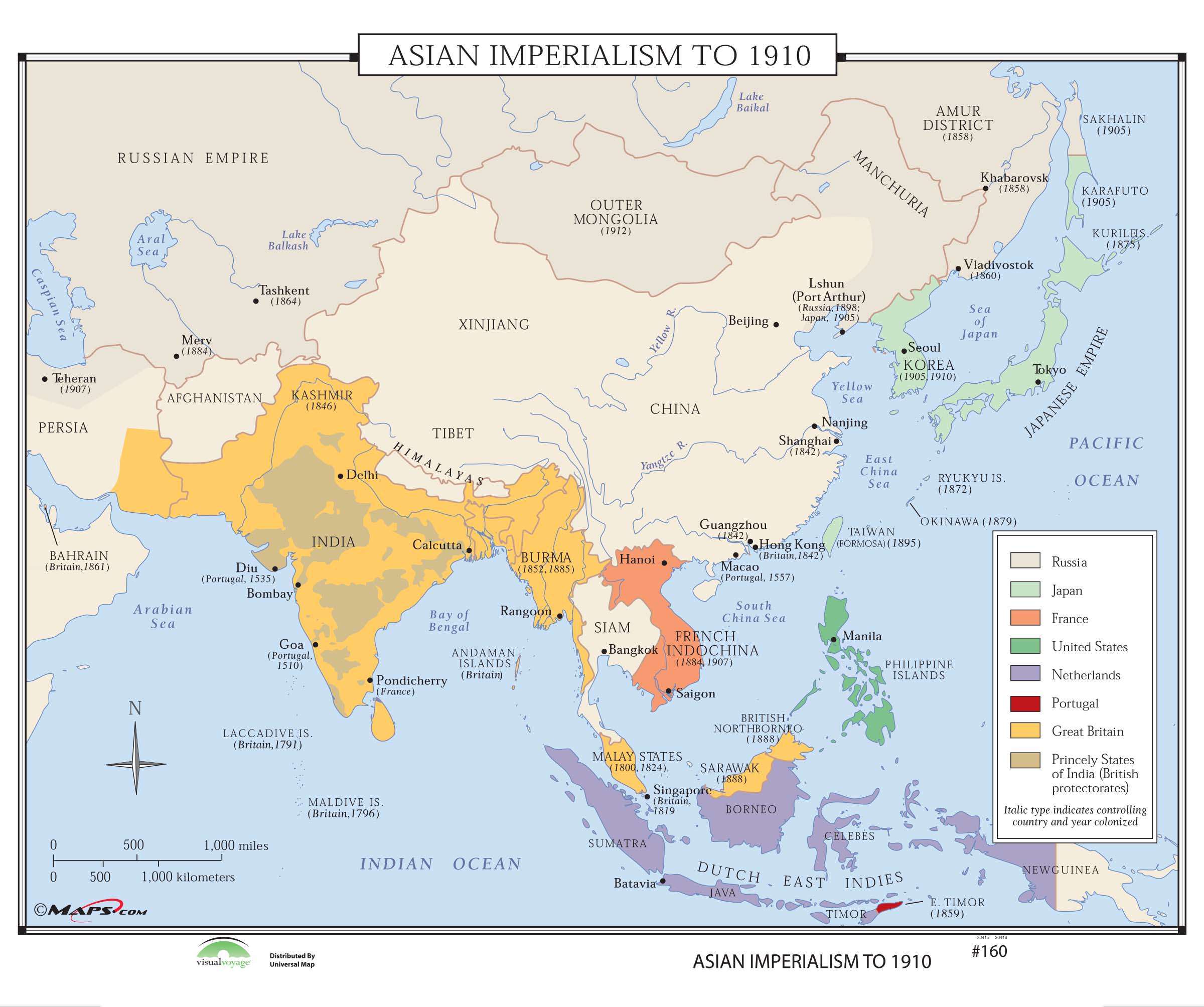
British Empire: The British Empire, with its sprawling network of colonies, had a profound impact on Asia. From India, the "jewel in the crown," to Malaya, Burma, and Hong Kong, British influence reshaped economies, introduced new administrative systems, and left an indelible mark on cultural landscapes.
French Empire: The French established colonies in Southeast Asia, particularly in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia, known collectively as French Indochina. French colonization left a lasting impact on these nations, influencing their political systems, educational institutions, and social structures.
Dutch Empire: The Dutch East India Company, a powerful trading organization, established a vast colonial presence in Indonesia. Dutch rule, marked by exploitation of resources and the imposition of a Dutch-centric system, profoundly impacted Indonesian society and economy.
Japanese Empire: While Japan itself was never a European colony, it rose to become a significant imperial power in Asia during the 20th century. Its expansionist policies, driven by ambitions for resources and regional dominance, led to the colonization of Korea, Manchuria, and parts of China.
The Legacy of Colonialism:
The map of Asian colonization is not just a historical artifact; it represents a complex legacy that continues to shape the continent’s present. The impact of colonialism can be observed in:
- Political Structures: Many Asian nations inherited colonial administrative systems, which have been adapted and reformed over time. However, the influence of colonial frameworks remains evident in government structures, legal systems, and bureaucratic processes.
- Economic Development: Colonial economies were often structured to benefit the colonizing power, leading to uneven development and resource exploitation. The legacy of these economic structures continues to influence trade patterns, industrialization, and economic inequalities within Asian nations.
- Social Structures: Colonial policies often reinforced existing social hierarchies and introduced new divisions based on race, ethnicity, and religion. These divisions have persisted, contributing to social tensions and identity politics in various Asian countries.
- Cultural Landscape: Colonial influence is evident in languages, literature, art, and architecture. The blending of indigenous and colonial cultures has created unique hybrid identities and artistic expressions across Asia.
Beyond the Map:
While the map of Asian colonization provides a valuable framework for understanding the continent’s history, it is important to remember that it is only a partial representation of a complex reality. The map does not capture the nuances of local resistance movements, the diverse experiences of different communities, or the complexities of post-colonial transitions.
Understanding the map of Asian colonization is not simply about charting historical boundaries; it is about appreciating the intricate interplay of power, culture, and identity that shaped the continent’s past and continues to influence its present.
FAQs about the Map of Asian Colonization:
1. What were the main motivations for European colonization of Asia?
European colonization of Asia was driven by a confluence of factors, including economic ambitions for new markets and resources, the desire to establish trading posts and control trade routes, and the pursuit of political and military dominance.
2. How did colonial rule impact Asian economies?
Colonial rule often led to the exploitation of Asian resources for the benefit of the colonizing power. This resulted in the development of economies heavily reliant on primary commodities, with limited industrialization and uneven distribution of wealth.
3. What were the social consequences of colonialism in Asia?
Colonial policies often reinforced existing social hierarchies and introduced new divisions based on race, ethnicity, and religion. This led to social tensions, discrimination, and the marginalization of certain communities.
4. What are some examples of resistance to colonial rule in Asia?
Throughout the history of Asian colonization, there were numerous resistance movements, both large-scale and localized. Examples include the Indian Rebellion of 1857, the Vietnamese resistance against French rule, and the Filipino struggle for independence.
5. What is the lasting legacy of colonialism in Asia?
The legacy of colonialism continues to shape Asia’s political landscapes, economic development, and social structures. The impact can be observed in the persistence of colonial administrative systems, the uneven distribution of wealth, and the lingering effects of social divisions.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Asian Colonization:
- Explore primary sources: Examining firsthand accounts from colonial periods, including diaries, letters, and official documents, can provide a deeper understanding of the experiences of both colonizers and colonized populations.
- Study the diverse perspectives: It is crucial to recognize the varied experiences of different communities within colonized territories. Examining the perspectives of indigenous groups, resistance movements, and marginalized populations can provide a more nuanced understanding of the historical narrative.
- Connect the map to contemporary issues: The map of Asian colonization can be used to analyze current political, economic, and social challenges facing various Asian nations. Understanding the historical context can provide valuable insights into present-day issues.
Conclusion:
The map of Asian colonization is a powerful tool for understanding the continent’s history, but it is not a complete narrative. It is a reminder of the complexities of power dynamics, the enduring impact of colonialism, and the resilience of Asian cultures and societies. By studying this map, we can gain valuable insights into the past, present, and future of Asia, fostering a deeper understanding of the continent’s rich and multifaceted heritage.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Historical Journey Through Asia: Understanding the Map of Colonization. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!