A Vital Tapestry: Understanding the African Forest Map
Related Articles: A Vital Tapestry: Understanding the African Forest Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Vital Tapestry: Understanding the African Forest Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Vital Tapestry: Understanding the African Forest Map

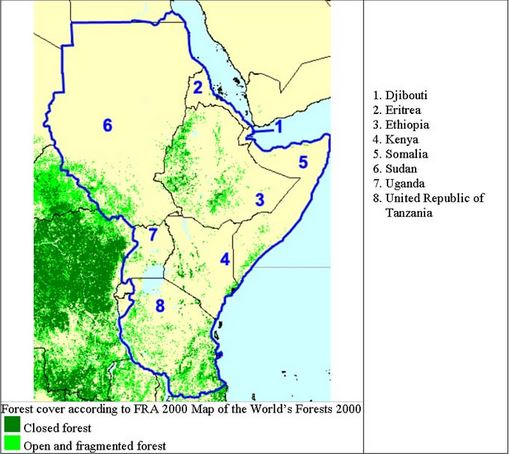
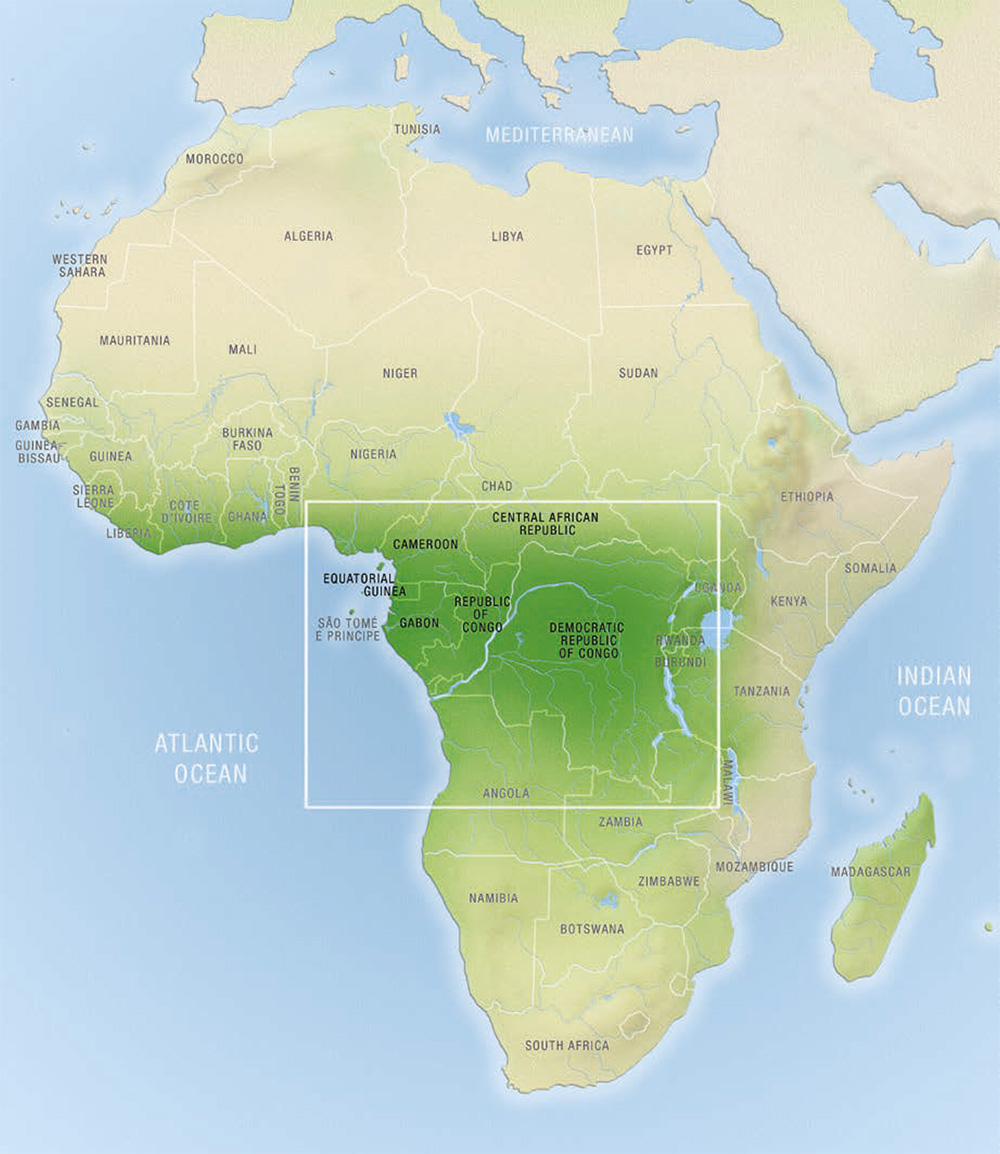
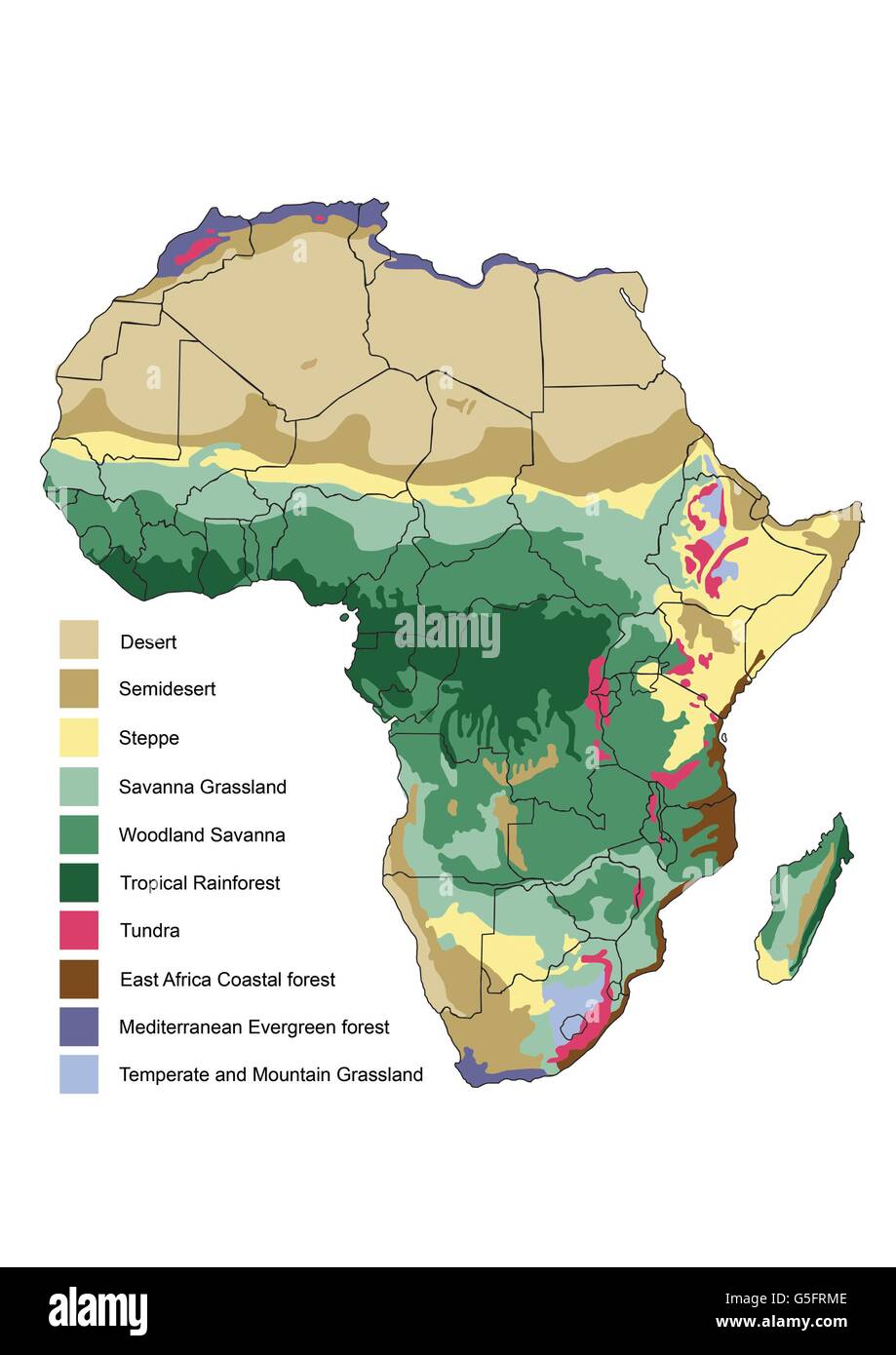
The African continent is a vast and diverse landscape, home to a staggering array of ecosystems, including its iconic forests. These forests, ranging from the dense rainforests of the Congo Basin to the drier woodlands of the Sahel, play a crucial role in the continent’s biodiversity, climate regulation, and the livelihoods of millions of people. Understanding the intricate tapestry of these forests requires a comprehensive and detailed map, one that reveals the distribution, composition, and changes occurring within these vital ecosystems.
The Importance of Mapping African Forests
The African forest map serves as a critical tool for a variety of purposes, providing valuable insights into the state of these ecosystems and informing crucial conservation and management strategies. Its significance lies in its ability to:
-
Document Forest Extent and Distribution: The map acts as a baseline for assessing the overall extent and distribution of forests across the continent. This information is essential for understanding the geographic patterns of forest cover and identifying key areas of biodiversity and carbon storage.
-
Monitor Forest Loss and Degradation: By comparing maps over time, researchers and policymakers can track deforestation rates, identify areas experiencing degradation, and understand the drivers behind these changes. This knowledge is crucial for implementing effective conservation measures and mitigating the impacts of deforestation.
-
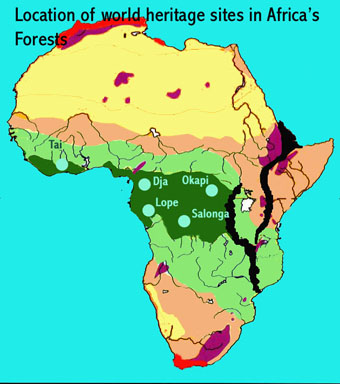
Identify Areas of High Conservation Value: The map helps to pinpoint areas of high biodiversity, unique ecosystems, and important carbon sinks. This information guides conservation efforts and the establishment of protected areas, ensuring the preservation of these vital natural resources.
-
Support Sustainable Forest Management: The map aids in the development of sustainable forest management plans, ensuring the long-term health and productivity of these ecosystems. This includes promoting sustainable harvesting practices, reducing deforestation, and fostering community-based forest management.
-
Inform Climate Change Mitigation Strategies: Forests play a crucial role in mitigating climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. The map helps to identify areas with high carbon storage potential, allowing for targeted interventions to enhance carbon sequestration and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Types of African Forest Maps
Several types of forest maps are used to understand the complexities of the African forest landscape. These include:
-
Static Maps: These maps depict the current state of forest cover, providing a snapshot of the distribution and extent of forests at a specific point in time.
-
Dynamic Maps: These maps capture the changes occurring in forest cover over time, revealing trends in deforestation, degradation, and regeneration.
-
Thematic Maps: These maps focus on specific aspects of the forest landscape, such as species distribution, carbon storage potential, or human population density.
Challenges in Mapping African Forests
Despite the importance of forest mapping, several challenges hinder its effectiveness:
-
Data Availability: Accessing accurate and up-to-date forest data is a major hurdle. This is often due to limited resources, lack of infrastructure, and the remoteness of many forest areas.
-
Technological Limitations: Remote sensing technologies, while valuable, have limitations in accurately mapping forest cover in dense and complex environments.
-
Political Instability: Conflicts and political instability can disrupt data collection efforts and limit access to important areas.
-
Financial Constraints: The cost of mapping projects can be significant, especially in developing countries where resources are often limited.
The Future of African Forest Mapping
Despite these challenges, advancements in technology and collaborative efforts are leading to improvements in African forest mapping. These include:
-
Use of High-Resolution Satellite Imagery: New satellite technologies provide higher resolution imagery, enabling more detailed and accurate forest mapping.
-
Integration of Remote Sensing and Field Data: Combining remote sensing data with ground-truth information from field surveys enhances the accuracy and reliability of forest maps.
-
Development of Open-Source Platforms: Open-source platforms facilitate data sharing and collaboration, enabling researchers and policymakers to access and utilize forest data more effectively.
-
Increased Investment in Forest Monitoring: Growing awareness of the importance of forest monitoring is leading to increased funding and investment in mapping projects.
FAQs on African Forest Mapping
1. What are the main types of forests found in Africa?
Africa is home to a diverse range of forest ecosystems, including:
-
Tropical Rainforests: These forests are characterized by high rainfall, dense vegetation, and a rich diversity of plant and animal life. Examples include the Congo Basin rainforest and the rainforest along the coast of West Africa.
-
Dry Forests: These forests receive less rainfall than rainforests and are dominated by deciduous trees that lose their leaves during the dry season. Examples include the Miombo woodlands of southern Africa and the Acacia woodlands of the Sahel.
-
Montane Forests: These forests occur at higher elevations and are characterized by cooler temperatures and unique plant and animal communities. Examples include the forests of the Ethiopian Highlands and the mountains of East Africa.
-
Mangrove Forests: These forests grow in coastal areas and are adapted to saline conditions. They play a crucial role in protecting coastlines from erosion and providing important habitats for marine life.
2. How is forest mapping used to protect biodiversity?
Forest maps help to identify areas of high biodiversity, allowing for targeted conservation efforts. This includes the establishment of protected areas, the development of species conservation plans, and the monitoring of threatened species.
3. How is forest mapping used to combat climate change?
Forests play a vital role in mitigating climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Forest maps help to identify areas with high carbon storage potential, allowing for targeted interventions to enhance carbon sequestration and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
4. How can I contribute to African forest mapping?
You can contribute to African forest mapping by:
-
Supporting organizations working on forest conservation and mapping.
-
Raising awareness about the importance of forests and the need for their protection.
-
Advocating for sustainable forest management practices.
-
Reducing your own carbon footprint.
Tips for Using African Forest Maps
-
Understand the scale and resolution of the map.
-
Consider the data source and accuracy of the map.
-
Use the map in conjunction with other data sources, such as field surveys and satellite imagery.
-
Interpret the map carefully and avoid drawing hasty conclusions.
Conclusion
The African forest map is an invaluable tool for understanding the state of these vital ecosystems and informing conservation and management strategies. By providing insights into forest extent, distribution, and changes over time, the map empowers policymakers, researchers, and communities to protect these invaluable resources for future generations. Continued investment in mapping technologies, data sharing initiatives, and collaborative efforts are crucial for ensuring the long-term health and resilience of Africa’s forests.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Vital Tapestry: Understanding the African Forest Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!