Demystifying Dementia: A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding The Condition
Demystifying Dementia: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Condition
Related Articles: Demystifying Dementia: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Condition
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Demystifying Dementia: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Condition. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Demystifying Dementia: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Condition
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Demystifying Dementia: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Condition
- 3.1 Understanding the Complexities of Dementia: A Conceptual Framework
- 3.2 Delving into the Different Types of Dementia
- 3.3 Exploring the Underlying Causes of Dementia
- 3.4 Navigating the Challenges of Dementia: Treatment and Management
- 3.5 Understanding the Impact of Dementia on Individuals and Families
- 3.6 Empowering Individuals and Families: Resources and Support
- 3.7 FAQs about Concept Maps and Dementia
- 3.8 Tips for Using Concept Maps for Dementia
- 3.9 Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Understanding
- 4 Closure
Demystifying Dementia: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Condition

Dementia, a debilitating neurocognitive disorder, affects millions globally, impacting individuals and their families profoundly. While research continues to unravel the complexities of this multifaceted condition, a deeper understanding of its nuances can empower individuals to navigate its challenges more effectively.
This comprehensive guide aims to provide a thorough explanation of dementia, its various forms, underlying causes, and potential treatments. It will explore the use of concept maps as a valuable tool for understanding and managing dementia, highlighting their unique benefits for individuals, caregivers, and healthcare professionals.
Understanding the Complexities of Dementia: A Conceptual Framework
Dementia is not a single disease but rather an umbrella term encompassing a range of neurocognitive disorders characterized by progressive decline in cognitive function, impacting memory, thinking, language, and behavior. These cognitive impairments significantly interfere with daily life activities and independent functioning.
Concept maps offer a powerful visual representation of the multifaceted nature of dementia. They provide a structured framework for understanding the various components of the condition, their interrelationships, and their impact on different aspects of an individual’s life.
A typical concept map for dementia might include:
- Central Concept: Dementia
-
Sub-concepts:
- Types of Dementia: Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, Lewy body dementia, frontotemporal dementia, mixed dementia.
- Cognitive Domains Affected: Memory, attention, executive function, language, visuospatial skills, social cognition.
- Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms: Agitation, anxiety, depression, delusions, hallucinations.
- Impact on Daily Life: Difficulty with activities of daily living, social isolation, caregiver burden.
- Risk Factors: Age, genetics, lifestyle, medical conditions.
- Treatment and Management: Medications, therapy, supportive care, lifestyle modifications.
Benefits of Using Concept Maps for Dementia:
- Visual Representation: Concept maps offer a clear and concise visual representation of complex information, making it easier to understand and remember.
- Interrelationships: They highlight the interconnectedness of various aspects of dementia, fostering a holistic understanding of the condition.
- Personalized Approach: Concept maps can be customized to suit individual needs and preferences, allowing for a personalized approach to understanding and managing dementia.
- Communication Tool: They serve as a valuable communication tool between patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals, promoting shared understanding and informed decision-making.
- Educational Resource: Concept maps can be used as educational resources for individuals with dementia, their families, and healthcare professionals, enhancing knowledge and awareness of the condition.
Delving into the Different Types of Dementia
While the concept map provides a broad overview, understanding the specific types of dementia is crucial for effective management and treatment.
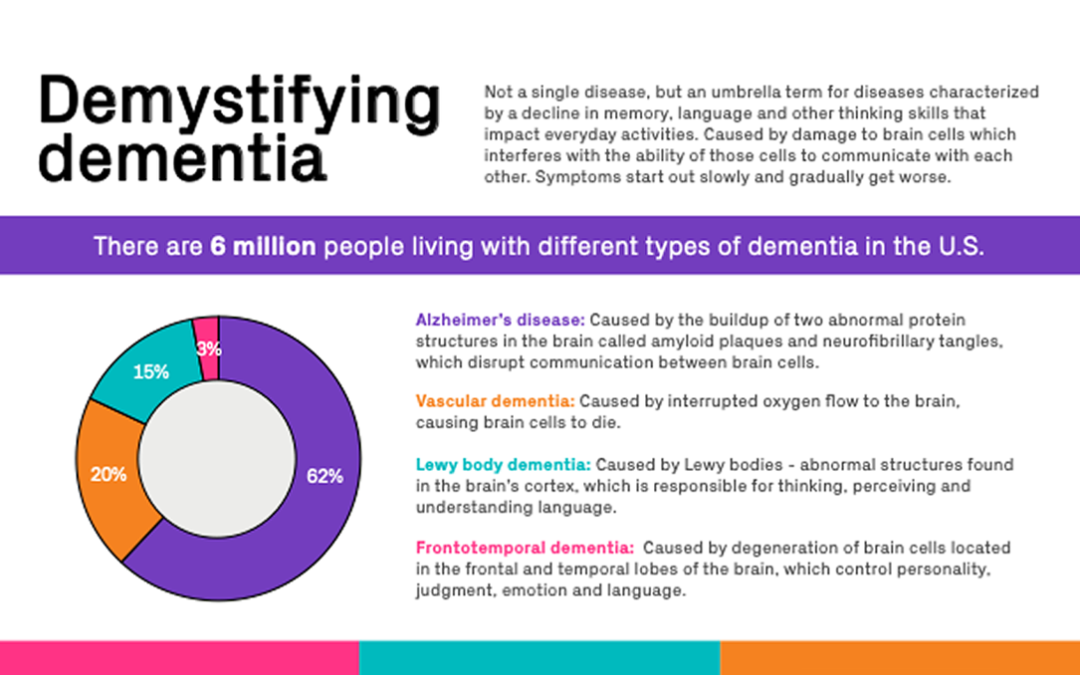
Alzheimer’s Disease: The most common type, accounting for 60-80% of dementia cases, is characterized by the formation of amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain, leading to progressive neuronal damage and cognitive decline.
Vascular Dementia: Caused by damage to blood vessels in the brain, often due to stroke or other vascular events, it results in cognitive impairment and may present with sudden onset or gradual progression.
Lewy Body Dementia: Characterized by the presence of Lewy bodies, abnormal protein deposits in the brain, this type of dementia often presents with fluctuating cognition, visual hallucinations, and movement disorders.
Frontotemporal Dementia: Affecting the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain, it primarily impacts behavior, personality, and language, causing significant changes in social behavior and communication.
Mixed Dementia: A combination of two or more types of dementia, often involving Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia, presents with a complex mix of symptoms and requires tailored management strategies.
Exploring the Underlying Causes of Dementia
While the exact causes of dementia are still being investigated, several risk factors have been identified, including:
- Age: The risk of dementia increases significantly with age, particularly after the age of 65.
- Genetics: Family history of dementia is a significant risk factor, suggesting a genetic predisposition.
- Lifestyle: Factors like smoking, unhealthy diet, lack of physical activity, and alcohol abuse can increase the risk of dementia.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions like diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol, and heart disease can contribute to the development of dementia.
- Head Injuries: Repeated head injuries, particularly concussions, have been linked to an increased risk of dementia.
Navigating the Challenges of Dementia: Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for dementia, various treatments and management strategies aim to slow down cognitive decline, manage symptoms, and improve quality of life for individuals with dementia and their families.
Medications: Several medications are available to treat specific symptoms of dementia, such as memory loss, agitation, and sleep disturbances. However, these medications do not cure dementia and may have side effects.
Therapy: Cognitive therapy, behavioral therapy, and support groups can help individuals with dementia maintain cognitive function, manage behavioral symptoms, and cope with the challenges of the condition.
Supportive Care: Caregivers play a crucial role in providing support and assistance to individuals with dementia, addressing their physical, emotional, and social needs.
Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and mental stimulation, can help slow down cognitive decline and improve overall well-being.
Understanding the Impact of Dementia on Individuals and Families
Dementia has a profound impact on individuals and their families, affecting various aspects of their lives:
- Cognitive Decline: The progressive decline in cognitive function can lead to difficulty with memory, thinking, language, and problem-solving, affecting daily life activities and independence.
- Behavioral and Psychological Changes: Individuals with dementia may experience behavioral and psychological symptoms like agitation, anxiety, depression, delusions, and hallucinations, which can be challenging to manage.
- Social Isolation: As the condition progresses, individuals with dementia may withdraw from social activities, leading to isolation and loneliness.
- Caregiver Burden: Caregivers face significant challenges in providing support and care for individuals with dementia, often experiencing stress, burnout, and emotional distress.
Empowering Individuals and Families: Resources and Support
Several resources and support systems are available to help individuals with dementia and their families cope with the challenges of the condition:
- Healthcare Professionals: Geriatricians, neurologists, and other healthcare professionals specializing in dementia can provide diagnosis, treatment, and management strategies.
- Support Groups: Support groups for individuals with dementia and their families provide a safe space to share experiences, connect with others, and receive emotional support.
- Caregiver Training: Training programs are available to educate caregivers on the best practices for providing care for individuals with dementia, including communication strategies, behavioral management techniques, and safety measures.
- Community Resources: Various community resources, such as home healthcare services, adult day care programs, and assisted living facilities, can provide support and care for individuals with dementia.
FAQs about Concept Maps and Dementia
1. How can concept maps help individuals with dementia?
Concept maps can help individuals with dementia by providing a visual representation of their condition, promoting understanding and awareness. They can also serve as a communication tool, facilitating better communication between patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals.
2. Can concept maps be used for all types of dementia?
Yes, concept maps can be used for all types of dementia, as they provide a flexible framework for understanding the unique characteristics and challenges of each type.
3. How can caregivers use concept maps to support individuals with dementia?
Caregivers can use concept maps to gain a deeper understanding of the condition, identify potential triggers for behavioral changes, and develop personalized care plans. They can also use concept maps as a communication tool to share information with other caregivers and healthcare professionals.
4. Can healthcare professionals use concept maps in their practice?
Yes, healthcare professionals can use concept maps to explain dementia to patients and their families, facilitate informed decision-making, and develop comprehensive treatment plans.
5. Are there any online resources available for creating concept maps for dementia?
Yes, several online tools and resources are available for creating concept maps, including free and paid options. These tools can help individuals, caregivers, and healthcare professionals create customized concept maps tailored to their specific needs.
Tips for Using Concept Maps for Dementia
- Start with a central concept: Begin by defining the central concept, such as "Dementia," and then branch out with sub-concepts related to the condition.
- Use clear and concise language: Keep the language simple and easy to understand, avoiding technical jargon.
- Use visual aids: Incorporate images, symbols, and colors to make the concept map more engaging and memorable.
- Personalize the map: Customize the map to reflect the individual’s specific needs and preferences.
- Review and update the map regularly: As the condition progresses or new information becomes available, review and update the concept map to ensure it remains relevant and informative.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Understanding
Dementia is a complex and multifaceted condition that presents significant challenges for individuals and their families. However, by embracing a comprehensive understanding of the condition, its various forms, and potential management strategies, individuals can navigate the challenges of dementia more effectively.
Concept maps offer a valuable tool for understanding and managing dementia, providing a visual representation of the condition, highlighting its interrelationships, and facilitating personalized care plans. By leveraging the power of visual learning, individuals, caregivers, and healthcare professionals can work together to improve the lives of those living with dementia.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Demystifying Dementia: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Condition. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!