Mapping The Global Fight Against Tuberculosis: A Visual Guide To Understanding And Combating The Disease
Mapping the Global Fight Against Tuberculosis: A Visual Guide to Understanding and Combating the Disease
Related Articles: Mapping the Global Fight Against Tuberculosis: A Visual Guide to Understanding and Combating the Disease
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Global Fight Against Tuberculosis: A Visual Guide to Understanding and Combating the Disease. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Global Fight Against Tuberculosis: A Visual Guide to Understanding and Combating the Disease

Tuberculosis (TB), a contagious bacterial infection primarily affecting the lungs, continues to pose a significant global health challenge. While significant strides have been made in controlling TB, particularly in developed nations, the disease persists, claiming millions of lives annually, primarily in low- and middle-income countries. Understanding the geographical distribution of TB is crucial for effective disease management and prevention. This article delves into the significance of TB maps, examining their role in visualizing the global burden of the disease, identifying high-risk areas, and informing targeted interventions.
Understanding the Power of Visualization: The Importance of TB Maps
Visual representations of data, particularly maps, are powerful tools for understanding complex phenomena. In the context of TB, maps offer a clear and intuitive way to:
- Identify Geographic Hotspots: By depicting the prevalence and incidence of TB across different regions, maps highlight areas with high disease burden, allowing for the allocation of resources and targeted interventions.
- Track Disease Trends: Maps can track changes in TB prevalence over time, providing valuable insights into the effectiveness of control programs and identifying emerging trends.
- Inform Policy Decisions: Visualizing the geographical distribution of TB enables policymakers to prioritize resource allocation, develop effective prevention strategies, and implement targeted interventions.
- Raise Awareness: Maps can effectively communicate the global impact of TB, raising awareness among the public, policymakers, and healthcare professionals.
Types of TB Maps and Their Applications
Various types of TB maps are employed to visualize different aspects of the disease, each offering unique insights:
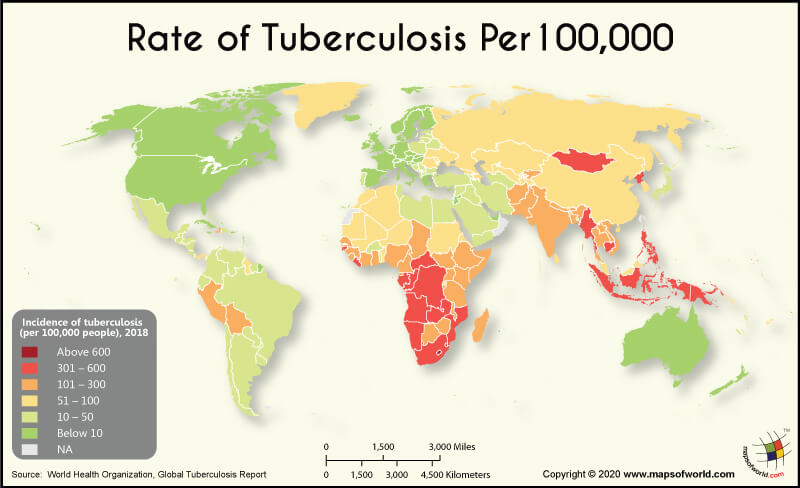
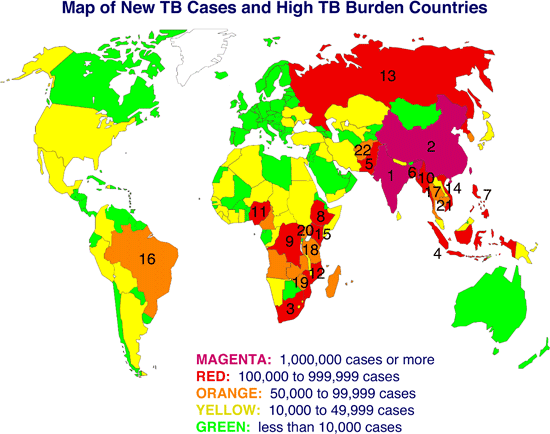
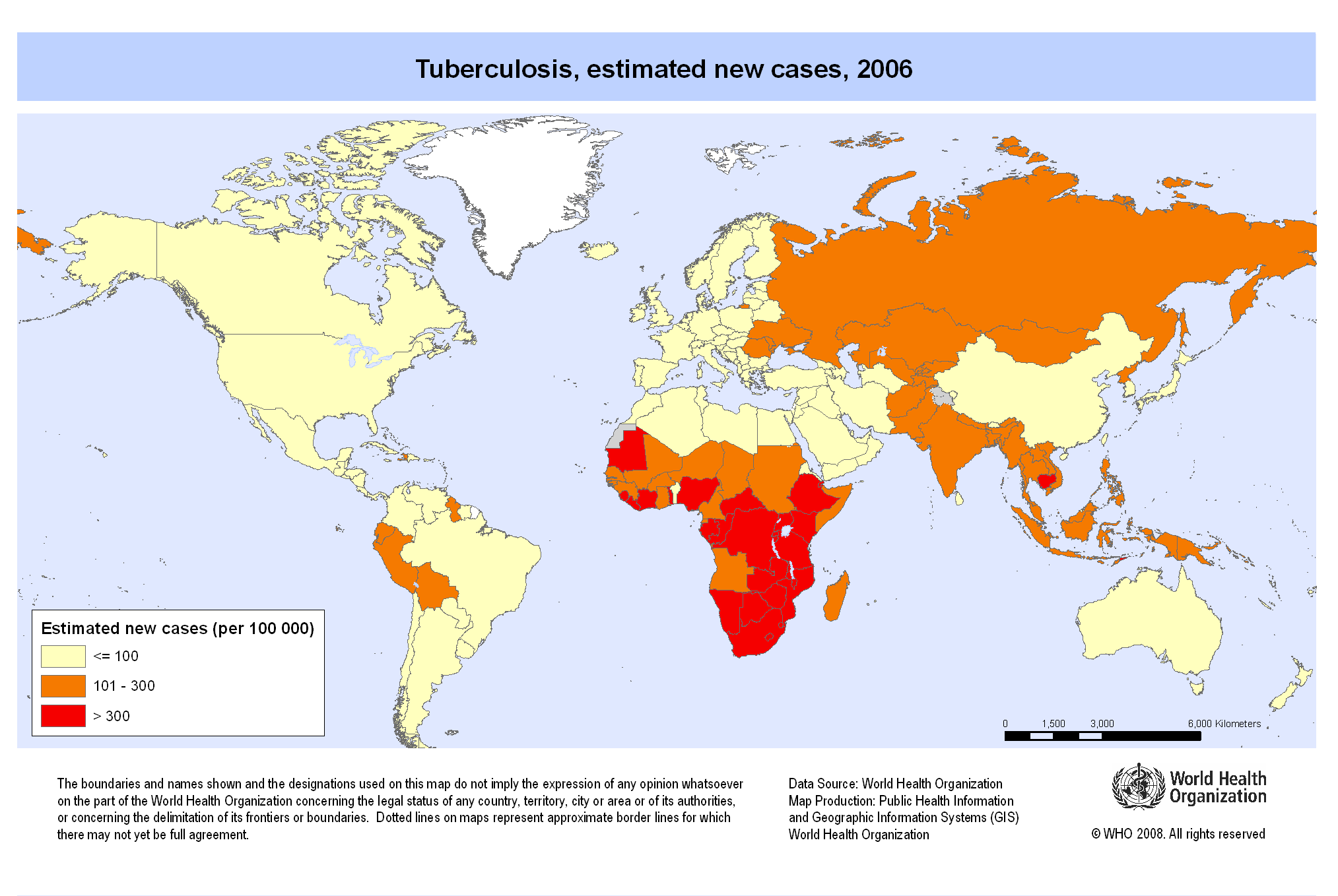
1. Prevalence Maps: These maps depict the percentage of individuals within a population who are infected with TB. They provide a snapshot of the overall disease burden in different regions.
2. Incidence Maps: These maps show the number of new TB cases reported in a specific time period, highlighting areas with active transmission of the disease.
3. Mortality Maps: These maps visualize the number of TB-related deaths in a region, providing insights into the disease’s impact on mortality rates.
4. Drug Resistance Maps: These maps illustrate the prevalence of drug-resistant TB, identifying areas with higher levels of resistance and necessitating tailored treatment strategies.
5. Risk Factor Maps: These maps combine information on various risk factors for TB, such as poverty, malnutrition, and HIV infection, to identify areas with high susceptibility to the disease.
Data Sources and Limitations of TB Maps
The accuracy and reliability of TB maps depend heavily on the quality and availability of data. Data sources for TB mapping include:
- National TB Programs: These programs collect data on TB cases, deaths, and treatment outcomes, providing valuable information for national-level mapping.
- World Health Organization (WHO): The WHO compiles and analyzes global TB data, generating comprehensive maps for international monitoring and research.
- Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs): NGOs working in TB control often collect data in specific regions, contributing to local-level mapping efforts.
Despite the valuable insights provided by TB maps, certain limitations need to be acknowledged:
- Data Availability: Data on TB prevalence and incidence may be limited in certain regions, particularly in low-income countries with weak surveillance systems.
- Data Quality: The accuracy of reported data can vary depending on factors such as reporting practices, diagnostic capabilities, and population density.
- Spatial Resolution: Maps often use aggregated data, which may not capture the nuances of disease distribution at the local level.
Engaging with TB Maps: A Call to Action
TB maps are not merely static visualizations; they are powerful tools for understanding and combating the disease. By leveraging these maps, we can:
- Prioritize Resource Allocation: Maps can guide the allocation of resources to areas with the highest TB burden, ensuring efficient and targeted interventions.
- Develop Effective Prevention Strategies: Maps can inform the development of prevention programs tailored to the specific needs of different regions.
- Improve Diagnosis and Treatment: Maps can help identify areas with low diagnostic rates and ensure timely access to effective treatment.
- Promote Collaboration and Research: Maps can facilitate collaboration between researchers, healthcare providers, and policymakers to address the challenges posed by TB.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about TB Maps
Q: What is the purpose of creating TB maps?
A: TB maps serve to visualize the global burden of the disease, identify high-risk areas, track disease trends, and inform targeted interventions.
Q: What data is used to create TB maps?
A: Data sources for TB mapping include national TB programs, the WHO, and NGOs working in TB control.
Q: What are the limitations of TB maps?
A: Limitations include data availability, data quality, and spatial resolution.
Q: How can TB maps be used to improve TB control?
A: Maps can guide resource allocation, inform prevention strategies, improve diagnosis and treatment, and promote collaboration and research.
Tips for Interpreting and Utilizing TB Maps
- Pay attention to the data source and methodology used to create the map.
- Consider the spatial resolution of the map and its limitations.
- Look for trends and patterns in the data, such as geographic clusters of high prevalence or incidence.
- Compare maps over time to track changes in TB burden and the effectiveness of control programs.
- Use maps to inform decision-making and prioritize resource allocation.
Conclusion: A Visual Roadmap to a TB-Free World
TB maps are essential tools for understanding and combating the global TB epidemic. They provide a visual roadmap for identifying high-risk areas, tracking disease trends, and informing targeted interventions. By leveraging the power of visualization, we can strengthen our efforts to achieve a world free from the scourge of tuberculosis.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Global Fight Against Tuberculosis: A Visual Guide to Understanding and Combating the Disease. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!