Mapping The Invasion: Understanding The Hemlock Woolly Adelgid’s Spread And Impact
Mapping the Invasion: Understanding the Hemlock Woolly Adelgid’s Spread and Impact
Related Articles: Mapping the Invasion: Understanding the Hemlock Woolly Adelgid’s Spread and Impact
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Invasion: Understanding the Hemlock Woolly Adelgid’s Spread and Impact. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Invasion: Understanding the Hemlock Woolly Adelgid’s Spread and Impact

The hemlock woolly adelgid (HWA), a tiny, sap-sucking insect, poses a significant threat to eastern hemlock trees across North America. Its impact on forest ecosystems and the landscape is profound, warranting a comprehensive understanding of its spread and the tools used to monitor its movement.
The Hemlock Woolly Adelgid: A Silent Threat
Native to East Asia, the HWA was first discovered in the United States in the 1950s, likely introduced through imported hemlock plants. This invasive species thrives in cool, humid environments, making eastern North America’s hemlock forests ideal habitat.
Understanding the HWA’s Impact
HWA feeds on the sap of hemlock trees, injecting a toxic saliva that disrupts the tree’s ability to transport water and nutrients. This feeding process causes the tree to weaken, eventually leading to death. The impact of HWA is multifaceted:
- Ecological Disruption: Hemlock trees are keystone species, playing a critical role in maintaining forest biodiversity. Their loss disrupts the ecosystem, affecting other species that depend on them for food, shelter, and nesting.
- Erosion and Landslide Risk: Hemlock forests stabilize slopes and prevent soil erosion. The loss of these trees increases the risk of landslides and erosion, impacting water quality and downstream ecosystems.
- Economic Losses: Hemlock forests provide valuable timber, recreational opportunities, and aesthetic benefits. The loss of these trees has significant economic consequences for timber industries, tourism, and property values.
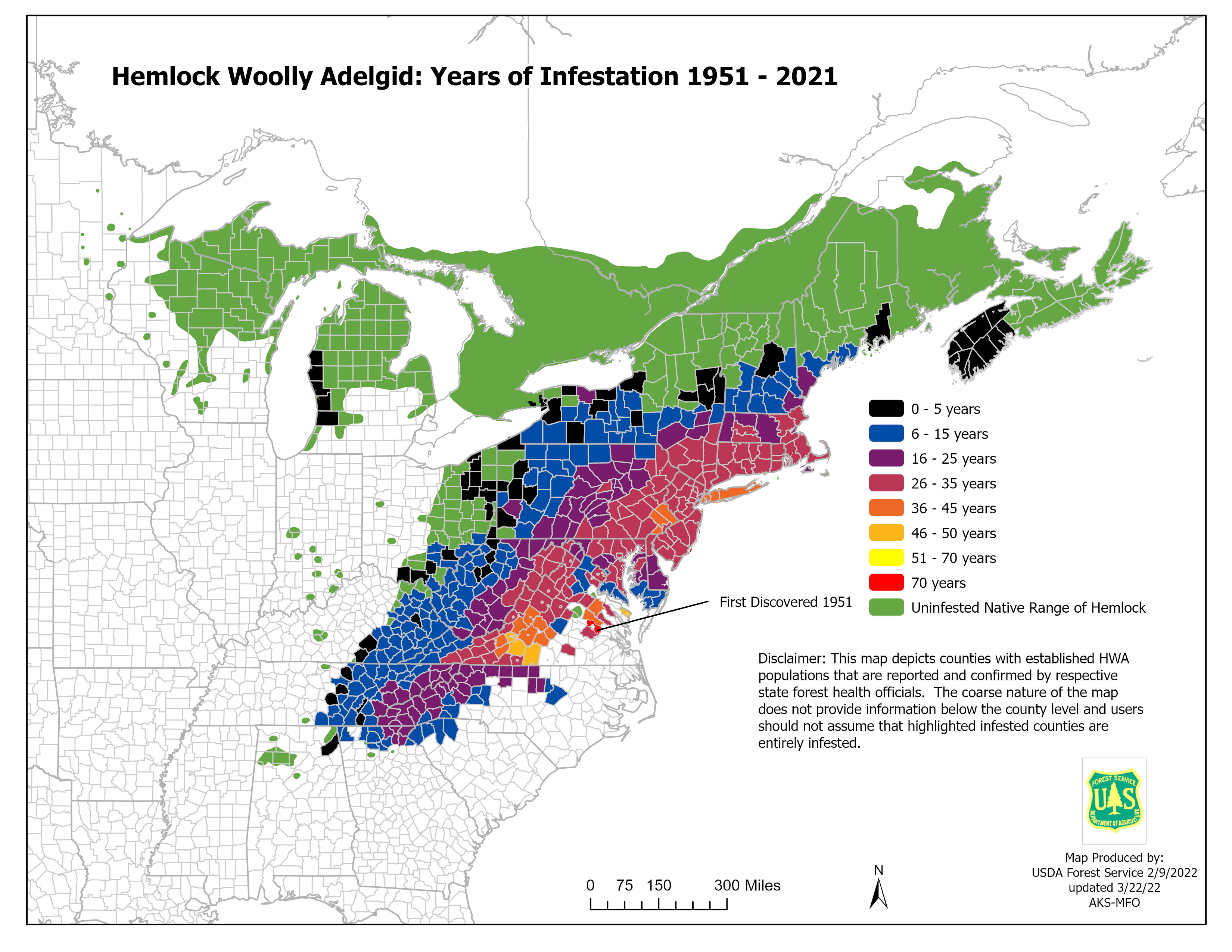
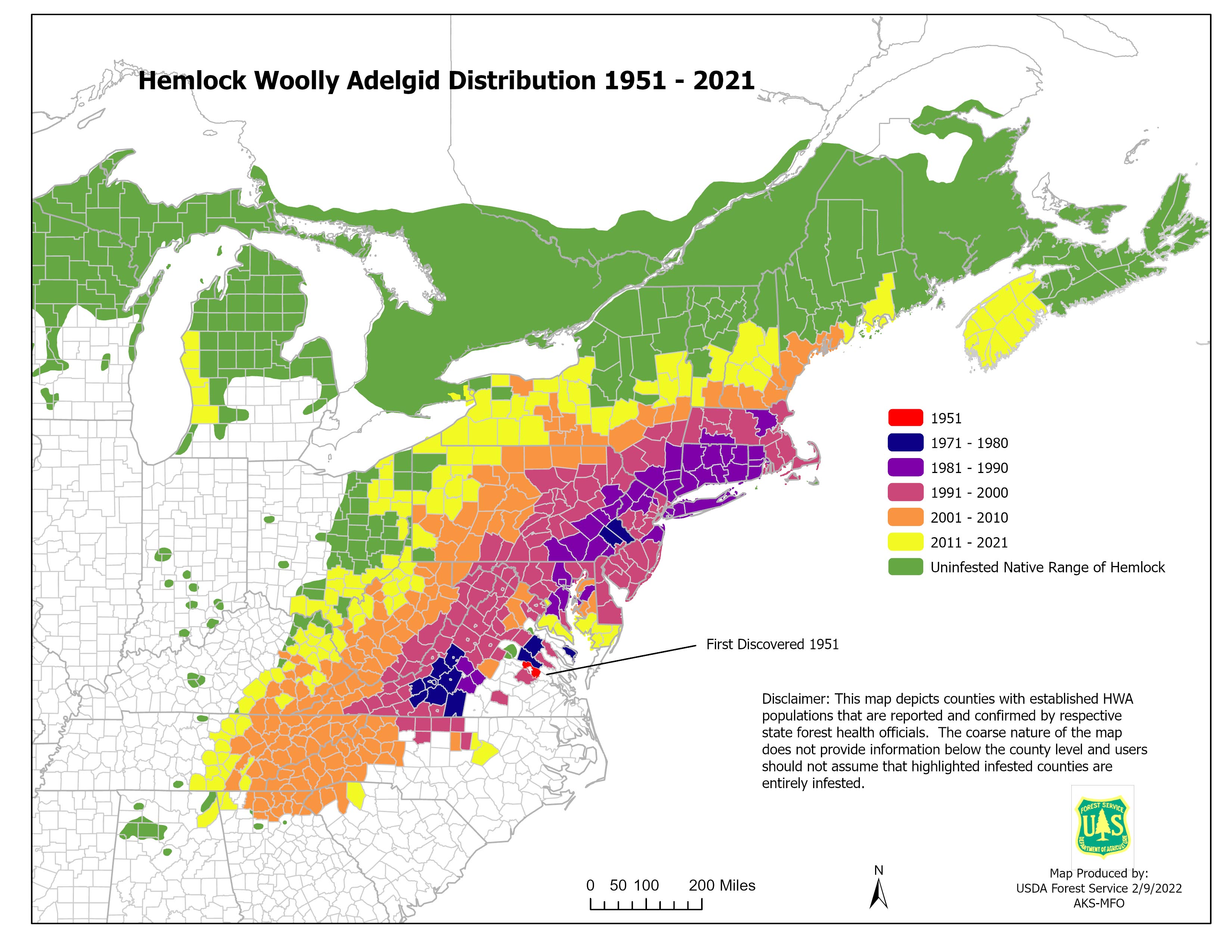
Mapping the Invasion: Tracking the HWA’s Spread
To combat the HWA, it is essential to understand its spread and distribution. This is where mapping plays a crucial role.
The Importance of Mapping
- Early Detection: Maps help identify areas where the HWA has been detected or is likely to be present. Early detection allows for swift intervention and containment efforts.
- Resource Allocation: Maps provide valuable information for allocating resources to areas most affected by the HWA. This ensures that control efforts are targeted and efficient.
- Research and Monitoring: Maps are essential tools for researchers studying the HWA’s biology, dispersal patterns, and the effectiveness of control measures.
Types of Maps Used to Track HWA
- Distribution Maps: These maps show the known distribution of the HWA across its range. They are updated regularly as new infestations are discovered.
- Risk Maps: These maps identify areas that are at high risk of HWA infestation based on factors like climate, forest composition, and proximity to known infestations.
- Control Effort Maps: These maps illustrate the areas where control measures have been implemented, such as the application of insecticides or the release of biological control agents.
Data Sources for HWA Mapping
- Surveys and Monitoring: Trained personnel conduct surveys to detect HWA presence in forests.
- Citizen Science: Public participation through citizen science programs helps expand the reach of HWA monitoring efforts.
- Remote Sensing: Aerial imagery and satellite data can be used to identify areas with potential HWA infestations.
Benefits of Using HWA Maps
- Enhanced Management: Maps provide valuable insights for developing effective management strategies to control the HWA.
- Public Awareness: Maps raise awareness about the HWA threat and encourage public participation in monitoring and control efforts.
- Research and Development: Maps facilitate research on the HWA’s biology, dispersal patterns, and the effectiveness of control measures.
FAQs about Hemlock Woolly Adelgid Maps
Q: How can I access HWA maps?
A: HWA maps are available through various online resources, including government agencies, universities, and non-profit organizations. Some examples include the USDA Forest Service, the Pennsylvania Department of Conservation and Natural Resources, and the Hemlock Woolly Adelgid Foundation.
Q: What information can I find on HWA maps?
A: HWA maps typically show the distribution of the insect, areas at risk of infestation, and the locations of control efforts. Some maps may also provide information on the severity of infestations and the effectiveness of control measures.
Q: How often are HWA maps updated?
A: The frequency of map updates varies depending on the organization maintaining the map and the availability of new data. However, maps are generally updated regularly to reflect the latest information on HWA distribution and control efforts.
Q: Can I contribute to HWA mapping efforts?
A: Yes, you can participate in citizen science programs to help monitor HWA populations and contribute to mapping efforts. Many organizations offer online platforms and resources to guide citizen scientists in their efforts.
Tips for Using HWA Maps
- Understand the Data: Familiarize yourself with the information presented on the map and the methods used to collect the data.
- Consider the Scale: Maps are often presented at different scales. Choose a map that provides the level of detail needed for your specific purpose.
- Use the Map in Conjunction with Other Resources: Combine map data with other information sources, such as field observations and scientific literature, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the HWA threat.
Conclusion
Mapping the spread of the hemlock woolly adelgid is a crucial step in mitigating its impact on eastern hemlock forests. These maps provide valuable insights for understanding the HWA’s distribution, risk areas, and control efforts. By utilizing these tools, researchers, land managers, and the public can work together to protect these vital ecosystems and ensure the long-term survival of eastern hemlock trees.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Invasion: Understanding the Hemlock Woolly Adelgid’s Spread and Impact. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!