Mapping the Silent Threat: Understanding Pine Bark Beetle Infestations
Related Articles: Mapping the Silent Threat: Understanding Pine Bark Beetle Infestations
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Silent Threat: Understanding Pine Bark Beetle Infestations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Silent Threat: Understanding Pine Bark Beetle Infestations

The seemingly quiet forests of North America harbor a silent threat – the pine bark beetle. These tiny insects, often overlooked due to their diminutive size, have the potential to wreak havoc on vast swaths of pine forests, leaving behind a trail of dead and dying trees. To effectively combat this threat, understanding the dynamics of pine bark beetle infestations and visualizing their spread through mapping is crucial.
Understanding the Enemy:
Pine bark beetles, specifically the mountain pine beetle (Dendroctonus ponderosae), are native to North America. While they play a natural role in forest ecosystems, their populations can explode under certain conditions, leading to devastating infestations. These conditions include:
- Climate Change: Warmer temperatures and drier conditions create ideal breeding grounds for beetles, allowing them to reproduce more rapidly and survive longer.
- Overcrowded Forests: Densely packed trees provide more opportunities for beetles to find suitable hosts and spread rapidly.
- Fire Suppression: The absence of natural wildfires, which historically thinned out forests, allows for the accumulation of susceptible trees, increasing the risk of infestation.
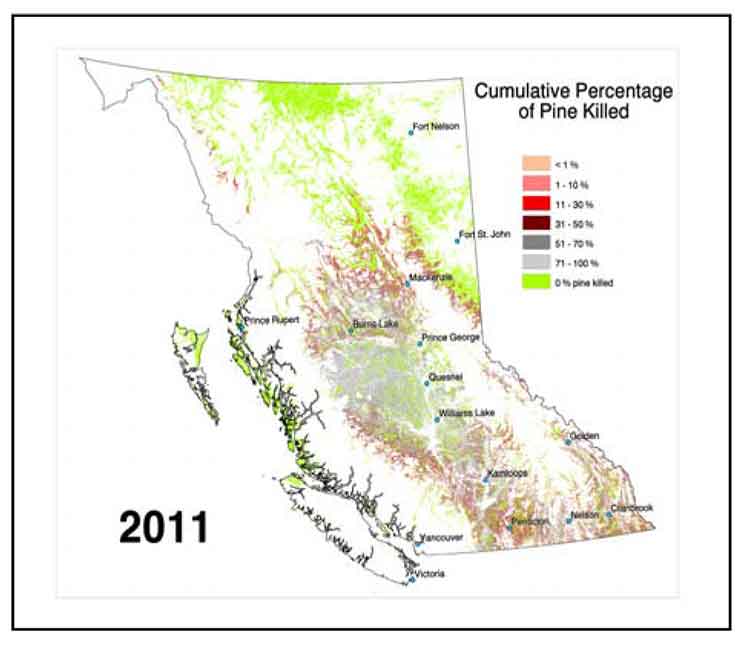
The Power of Visualization: Mapping the Infestation
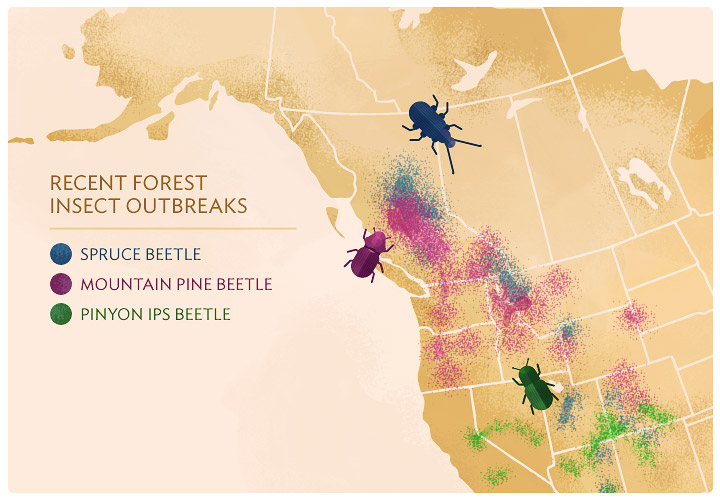
Mapping pine bark beetle infestations serves as a powerful tool for understanding the spread of these destructive insects. These maps provide valuable insights into:
- Infestation Hotspots: Identifying areas with high concentrations of beetle activity helps prioritize resource allocation for control efforts.
- Spread Patterns: Tracking the movement of infestations over time reveals how beetles are dispersing and allows for proactive measures to be taken in areas at risk.
- Impact Assessment: Mapping helps assess the extent of damage to forests, informing management decisions and providing data for economic and ecological impact studies.
Types of Maps and Their Applications:
Various types of maps are employed to visualize pine bark beetle infestations, each offering unique perspectives:
- Distribution Maps: These maps depict the geographic spread of infestations, indicating the presence of beetles in specific areas.
- Severity Maps: These maps visualize the intensity of infestations, highlighting areas with high levels of beetle activity and damage.
- Risk Maps: These maps predict the likelihood of future infestations based on factors like forest density, climate, and past infestation history.
- Monitoring Maps: These maps track the progression of infestations over time, providing real-time updates on the situation.
Benefits of Pine Bark Beetle Infestation Maps:
- Early Detection: Maps enable early identification of infestations, facilitating timely interventions and reducing the severity of damage.
- Targeted Management: Maps help prioritize control efforts, focusing resources on areas with the highest infestation risk or severity.
- Resource Allocation: Maps provide valuable data for allocating resources effectively, ensuring efficient use of funding and manpower.
- Public Awareness: Maps raise public awareness about the threat of pine bark beetles and encourage community involvement in monitoring and control efforts.
- Scientific Research: Maps provide valuable data for researchers studying the ecology and behavior of pine bark beetles, leading to improved understanding and management strategies.
FAQs about Pine Bark Beetle Infestation Maps:
Q: How are pine bark beetle infestation maps created?
A: Maps are created using various data sources, including:
- Aerial Surveys: Visual inspection of forest areas from airplanes or helicopters to identify areas with signs of infestation.
- Ground Surveys: Direct inspection of trees by forest managers to assess the extent and severity of damage.
- Remote Sensing: Using satellite imagery and aerial photographs to detect changes in forest health, indicating potential infestations.
- Citizen Science: Engaging the public in reporting observations of beetle activity or tree damage.
Q: Where can I find pine bark beetle infestation maps?
A: Infestation maps are often available from:
- Government Agencies: State and federal forestry agencies responsible for managing forest resources.
- Research Institutions: Universities and research centers conducting studies on pine bark beetles.
- Non-profit Organizations: Conservation groups working to protect forests from pests and diseases.
- Online Databases: Publicly available databases and mapping platforms often provide access to infestation data.
Q: What can I do to help prevent pine bark beetle infestations?
A: You can contribute to preventing infestations by:
- Supporting Responsible Forest Management: Encourage sustainable forestry practices that promote healthy forest ecosystems.
- Reporting Suspected Infestations: Contact local forestry agencies if you observe signs of beetle activity or tree damage.
- Planting Diverse Trees: Create a more resilient forest by planting a variety of tree species, reducing the susceptibility to single-species pests.
- Supporting Research and Control Efforts: Donate to organizations working to combat pine bark beetle infestations and develop effective control strategies.
Tips for Using Pine Bark Beetle Infestation Maps:
- Understand the Scale: Pay attention to the scale of the map to interpret the data accurately.
- Consider Data Sources: Evaluate the reliability and accuracy of the data used to create the map.
- Interpret the Data: Understand the different symbols and colors used to represent infestation levels and severity.
- Use the Map for Decision-Making: Utilize the information provided by the map to make informed decisions about forest management and conservation efforts.
Conclusion:
Pine bark beetle infestations pose a significant threat to North American forests, impacting biodiversity, timber production, and overall ecosystem health. Mapping these infestations provides crucial information for understanding the dynamics of beetle spread, prioritizing management efforts, and developing effective control strategies. By leveraging the power of visualization, we can better protect our forests and ensure their resilience in the face of this silent threat.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Silent Threat: Understanding Pine Bark Beetle Infestations. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!