Navigating The Gulf: A Comprehensive Guide To The Region’s Geography And Importance
Navigating the Gulf: A Comprehensive Guide to the Region’s Geography and Importance
Related Articles: Navigating the Gulf: A Comprehensive Guide to the Region’s Geography and Importance
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Gulf: A Comprehensive Guide to the Region’s Geography and Importance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Gulf: A Comprehensive Guide to the Region’s Geography and Importance

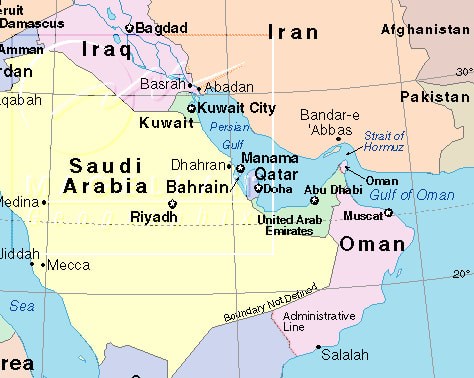
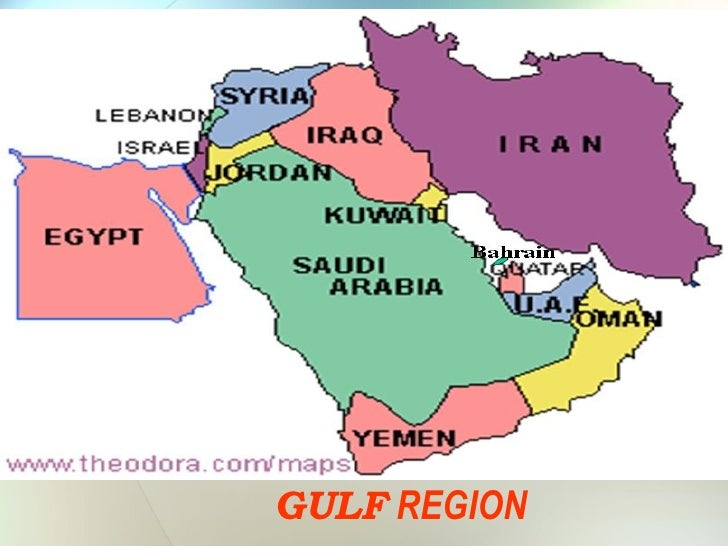
The Gulf region, nestled in the heart of the Middle East, is a dynamic and influential area with a rich history and diverse landscape. Understanding the geography of this region is crucial for comprehending its political, economic, and cultural significance on a global scale. This comprehensive guide delves into the map of the Gulf countries, exploring their geographical features, cultural nuances, and the factors that contribute to their importance on the world stage.
The Geographic Landscape:
The Gulf region is defined by the Persian Gulf, a vast body of water that stretches from the Strait of Hormuz in the east to the Arabian Peninsula in the west. The region encompasses a unique blend of geographical features, including:
- Coastal Plains: The Gulf’s coastline is characterized by extensive, low-lying plains, particularly in Kuwait, Bahrain, and the eastern regions of Saudi Arabia. These plains are often fertile and provide essential agricultural land.
- Desert Landscapes: The majority of the Gulf region is dominated by vast, arid deserts, such as the Rub’ al Khali (Empty Quarter) in Saudi Arabia. These deserts are characterized by extreme temperatures, sparse vegetation, and unique geological formations.
- Mountain Ranges: The region’s eastern edge features mountain ranges, such as the Zagros Mountains in Iran and the Oman Mountains, which contribute to significant rainfall and diverse ecosystems.
- Oases: In the midst of the desert, oases provide vital sources of water and vegetation, supporting local communities and agriculture.
The Gulf Countries:
The Gulf region is home to six major countries, each with its own distinct identity and cultural heritage:
-
Saudi Arabia: The largest country in the region, Saudi Arabia is a dominant force in the Gulf and holds immense economic and political influence. Its vast oil reserves have made it a global energy powerhouse, and its cultural heritage is deeply rooted in Islam.
-
United Arab Emirates (UAE): Known for its modern cities, luxurious tourism, and ambitious development projects, the UAE has become a global economic hub. Dubai, its most prominent city, is a symbol of innovation and architectural marvels.
-
Kuwait: A relatively small but wealthy country, Kuwait is known for its vast oil reserves and its commitment to economic diversification. Its capital, Kuwait City, is a vibrant commercial center.
-
Qatar: Qatar has emerged as a major player in the global energy market thanks to its vast natural gas reserves. It is also known for its investments in education, healthcare, and infrastructure.
-
Oman: Situated on the eastern edge of the Arabian Peninsula, Oman is known for its scenic landscapes, diverse wildlife, and ancient culture. Its strategic location has made it a vital trading hub throughout history.
-
Bahrain: The smallest Gulf country, Bahrain is a major financial center and a significant player in the regional tourism industry. Its strategic location and historical significance have made it a cultural melting pot.
The Importance of the Gulf Region:
The Gulf region’s importance extends far beyond its geographical location. Its strategic position, vast natural resources, and cultural significance have made it a critical player in the global economy and a focal point for international relations. Key factors contributing to its importance include:
- Energy Resources: The Gulf region holds the world’s largest reserves of oil and natural gas, making it a crucial source of energy for global markets. This wealth has fueled economic growth and development in the region.
- Trade and Commerce: The Gulf’s strategic location at the crossroads of major trade routes has made it a vital hub for international commerce. Ports like Dubai and Jebel Ali have become major gateways for global trade.
- Cultural Heritage: The Gulf region boasts a rich cultural heritage, steeped in history, tradition, and Islamic values. Its architectural marvels, traditional crafts, and vibrant arts scene attract tourists from around the world.
- Political Influence: The Gulf region’s wealth and geopolitical significance have given it considerable influence in international affairs. Its political stability and security are crucial for global energy markets and regional peace.
- Innovation and Development: The Gulf countries have invested heavily in infrastructure, technology, and education, leading to significant economic growth and modernization. They are increasingly becoming centers for innovation and technological advancements.
FAQs about the Gulf Countries:
1. What are the main languages spoken in the Gulf countries?
- Arabic is the official language of all Gulf countries. However, English is widely spoken, particularly in business and tourism sectors.
2. What are the major religions practiced in the Gulf region?
- Islam is the dominant religion in the Gulf countries. The majority of the population adheres to Sunni Islam, while Shia Islam is also prevalent in certain areas.
3. What are the main economic activities in the Gulf countries?
- The Gulf countries’ economies are primarily driven by oil and natural gas production. However, they are diversifying their economies through investments in tourism, finance, technology, and real estate.
4. What are some of the major challenges facing the Gulf region?
- The Gulf region faces challenges such as water scarcity, environmental degradation, political instability, and economic diversification.
5. What are the future prospects for the Gulf region?
- The Gulf region has significant potential for continued economic growth and development. Its strategic location, vast resources, and commitment to innovation position it for a bright future.
Tips for Understanding the Gulf Region:
- Engage with local culture: Explore the region’s rich cultural heritage by visiting museums, art galleries, and traditional markets.
- Learn about the history: Gain a deeper understanding of the region’s historical context by visiting ancient sites and learning about its past.
- Stay informed about current events: Keep abreast of political and economic developments in the region to gain a comprehensive perspective.
- Respect local customs: Be mindful of local customs and traditions to ensure a respectful and enjoyable experience.
Conclusion:
The Gulf region is a complex and fascinating area that holds immense significance on a global scale. Its geographical features, cultural heritage, and economic power have made it a crucial player in the world. Understanding the map of the Gulf countries provides a framework for appreciating the region’s unique blend of history, culture, and modern advancements. By engaging with its diverse landscapes, cultural nuances, and political realities, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the region’s dynamic role in shaping the world today.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Gulf: A Comprehensive Guide to the Region’s Geography and Importance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!