Navigating the World in 3D: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Applications
Related Articles: Navigating the World in 3D: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Applications
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World in 3D: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Applications. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the World in 3D: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Applications
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the World in 3D: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Applications
- 3.1 The Evolution of Mapping: From Flat to Immersive
- 3.2 Understanding the Essence of 3D Map Applications
- 3.3 The Diverse Applications of 3D Maps
- 3.4 Navigating the Landscape: A Look at Popular 3D Map Applications
- 3.5 The Future of 3D Mapping: Exploring Emerging Trends
- 3.6 Frequently Asked Questions about 3D Map Applications
- 3.7 Tips for Using 3D Map Applications Effectively
- 3.8 Conclusion: The Future of Navigation and Exploration
- 4 Closure
Navigating the World in 3D: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Applications
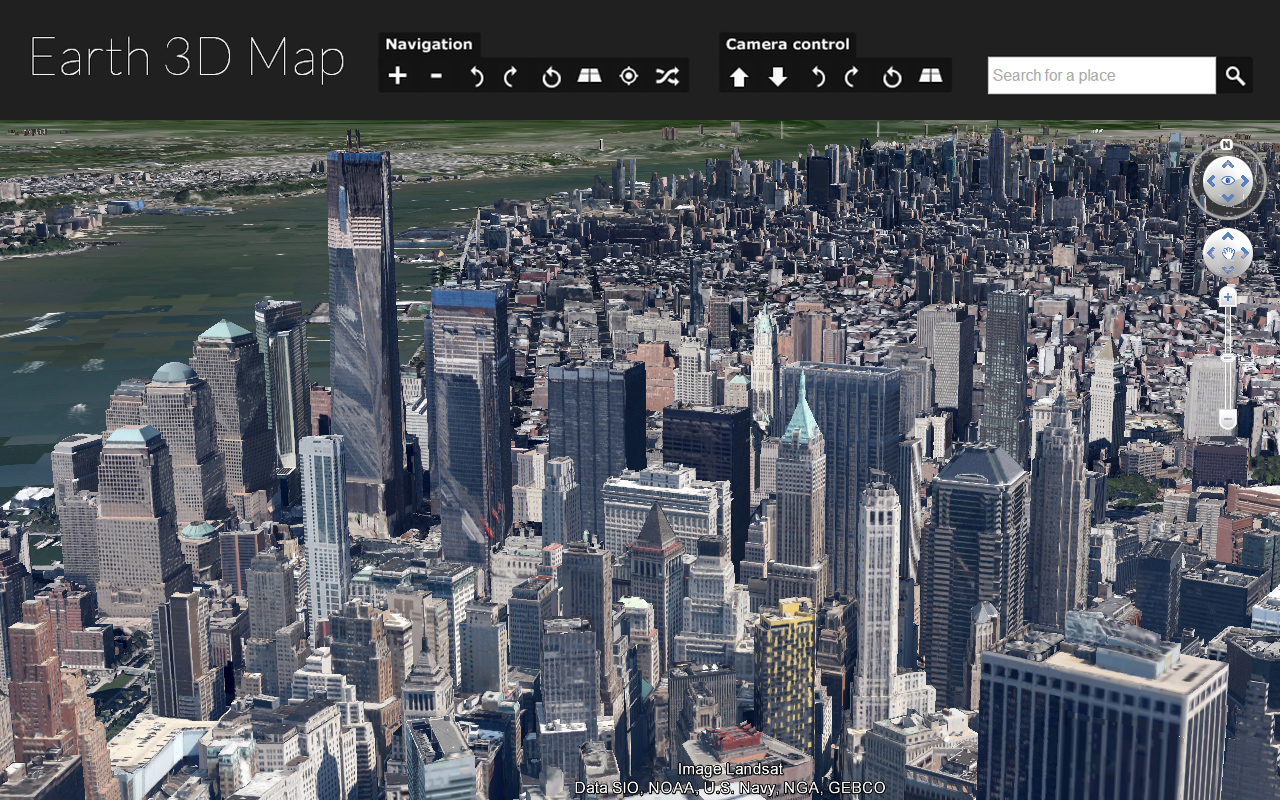
In the digital age, where information is readily available at our fingertips, the way we navigate and explore the world has undergone a profound transformation. Traditional paper maps have been replaced by interactive, dynamic applications that offer a wealth of information and an immersive experience. Among these innovative tools, 3D map applications stand out, providing users with a unique perspective and unparalleled functionality. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of 3D map applications, exploring their benefits, functionalities, and impact on various industries.
The Evolution of Mapping: From Flat to Immersive
The evolution of mapping technology has been a gradual yet remarkable journey. Early maps were primarily two-dimensional representations of the world, often limited by the accuracy of available data and the constraints of physical mediums. The advent of digital technology ushered in a new era of mapping, where data could be captured, processed, and displayed with unprecedented precision.
The introduction of 3D technology further revolutionized the mapping landscape. By incorporating depth and perspective, 3D maps allow users to visualize the world in a more realistic and intuitive manner. This shift from flat to immersive representations has had a significant impact on how we interact with maps and the information they convey.
Understanding the Essence of 3D Map Applications
3D map applications leverage advanced computer graphics and data processing techniques to create interactive, three-dimensional representations of geographic locations. These applications utilize diverse data sources, including aerial imagery, satellite data, and ground-based scans, to generate highly detailed and accurate models of the real world.
Key features that distinguish 3D map applications include:
- Realistic 3D Visualization: Users can explore landscapes, buildings, and urban environments from various angles, gaining a comprehensive understanding of spatial relationships and features.
- Interactive Exploration: Users can zoom, pan, and rotate the map to examine specific areas of interest, allowing for detailed analysis and exploration.
- Data Integration: 3D map applications can integrate diverse data layers, such as traffic information, weather conditions, points of interest, and real-time updates, providing a holistic view of the environment.
- Measurement and Analysis: 3D map applications facilitate accurate measurements of distances, areas, and volumes, supporting planning, design, and construction projects.
- Augmented Reality Integration: Some 3D map applications integrate augmented reality features, overlaying digital information onto the real world, enhancing user interaction and providing contextual insights.
The Diverse Applications of 3D Maps
The versatility of 3D map applications extends across numerous industries and sectors, revolutionizing how we navigate, plan, and understand the world around us.
Navigation and Transportation:
- Real-time Traffic Updates: 3D maps provide real-time traffic information, enabling drivers to choose optimal routes and avoid congestion.
- Public Transportation Planning: Users can visualize bus routes, train lines, and subway networks, making it easier to plan efficient commutes.
- Navigation for Pedestrians: 3D maps offer detailed street-level views, assisting pedestrians in finding their way through unfamiliar areas.
Urban Planning and Development:
- City Planning and Design: 3D maps enable urban planners to create virtual models of proposed developments, facilitating visualization and stakeholder engagement.
- Infrastructure Management: 3D maps provide a comprehensive view of utilities, roads, and other infrastructure, supporting maintenance and repair efforts.
- Disaster Response: 3D maps can be used to assess damage after natural disasters, guiding relief efforts and facilitating reconstruction.
Real Estate and Property Management:
- Virtual Property Tours: 3D maps allow potential buyers to explore properties remotely, providing a realistic sense of space and layout.
- Property Valuation: 3D maps can be used to analyze property features, such as size, location, and surrounding amenities, aiding in property valuation.
- Facility Management: 3D maps facilitate efficient management of large facilities, such as shopping malls and industrial complexes, by providing an interactive overview of floor plans and layouts.
Tourism and Travel:
- Destination Exploration: 3D maps allow travelers to virtually explore destinations before arriving, providing a comprehensive understanding of attractions and landmarks.
- Virtual Tours of Museums and Historical Sites: 3D maps can create interactive tours of museums and historical sites, enhancing the visitor experience.
- Outdoor Recreation: 3D maps aid in planning hiking trails, biking routes, and other outdoor activities, providing elevation data and terrain information.
Education and Research:
- Geography and Earth Science Education: 3D maps offer interactive and engaging tools for teaching geography, geology, and other earth science concepts.
- Historical Research: 3D maps can be used to reconstruct historical landscapes and cities, providing valuable insights into the past.
- Environmental Studies: 3D maps facilitate the analysis of environmental data, such as deforestation rates, pollution levels, and climate change impacts.
Military and Defense:
- Battlefield Simulation: 3D maps are essential for military training, providing realistic simulations of combat scenarios and terrains.
- Intelligence Gathering: 3D maps can be used to analyze satellite imagery and other intelligence data, providing valuable insights into enemy operations.
- Strategic Planning: 3D maps support strategic planning by visualizing troop movements, supply lines, and potential attack routes.
Healthcare and Medicine:
- Medical Imaging: 3D maps are used in medical imaging, allowing doctors to visualize organs, tissues, and bones in three dimensions.
- Surgical Planning: 3D maps facilitate surgical planning by providing detailed models of the patient’s anatomy, enhancing surgical precision.
- Healthcare Facility Design: 3D maps support the design of healthcare facilities, ensuring optimal patient flow, accessibility, and safety.
Navigating the Landscape: A Look at Popular 3D Map Applications
The market for 3D map applications is diverse, offering a wide range of options for users with varying needs and preferences. Some of the most popular and widely used 3D map applications include:
- Google Earth: A widely recognized application that provides a comprehensive 3D view of the Earth, offering satellite imagery, aerial photography, and street-level views. Google Earth integrates various data layers, including historical imagery, points of interest, and user-generated content.
- ArcGIS Pro: A professional-grade geographic information system (GIS) software that offers advanced 3D mapping capabilities. ArcGIS Pro allows users to create, manage, and analyze 3D geospatial data, supporting a wide range of applications in urban planning, environmental management, and resource management.
- Cesium: A JavaScript library that enables developers to create interactive 3D globes and maps. Cesium is widely used in web-based mapping applications, offering high-performance rendering and data visualization capabilities.
- Unity: A popular game engine that also provides robust 3D mapping features. Unity allows developers to create immersive 3D environments and interactive maps, supporting applications in virtual reality, augmented reality, and simulation.
- Unreal Engine: Another powerful game engine that offers advanced 3D mapping capabilities. Unreal Engine is known for its realistic graphics and immersive experiences, making it suitable for creating high-quality 3D maps for various purposes.
The Future of 3D Mapping: Exploring Emerging Trends
The field of 3D mapping is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and the growing demand for immersive and interactive experiences. Some of the emerging trends shaping the future of 3D map applications include:
- Enhanced Reality: The convergence of 3D mapping with augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies is creating new possibilities for user interaction and exploration. AR overlays digital information onto the real world, while VR immerses users in a virtual environment.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: AI algorithms are being incorporated into 3D map applications to enhance data analysis, route optimization, and predictive modeling. AI-powered features can provide users with personalized recommendations, real-time traffic predictions, and dynamic route suggestions.
- Data Visualization and Analytics: 3D map applications are becoming increasingly sophisticated in their ability to visualize and analyze complex datasets. Advanced visualization techniques enable users to gain deeper insights into spatial patterns, trends, and relationships within data.
- Blockchain and Decentralized Data: Blockchain technology is emerging as a potential solution for secure and transparent data management in 3D mapping. Decentralized data storage can enhance data integrity and accessibility, facilitating collaboration and data sharing.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: The integration of 3D maps with IoT devices, such as sensors and smart devices, can provide real-time data feeds, enriching the user experience and enabling dynamic updates.
Frequently Asked Questions about 3D Map Applications
Q: What are the benefits of using 3D map applications?
A: 3D map applications offer numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Visualization: 3D maps provide a more realistic and intuitive representation of the world, enhancing spatial understanding.
- Enhanced Navigation: 3D maps facilitate efficient navigation by providing real-time traffic information, optimized routes, and street-level views.
- Data Integration and Analysis: 3D maps can integrate diverse data layers, enabling users to analyze and interpret spatial relationships and patterns.
- Improved Planning and Decision-Making: 3D maps support planning and decision-making in various industries by providing a comprehensive view of the environment and data.
- Immersive User Experiences: 3D maps offer interactive and engaging experiences, enhancing user engagement and exploration.
Q: How do 3D map applications create realistic 3D models?
A: 3D map applications utilize a combination of techniques to create realistic 3D models:
- Aerial Imagery and Satellite Data: High-resolution aerial photographs and satellite imagery capture the Earth’s surface from above, providing a comprehensive view of landscapes, buildings, and infrastructure.
- Ground-Based Scans: Ground-based laser scanners capture detailed 3D data of specific areas, providing precise measurements of buildings, terrain, and other features.
- Computer Graphics and Rendering: Advanced computer graphics algorithms and rendering techniques are used to process and display the captured data, creating realistic 3D models.
Q: What are the limitations of 3D map applications?
A: While 3D map applications offer significant benefits, they also have limitations:
- Data Accuracy and Completeness: The accuracy and completeness of 3D models depend on the quality and availability of data sources.
- Computational Resources: Rendering and processing 3D models require significant computational resources, potentially impacting performance on older devices or with limited internet connectivity.
- Privacy Concerns: The use of 3D maps raises privacy concerns, as they can capture and display detailed information about individuals and locations.
- Cost and Complexity: Developing and maintaining 3D map applications can be expensive and complex, requiring specialized skills and resources.
Q: How can I use 3D map applications in my work or personal life?
A: 3D map applications have diverse applications, ranging from personal navigation to professional planning and research. Some specific examples include:
- Finding the best route to work or a destination.
- Exploring potential vacation destinations or planning a hiking trip.
- Analyzing traffic patterns and identifying potential congestion points.
- Designing and visualizing new buildings or infrastructure projects.
- Conducting environmental impact assessments and monitoring changes in landscapes.
- Creating immersive virtual tours of museums, historical sites, or properties.
Tips for Using 3D Map Applications Effectively
- Choose the Right Application: Select a 3D map application that meets your specific needs and requirements, considering features, data sources, and industry-specific capabilities.
- Familiarize Yourself with the Interface: Spend time exploring the application’s interface and learning its various features and functionalities.
- Utilize Data Layers: Explore and leverage the available data layers, such as traffic information, weather conditions, points of interest, and historical imagery, to enhance your analysis and understanding.
- Experiment with Visualization Options: Experiment with different visualization options, such as perspective views, aerial views, and cross-sections, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the data.
- Consider Privacy Implications: Be mindful of privacy concerns when using 3D maps, especially when sharing or publishing data.
- Stay Updated with New Features: Keep up-to-date with new features and updates to 3D map applications, as technology and data sources are constantly evolving.
Conclusion: The Future of Navigation and Exploration
3D map applications have transformed the way we navigate, explore, and understand the world around us. These powerful tools provide a unique perspective, enabling users to visualize and analyze spatial data with unprecedented detail and accuracy. As technology continues to advance, 3D map applications are poised to become even more sophisticated and integrated into our lives, shaping the future of navigation, planning, and exploration. From personal navigation to professional applications, the possibilities offered by 3D map applications are vast and continue to expand, promising a future where we can interact with the world in more immersive and insightful ways.

![3D World Map Printable Globe in PDF [3d World Map Vector]](https://worldmapgeo.com/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/map-of-the-world-3d-1-930x620.jpg)





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World in 3D: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Applications. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!