The Berlin Blockade: A Map of Cold War Tensions
Related Articles: The Berlin Blockade: A Map of Cold War Tensions
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Berlin Blockade: A Map of Cold War Tensions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Berlin Blockade: A Map of Cold War Tensions
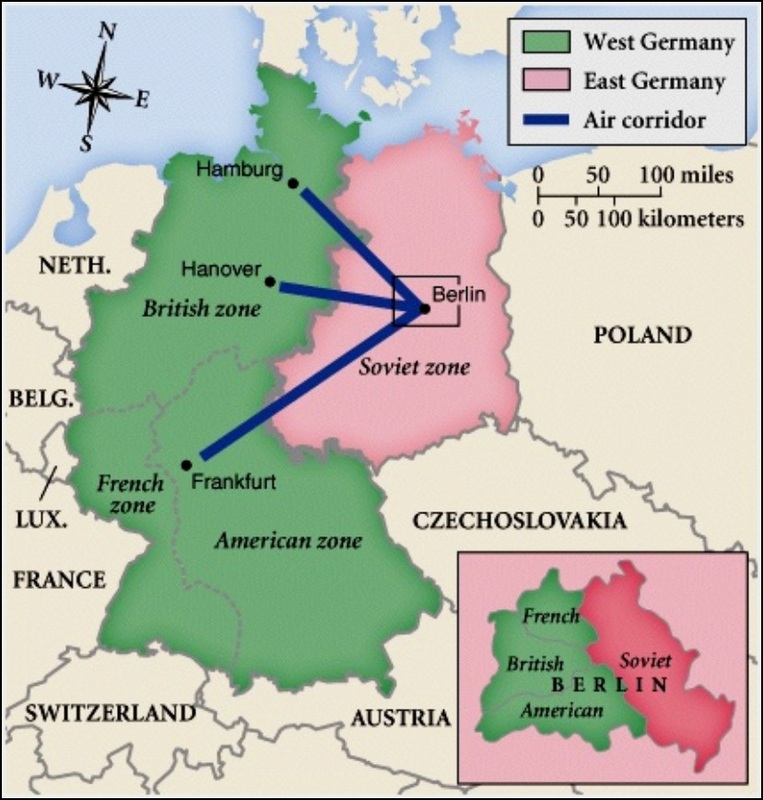
The Berlin Blockade, a defining moment in the early Cold War, stands as a testament to the intricate geopolitical landscape that emerged after World War II. This historical event, which spanned from June 1948 to May 1949, saw the Soviet Union impose a blockade on West Berlin, an enclave of Allied-controlled territory nestled within Soviet-occupied East Germany. This blockade, aimed at forcing the Western Allies to relinquish their control over West Berlin, became a pivotal flashpoint in the burgeoning ideological conflict between the West and the Soviet bloc.
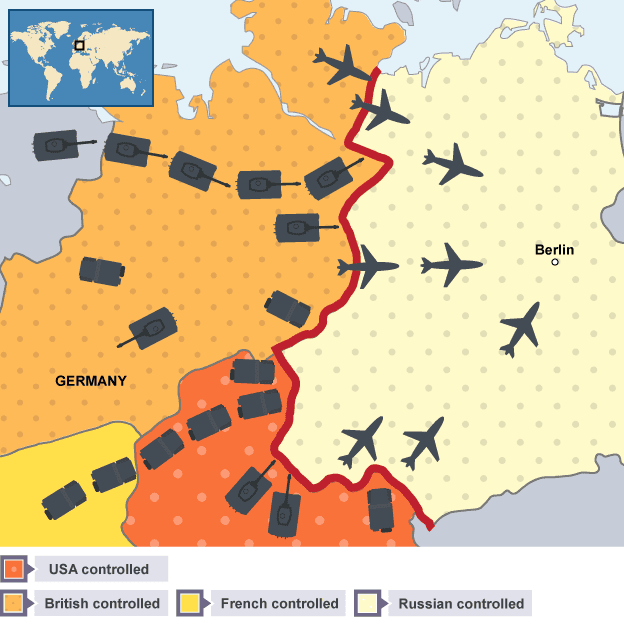
Understanding the Berlin Blockade Map:
A map of the Berlin Blockade offers a crucial visual representation of the complex geopolitical situation that unfolded during this period. It highlights the following key elements:
1. The Division of Germany:
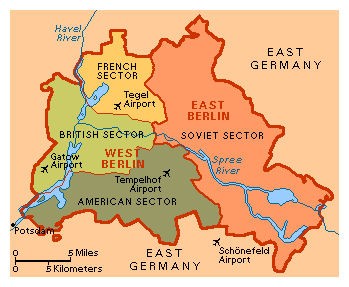
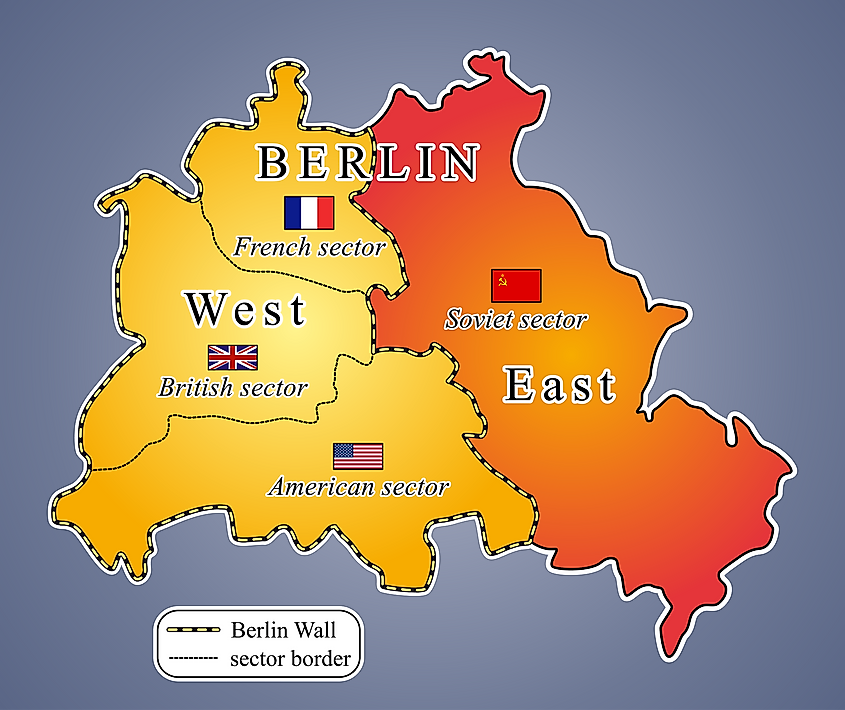
Post-World War II, Germany was divided into four occupation zones, with the United States, the United Kingdom, France, and the Soviet Union each assuming responsibility for a specific sector. Berlin, the nation’s capital, also faced a similar fate, divided into four sectors mirroring the occupation zones of Germany.
2. The Enclave of West Berlin:
The map clearly depicts West Berlin, controlled by the Western Allies, as an enclave deeply embedded within Soviet-controlled East Germany. This geographical anomaly, a legacy of wartime agreements, became the focal point of the blockade.
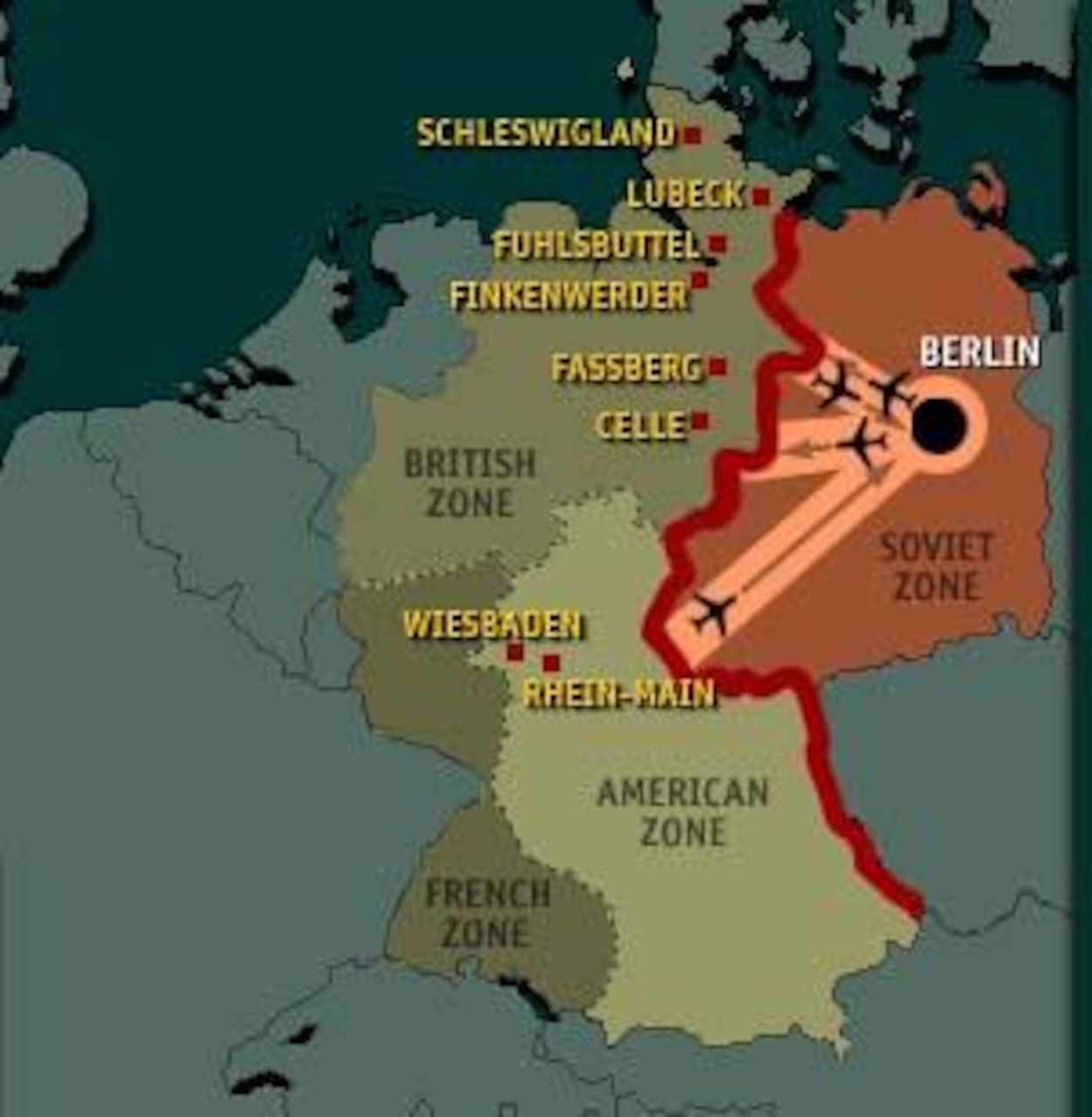
3. The Berlin Airlift:
The map also illustrates the crucial role of the Berlin Airlift, a massive logistical operation undertaken by the Western Allies to supply West Berlin with essential goods and provisions. The map might showcase the air corridors used by Allied aircraft, highlighting the vital role played by air bases in West Germany and the United States.
4. The Iron Curtain:
The Berlin Blockade map implicitly showcases the emerging Iron Curtain, a symbolic representation of the ideological and political divide that separated Western Europe from Eastern Europe. The physical presence of the Soviet-controlled East Germany surrounding West Berlin serves as a tangible manifestation of this division.
The Significance of the Berlin Blockade Map:
The Berlin Blockade map serves as a powerful tool for understanding the following:
- The Geopolitical Landscape: The map provides a clear visual representation of the division of Germany and the enclave of West Berlin, highlighting the complex geopolitical landscape of post-war Europe.
- The Strategic Importance of Berlin: The map underscores the strategic importance of Berlin, a city that became a focal point of Cold War tensions due to its unique geographical location and the symbolic significance it held for both sides.
- The Role of the Airlift: The map illustrates the crucial role played by the Berlin Airlift, a testament to the Western Allies’ commitment to West Berlin and a symbol of their determination to resist Soviet pressure.
- The Rise of the Cold War: The map offers a snapshot of the emerging Cold War, highlighting the ideological and political divide that was rapidly solidifying between the West and the Soviet bloc.
The Berlin Blockade: A Turning Point in History:
The Berlin Blockade stands as a critical turning point in history, marking the beginning of a protracted period of Cold War tensions and the emergence of a new geopolitical order. The blockade’s significance extends beyond the immediate crisis it generated, shaping the course of global affairs in the decades to come.
FAQs: The Berlin Blockade Map
1. Why was Berlin divided after World War II?
Berlin, like Germany, was divided into four occupation zones after World War II. This division was a consequence of the Allied victory and the decision to jointly administer Germany during the postwar period. The city’s strategic location and its symbolic importance as the German capital made it a focal point of Allied negotiations.
2. Why did the Soviet Union impose the blockade?
The Soviet Union imposed the blockade on West Berlin in June 1948, seeking to force the Western Allies to relinquish their control over the city. The Soviets believed that by cutting off West Berlin’s access to supplies, they could pressure the Western Allies into accepting Soviet demands for a unified, Soviet-controlled Germany.
3. What was the Berlin Airlift?
The Berlin Airlift was a massive logistical operation undertaken by the Western Allies to supply West Berlin with essential goods and provisions during the blockade. For nearly a year, Allied aircraft flew in food, fuel, and other necessities, successfully circumventing the Soviet blockade and preventing the city from succumbing to starvation or economic collapse.
4. How did the Berlin Blockade end?
The Berlin Blockade ended in May 1949 when the Soviet Union lifted the blockade. The Soviets realized that their efforts to force the Western Allies out of Berlin had failed, and the airlift had proven to be a successful countermeasure. The blockade’s failure also contributed to the further hardening of the Cold War divide, solidifying the division of Germany and Europe.
5. What are the lasting consequences of the Berlin Blockade?
The Berlin Blockade had several lasting consequences:
- The Division of Germany: The blockade solidified the division of Germany into East and West, a division that would persist for decades.
- The Strengthening of NATO: The blockade contributed to the formation of NATO, a military alliance of Western nations aimed at deterring Soviet aggression.
- The Escalation of the Cold War: The blockade further escalated Cold War tensions, leading to a period of heightened geopolitical instability.
Tips for Understanding the Berlin Blockade Map:
- Focus on the Enclave: Pay close attention to the geographical location of West Berlin, highlighting its status as an enclave within Soviet-controlled East Germany.
- Identify Key Locations: Identify key locations such as the air corridors used during the airlift, the major air bases, and the borders between the occupation zones.
- Consider the Symbolic Significance: Understand the symbolic significance of Berlin, a city that became a focal point of Cold War tensions and a symbol of the ideological struggle between the West and the Soviet bloc.
- Relate the Map to Historical Events: Connect the map to key events such as the division of Germany, the imposition of the blockade, and the airlift.
Conclusion: The Berlin Blockade Map – A Legacy of Cold War Tensions
The Berlin Blockade map serves as a powerful reminder of the complex geopolitical landscape that emerged after World War II. This map, by highlighting the division of Germany, the strategic importance of Berlin, and the role of the airlift, offers a visual representation of the Cold War’s beginnings and its enduring impact on the global order. The Berlin Blockade, a defining moment in history, continues to resonate today as a cautionary tale of ideological conflict and the enduring power of resilience in the face of adversity.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Berlin Blockade: A Map of Cold War Tensions. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!