The Heptarchy: Unpacking The Geographic And Political Landscape Of Early England
The Heptarchy: Unpacking the Geographic and Political Landscape of Early England
Related Articles: The Heptarchy: Unpacking the Geographic and Political Landscape of Early England
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Heptarchy: Unpacking the Geographic and Political Landscape of Early England. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Heptarchy: Unpacking the Geographic and Political Landscape of Early England

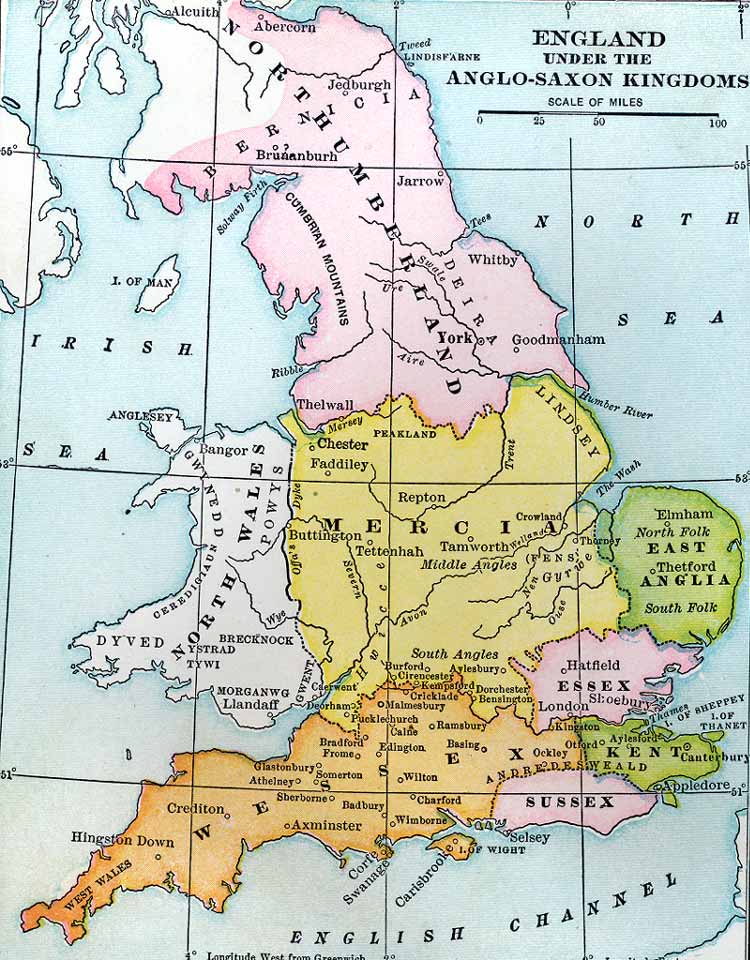
The term "Heptarchy" refers to a period in early English history, roughly spanning the 6th to 9th centuries, characterized by the existence of seven Anglo-Saxon kingdoms. These kingdoms, often depicted on a "Heptarchy Map," were not rigidly defined or static entities, and their boundaries fluctuated over time. Understanding the Heptarchy is crucial for comprehending the evolution of England’s political and cultural landscape, setting the stage for the emergence of a unified English nation.
Understanding the Kingdoms
The seven kingdoms commonly associated with the Heptarchy are:
- Northumbria: Occupying the northeastern region of England, Northumbria was a powerful kingdom known for its cultural achievements, including the development of the Lindisfarne Gospels.
- Mercia: Located in the Midlands, Mercia was a dominant force in the 7th and 8th centuries, expanding its influence westward and eventually controlling a significant portion of England.
- East Anglia: Situated in the eastern part of England, East Anglia was known for its strong maritime connections and its role in the spread of Christianity.
- Essex: Located in the southeast, Essex was one of the earliest Anglo-Saxon kingdoms and played a significant role in the conversion of England to Christianity.
- Kent: Located in the southeast, Kent was the first Anglo-Saxon kingdom to establish a royal dynasty and played a crucial role in the introduction of Christianity to England.
- Sussex: Situated in the south, Sussex was a smaller kingdom that was eventually absorbed by Wessex.
- Wessex: Located in the southwest, Wessex emerged as a powerful force in the 9th century under the leadership of Alfred the Great, ultimately uniting England under its rule.
A Dynamic and Shifting Landscape
It is important to note that the Heptarchy was not a static entity. The boundaries of these kingdoms shifted constantly, influenced by war, alliances, and political maneuvering. For example, Mercia’s dominance in the 7th and 8th centuries saw its territory expand significantly, while the decline of Northumbria in the 8th century led to the rise of Wessex.
The Heptarchy Map: A Visual Representation
The Heptarchy Map provides a visual representation of the geographical divisions and political realities of early England. It serves as a valuable tool for understanding the complex interplay of power, alliances, and conflict that shaped the Anglo-Saxon world.
Key Features of the Heptarchy Map:
- Geographic Boundaries: The map clearly demarcates the territories controlled by each kingdom, providing a visual understanding of their geographic extent.
- Kingdom Names and Capitals: The map typically identifies each kingdom by name and often highlights its capital city, providing context for its political and administrative center.
- Historical Events: Some maps may incorporate historical events, such as major battles or the spread of Christianity, adding depth to the visual narrative.
- Visual Representation of Power Dynamics: The size and prominence of kingdoms on the map can convey their relative power and influence at a particular point in time.
The Legacy of the Heptarchy
The Heptarchy was a crucial period in English history, laying the groundwork for the emergence of a unified England. The conflicts, alliances, and cultural exchanges between these kingdoms shaped the political, social, and religious landscape of the nation. The Heptarchy also played a vital role in the spread of Christianity in England, leading to the establishment of powerful monasteries and the development of Anglo-Saxon art and literature.
Beyond the Map: Understanding the Complexities
While the Heptarchy Map provides a valuable visual framework for understanding early English history, it is important to remember that the reality was far more complex. The kingdoms were not always unified entities, and their boundaries were constantly shifting. Furthermore, the map does not fully capture the intricate social, cultural, and religious dynamics that shaped the lives of people during this period.
FAQs
Q: What is the significance of the Heptarchy in English history?
A: The Heptarchy represents a crucial period in English history, marking the transition from smaller, independent kingdoms to a more unified nation. It played a vital role in shaping the political, cultural, and religious landscape of England, laying the groundwork for the emergence of a powerful Anglo-Saxon kingdom.
Q: Why is the Heptarchy Map important?
A: The Heptarchy Map provides a visual representation of the geographic divisions and political realities of early England. It serves as a valuable tool for understanding the complex interplay of power, alliances, and conflict that shaped the Anglo-Saxon world.
Q: How did the Heptarchy eventually lead to a unified England?
A: The Heptarchy saw a constant struggle for dominance between the kingdoms. The rise of Wessex under Alfred the Great and his successors eventually led to the unification of England under their rule.
Q: What were the major cultural achievements of the Heptarchy period?
A: The Heptarchy was a period of significant cultural development, marked by the spread of Christianity, the establishment of powerful monasteries, and the development of Anglo-Saxon art and literature.
Q: What are the limitations of using a Heptarchy Map to understand early English history?
A: The Heptarchy Map provides a simplified representation of a complex period in history. It does not fully capture the intricate social, cultural, and religious dynamics that shaped the lives of people during this time.
Tips for Understanding the Heptarchy
- Study Primary Sources: Explore primary sources like Anglo-Saxon chronicles and historical accounts to gain a deeper understanding of the events and personalities of the Heptarchy period.
- Explore Historical Context: Understand the broader historical context of the Heptarchy, including the arrival of the Anglo-Saxons in Britain and the spread of Christianity.
- Consider the Role of Geography: Analyze the influence of geography on the development of the Heptarchy kingdoms, including their location, resources, and strategic importance.
- Examine Power Dynamics: Study the complex relationships between the kingdoms, including their alliances, conflicts, and shifting power balances.
- Focus on Cultural Developments: Explore the cultural achievements of the Heptarchy period, including the development of art, literature, and religious institutions.
Conclusion
The Heptarchy Map serves as a valuable visual tool for understanding the complex and dynamic political landscape of early England. It provides a snapshot of the seven kingdoms that shaped the nation’s early history, highlighting their geographical boundaries, political centers, and relative power dynamics. While the map offers a simplified representation, it remains a crucial resource for appreciating the historical complexities of this period, paving the way for a deeper understanding of the forces that ultimately led to the unification of England.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-120575246-58fa7a123df78ca1591effcc.jpg)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Heptarchy: Unpacking the Geographic and Political Landscape of Early England. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!