Uncovering the Past: The Importance of Abandoned Pipeline Maps
Related Articles: Uncovering the Past: The Importance of Abandoned Pipeline Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Uncovering the Past: The Importance of Abandoned Pipeline Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Uncovering the Past: The Importance of Abandoned Pipeline Maps
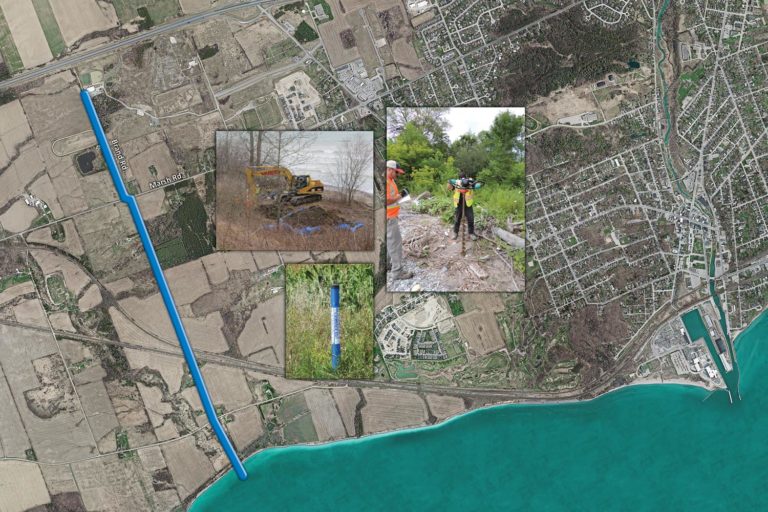

The landscape of our world is crisscrossed by a vast network of pipelines, arteries carrying vital resources like oil, gas, and water. While these pipelines serve crucial roles in modern society, many have fallen into disuse, becoming relics of past industrial activity. These abandoned pipelines, though seemingly forgotten, hold significant value, and their accurate mapping is crucial for a variety of reasons.
Understanding the Legacy: Why Abandoned Pipeline Maps Matter
Abandoned pipelines, often buried beneath the surface, present a unique set of challenges and opportunities. They represent a potential environmental hazard, a historical record, and a potential resource. Mapping these pipelines provides a comprehensive understanding of their location, construction, and potential risks, enabling informed decisions regarding their management and remediation.
Environmental Stewardship: Mitigating Risks
Abandoned pipelines can pose significant environmental risks. Corrosion, leaks, and spills can contaminate soil and water sources, impacting ecosystems and human health. Accurate pipeline maps serve as essential tools for environmental protection, allowing for:
- Targeted Inspections: Identifying the location and condition of abandoned pipelines enables focused inspections, allowing for early detection of leaks and potential environmental hazards.
- Remediation Planning: Detailed maps facilitate the development of effective remediation strategies, ensuring the safe and efficient removal or sealing of hazardous pipelines.
- Pollution Prevention: By providing a clear picture of potential contamination sources, abandoned pipeline maps aid in preventing future pollution events and safeguarding sensitive ecosystems.
Historical Preservation: Uncovering the Past
Abandoned pipelines are not just inert structures; they are historical artifacts reflecting the evolution of infrastructure and industrial development. Their mapping provides valuable insights into:
- Industrial History: Pipeline maps reveal the past patterns of resource extraction, transportation, and consumption, offering a glimpse into the history of industrial development.
- Technological Advancements: Tracing the evolution of pipeline technology, materials, and construction methods through mapping provides a valuable resource for researchers and historians.
- Cultural Heritage: Abandoned pipelines can be intertwined with local communities and industries, offering insights into their history, economic development, and cultural landscape.
Resource Management: Optimizing Future Use
Despite being abandoned, pipelines can hold untapped potential. Mapping these structures can facilitate:
- Re-purposing: Abandoned pipelines can be repurposed for new uses, such as transporting renewable energy sources or providing infrastructure for water management.
- Resource Recovery: Mapping can identify sections of pipelines that can be salvaged for their materials, reducing waste and promoting resource efficiency.
- Land Use Planning: Accurate pipeline maps help inform land use decisions, ensuring that development projects avoid potential conflicts with existing infrastructure.
Challenges and Solutions in Mapping Abandoned Pipelines
Mapping abandoned pipelines presents unique challenges:
- Lack of Documentation: Historical records may be incomplete or inaccessible, making it difficult to locate and identify abandoned pipelines.
- Underground Infrastructure: Pipelines are often buried, requiring specialized techniques and equipment for their detection and mapping.
- Environmental Conditions: Weather, terrain, and vegetation can hinder mapping efforts, requiring careful planning and adaptation.
To overcome these challenges, a multi-faceted approach is required:
- Historical Research: Thorough research of historical documents, maps, and aerial photographs can provide valuable clues regarding pipeline locations.
- Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR): GPR technology can detect buried pipelines by sending electromagnetic waves into the ground and analyzing their reflections.
- Aerial Surveys: Aerial photography and LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) can provide high-resolution images and elevation data, aiding in the identification of pipeline corridors.
- GIS (Geographic Information Systems): GIS software provides a powerful platform for organizing, analyzing, and visualizing mapping data, enabling the creation of comprehensive and interactive pipeline maps.
FAQs on Abandoned Pipeline Maps
Q: Who is responsible for maintaining abandoned pipelines?
A: The responsibility for abandoned pipelines often falls on the original owner or operator, but this can be complex depending on the age of the pipeline, the regulatory environment, and the legal framework.
Q: How can I find information about abandoned pipelines in my area?
A: Contact your local government, environmental agencies, or utility companies. They may have records or resources related to abandoned pipelines.
Q: What happens to an abandoned pipeline once it’s mapped?
A: The fate of an abandoned pipeline depends on its condition, environmental impact, and potential for reuse. Options include removal, sealing, or repurposing.
Q: Are there any legal implications for owning an abandoned pipeline?
A: Yes, there can be legal liabilities associated with owning an abandoned pipeline, including environmental damage, property damage, and potential health risks.
Tips for Working with Abandoned Pipeline Maps
- Collaborate: Engage with stakeholders including government agencies, environmental groups, and local communities to ensure comprehensive mapping and effective management of abandoned pipelines.
- Leverage Technology: Utilize advanced mapping technologies like GPR, LiDAR, and GIS to ensure accurate and detailed mapping.
- Promote Transparency: Make mapping data readily available to relevant parties, fostering collaboration and informed decision-making.
- Prioritize Safety: Ensure the safety of personnel involved in mapping and remediation activities, following strict safety protocols.
Conclusion: Embracing the Legacy of Abandoned Pipelines
Abandoned pipelines represent a complex legacy, carrying both potential risks and opportunities. Mapping these structures is not merely a technical exercise; it is a crucial step in ensuring environmental protection, preserving historical knowledge, and optimizing resource management. By embracing the challenge of mapping abandoned pipelines, we can unlock their value, mitigate potential hazards, and create a more sustainable future.
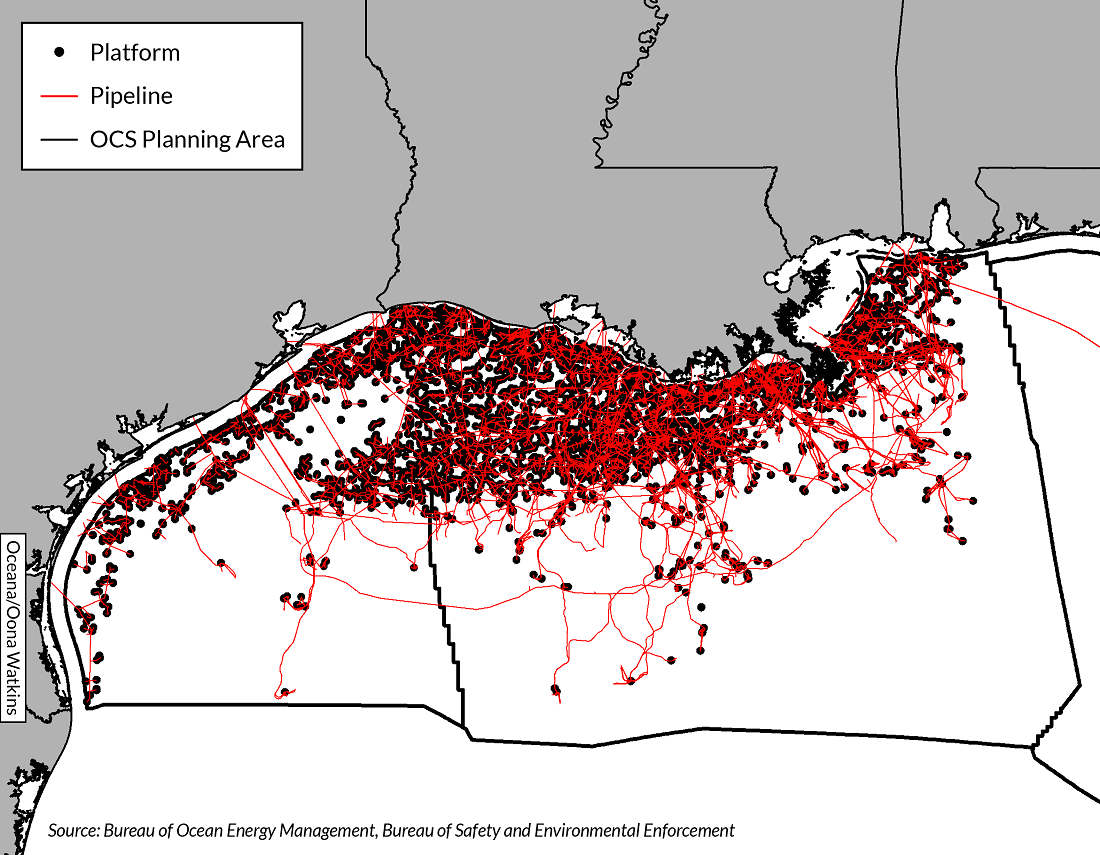
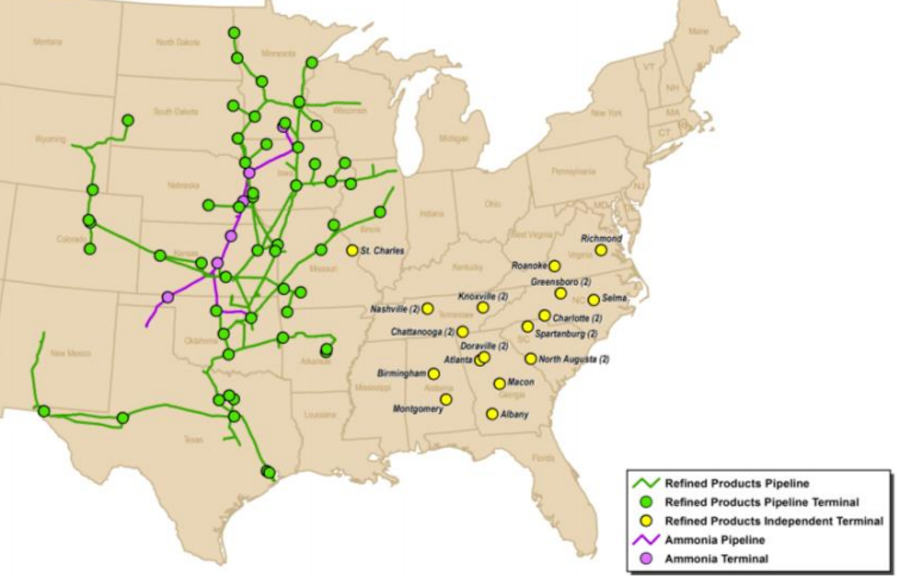
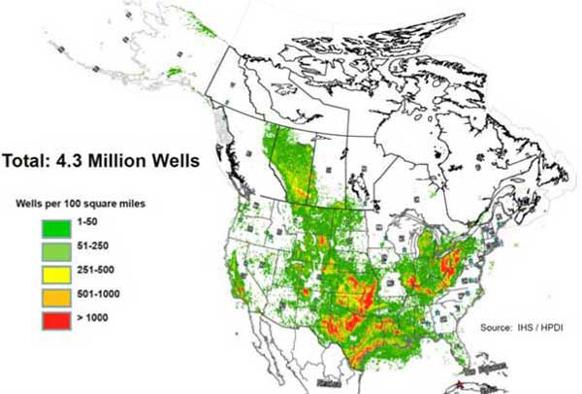
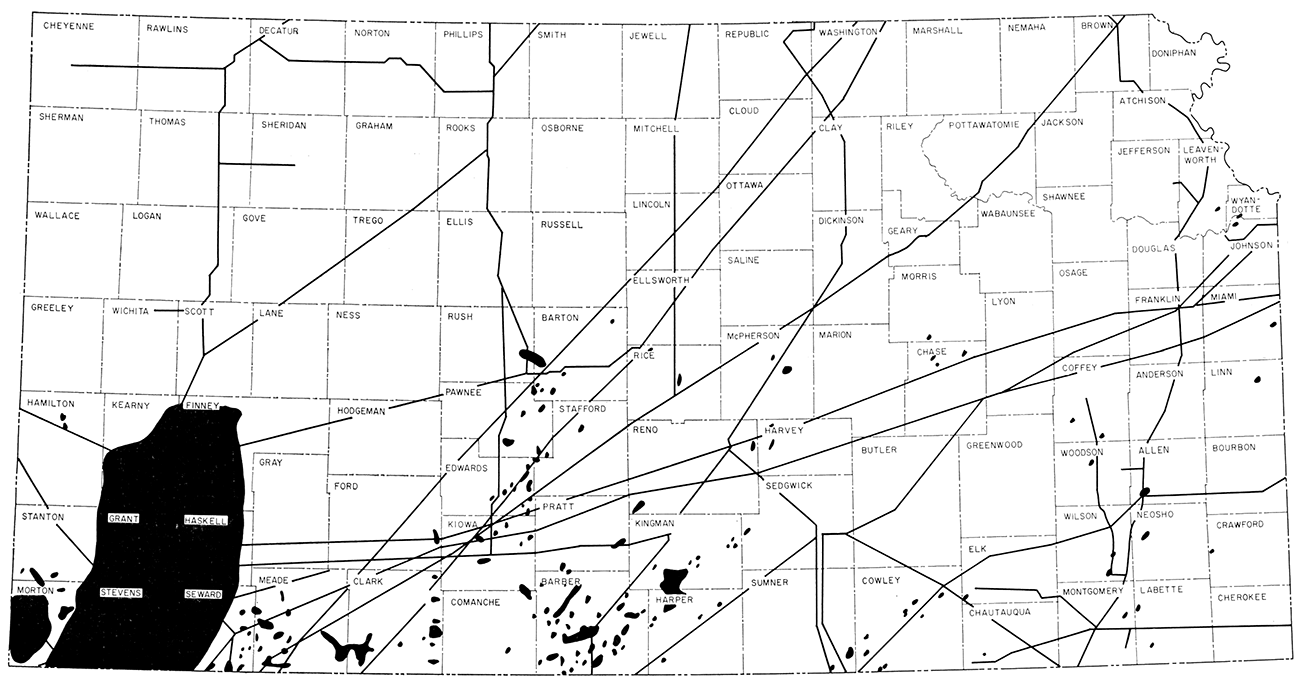

![]()
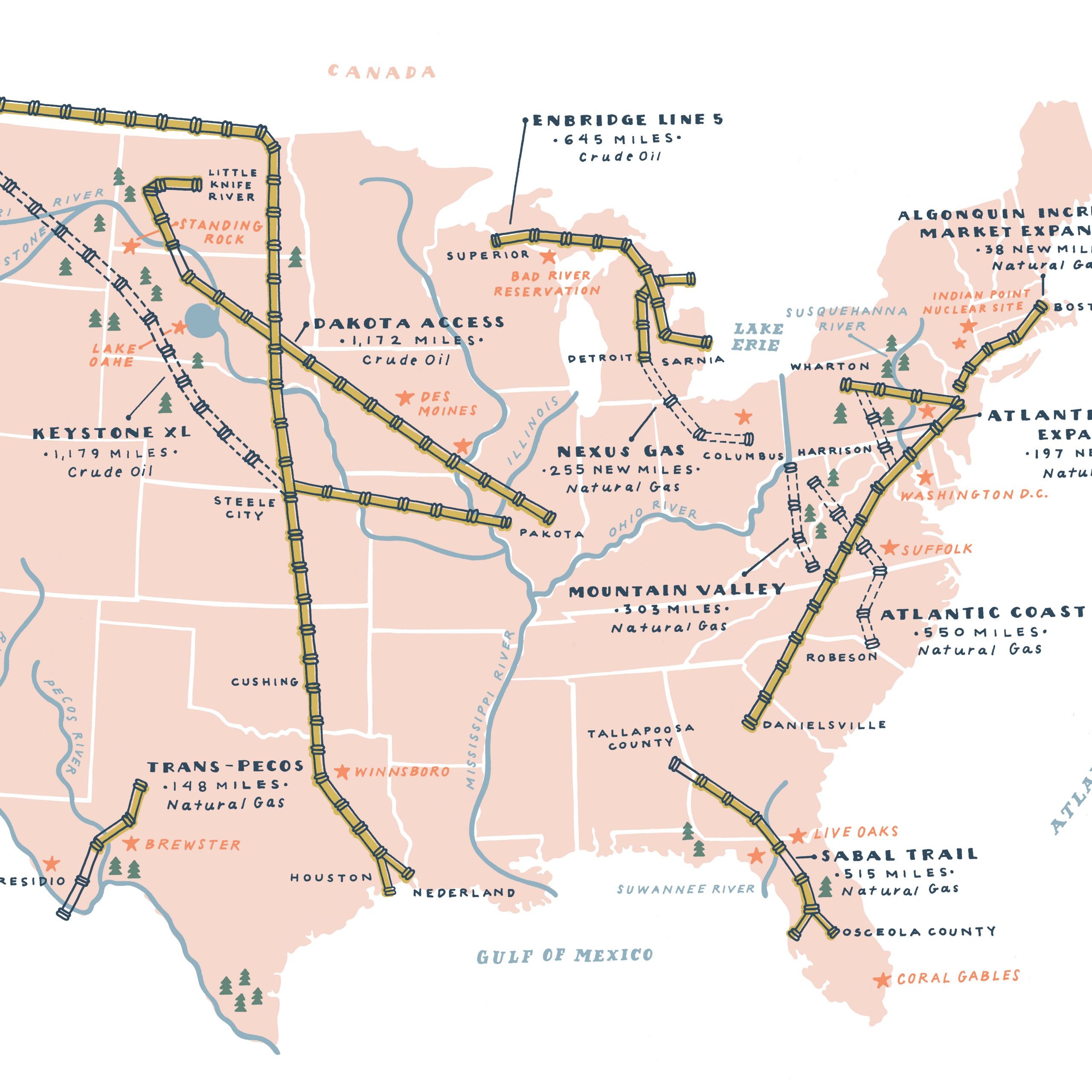
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Uncovering the Past: The Importance of Abandoned Pipeline Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!