Understanding The Global Forecast System (GFS) Snow Map: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Global Forecast System (GFS) Snow Map: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Global Forecast System (GFS) Snow Map: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Global Forecast System (GFS) Snow Map: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the Global Forecast System (GFS) Snow Map: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the Global Forecast System (GFS) Snow Map: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 What is the GFS Snow Map?
- 3.2 How the GFS Snow Map Works
- 3.3 Applications of the GFS Snow Map
- 3.4 Benefits of the GFS Snow Map
- 3.5 Understanding the GFS Snow Map: Key Considerations
- 3.6 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the GFS Snow Map
- 3.7 Tips for Using the GFS Snow Map
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding the Global Forecast System (GFS) Snow Map: A Comprehensive Guide

The Global Forecast System (GFS) snow map is a valuable tool for anyone interested in predicting snowfall and its potential impact. Developed by the National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP), the GFS model provides a detailed analysis of atmospheric conditions and generates forecasts for various meteorological variables, including snowfall accumulation. This article will explore the GFS snow map, its applications, and its significance for diverse stakeholders.
What is the GFS Snow Map?
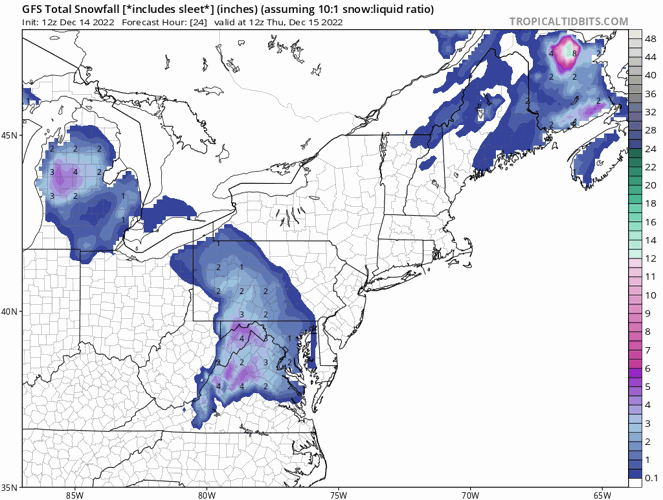
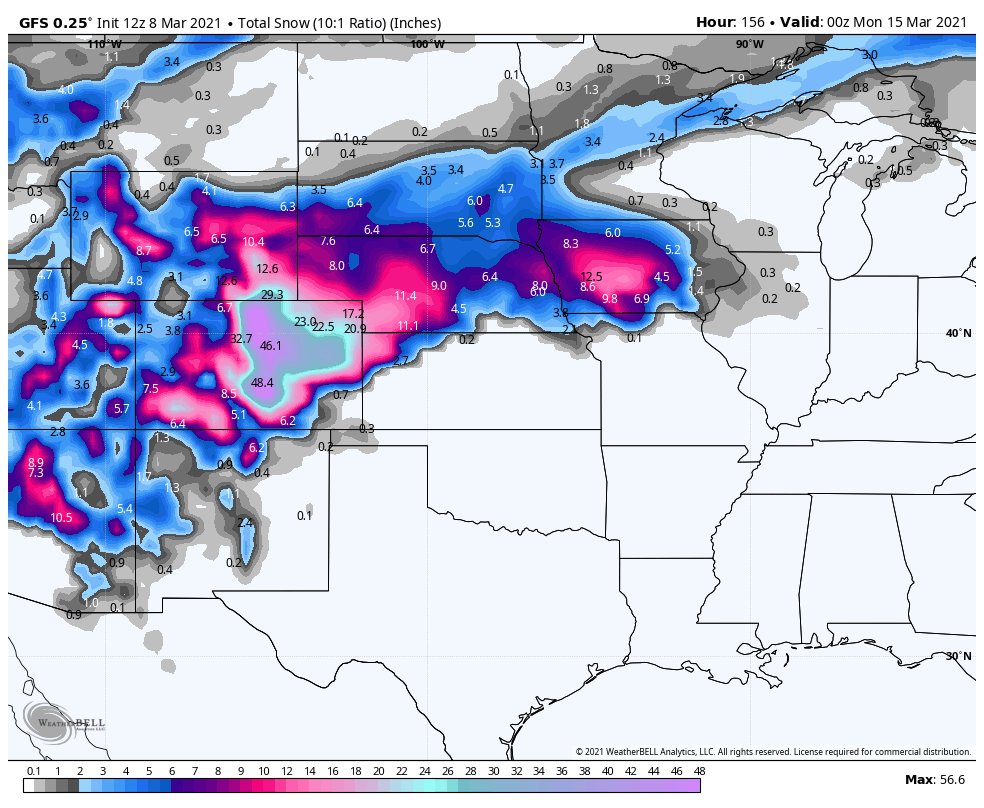
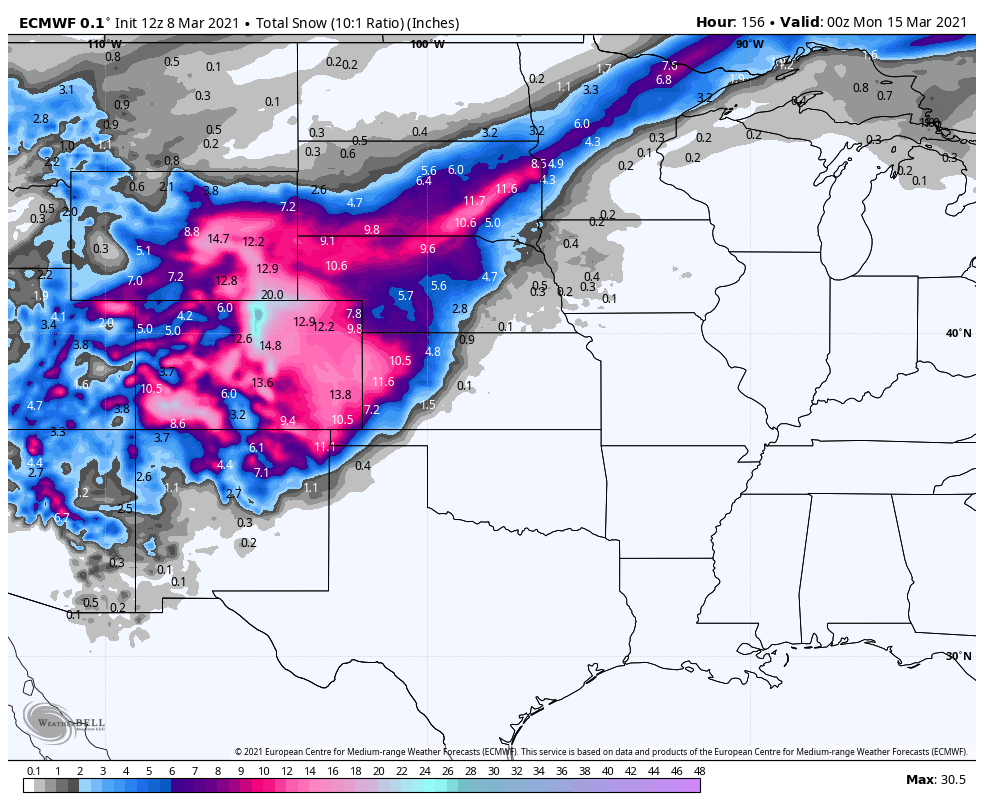
The GFS snow map is a visual representation of predicted snowfall accumulation over a specific period. It utilizes data from the GFS model, a complex numerical weather prediction system that simulates atmospheric processes. The map displays areas where snowfall is anticipated, along with estimated snowfall amounts, helping users understand the potential impact of snow events.
How the GFS Snow Map Works
The GFS model relies on a vast amount of data, including:
- Observations: Data from weather stations, satellites, and other sources provide a snapshot of current atmospheric conditions.
- Numerical Simulations: The model uses mathematical equations to simulate atmospheric processes, such as wind, temperature, and precipitation.
- Forecast Outputs: The GFS model generates forecasts for various meteorological variables, including snowfall accumulation, at different time intervals and spatial resolutions.
The GFS snow map visualizes these forecast outputs, presenting a clear picture of predicted snowfall patterns.
Applications of the GFS Snow Map
The GFS snow map finds applications in various sectors, including:
- Weather Forecasting: Meteorologists rely on the GFS snow map to predict snowfall events, assess their intensity, and provide timely warnings to the public.
- Transportation: Highway departments utilize the map to plan for snow removal operations, ensuring safe road conditions.
- Energy: Utilities companies use the GFS snow map to anticipate potential disruptions to power grids caused by snowstorms.
- Agriculture: Farmers use the map to plan for potential impacts of snow on crops and livestock.
- Outdoor Recreation: Ski resorts and other outdoor enthusiasts use the GFS snow map to forecast snow conditions and plan activities.
- Emergency Management: Emergency responders utilize the map to prepare for potential snow-related emergencies, such as power outages or transportation disruptions.
Benefits of the GFS Snow Map
The GFS snow map offers several benefits:
- Improved Snowfall Prediction: The map provides a comprehensive overview of predicted snowfall patterns, enhancing the accuracy of snowfall forecasts.
- Enhanced Planning: The GFS snow map enables stakeholders to plan for potential snow events, mitigating risks and ensuring preparedness.
- Improved Decision Making: By providing timely and accurate information, the GFS snow map empowers decision-makers to make informed choices regarding snow-related operations.
- Increased Awareness: The map raises awareness about potential snow events, encouraging individuals and organizations to take necessary precautions.
Understanding the GFS Snow Map: Key Considerations
When interpreting the GFS snow map, it’s essential to consider the following:
- Forecast Accuracy: The GFS model, like any weather prediction system, has limitations. Forecast accuracy can vary depending on factors such as the time horizon and the complexity of the weather system.
- Spatial Resolution: The GFS snow map displays predicted snowfall at a specific spatial resolution, meaning it may not capture localized variations in snowfall amounts.
- Model Limitations: The GFS model is a complex system that relies on numerous assumptions and simplifications. It may not accurately represent all atmospheric processes, leading to potential inaccuracies in snowfall forecasts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the GFS Snow Map
1. How often is the GFS snow map updated?
The GFS model runs four times daily, generating new forecasts every six hours. The snow map is updated accordingly, providing the most up-to-date information on predicted snowfall.
2. How accurate is the GFS snow map?
The accuracy of the GFS snow map depends on various factors, including the time horizon of the forecast and the complexity of the weather system. However, the GFS model is considered a reliable tool for predicting snowfall events, particularly for longer-range forecasts.
3. What are the units used for snowfall accumulation on the GFS snow map?
The GFS snow map typically displays snowfall accumulation in inches or centimeters. The specific unit used may vary depending on the source of the map.
4. Is the GFS snow map available for specific locations?
Yes, the GFS snow map is available for various locations worldwide. Users can access the map through various online platforms, such as the National Weather Service website.
5. Can I use the GFS snow map for planning outdoor activities?
Yes, the GFS snow map can provide useful information for planning outdoor activities, especially those that are affected by snowfall conditions, such as skiing or snowboarding.
Tips for Using the GFS Snow Map
- Check multiple sources: Compare the GFS snow map with other weather forecasts to get a more comprehensive understanding of potential snowfall events.
- Consider the time horizon: Be aware that forecast accuracy decreases as the time horizon increases.
- Understand the spatial resolution: Recognize that the GFS snow map may not capture localized variations in snowfall amounts.
- Stay informed: Monitor weather updates and adjust plans accordingly, especially during winter storms.
Conclusion
The GFS snow map is a valuable resource for anyone interested in predicting snowfall and its potential impact. By providing a comprehensive overview of predicted snowfall patterns, the map empowers stakeholders to plan for snow events, mitigate risks, and make informed decisions. While the GFS model has limitations, it remains a reliable tool for understanding snowfall patterns and making informed decisions regarding snow-related activities. By staying informed and utilizing the GFS snow map effectively, individuals and organizations can better prepare for and manage the challenges posed by winter storms.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Global Forecast System (GFS) Snow Map: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!