Unlocking California’s Energy Potential: A Comprehensive Look At Hydraulic Fracturing
Unlocking California’s Energy Potential: A Comprehensive Look at Hydraulic Fracturing
Related Articles: Unlocking California’s Energy Potential: A Comprehensive Look at Hydraulic Fracturing
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unlocking California’s Energy Potential: A Comprehensive Look at Hydraulic Fracturing. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unlocking California’s Energy Potential: A Comprehensive Look at Hydraulic Fracturing
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unlocking California’s Energy Potential: A Comprehensive Look at Hydraulic Fracturing
- 3.1 Mapping California’s Fracking Landscape
- 3.2 Understanding the Economic Benefits of Fracking in California
- 3.3 Addressing Environmental Concerns: A Balancing Act
- 3.4 Navigating the Regulatory Landscape: Balancing Environmental Protection and Economic Development
- 3.5 FAQs: Addressing Key Questions about Fracking in California
- 3.6 Tips for Understanding Fracking in California
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unlocking California’s Energy Potential: A Comprehensive Look at Hydraulic Fracturing
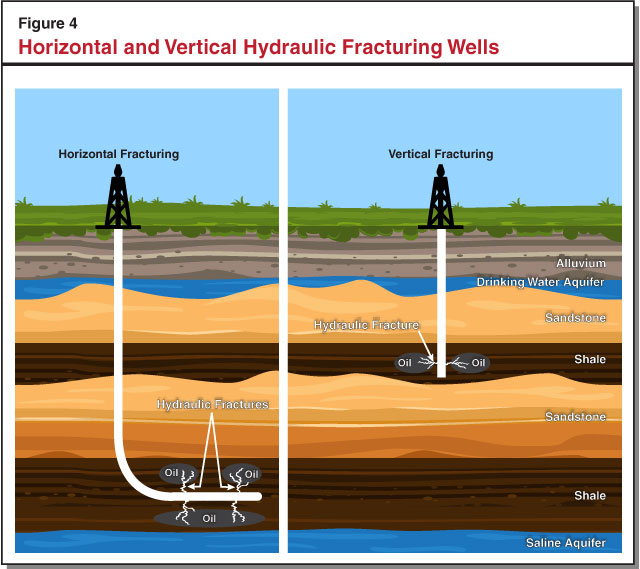
Hydraulic fracturing, commonly known as fracking, has emerged as a significant player in the global energy landscape, revolutionizing the extraction of natural gas and oil from unconventional shale formations. In California, the debate surrounding fracking has been particularly intense, fueled by concerns about environmental impacts and the potential for seismic activity. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of fracking in California, exploring its geographical distribution, economic implications, environmental concerns, and regulatory framework.
Mapping California’s Fracking Landscape
The geographical distribution of fracking activity in California is not uniform, with specific regions experiencing higher levels of activity than others. The primary areas of interest are:
1. The San Joaquin Valley: This region, located in the central part of the state, holds vast reserves of shale gas and oil. It has been a focal point of fracking operations, with significant activity in counties like Kern, Fresno, and Monterey.
2. The Monterey Shale Formation: This geological formation stretches across a significant portion of central and southern California, extending from the San Joaquin Valley to the coast. It is considered a promising source of unconventional oil and gas, attracting considerable investment and exploration efforts.
3. The Los Angeles Basin: This basin, encompassing Los Angeles and surrounding areas, has been the subject of debate regarding potential fracking activities. While fracking operations have been limited in the basin due to concerns about urban proximity and potential environmental impacts, exploration and development continue.
4. The Ventura Basin: Located in Ventura County, this basin also holds potential for shale gas and oil extraction. However, fracking activity in this region has been relatively limited, with ongoing discussions regarding its environmental implications.
Understanding the Economic Benefits of Fracking in California
The potential economic benefits of fracking in California are significant, attracting considerable interest from energy companies and policymakers alike. The key economic advantages include:
1. Job Creation: Fracking operations require a substantial workforce, leading to the creation of jobs in various sectors, including drilling, engineering, logistics, and manufacturing. This employment boost can have a positive impact on local economies, particularly in regions experiencing economic hardship.
2. Tax Revenue: Fracking activities generate significant tax revenue for state and local governments. These funds can be used to finance public services, infrastructure projects, and educational initiatives, contributing to overall economic development.
3. Energy Independence: By increasing domestic energy production, fracking can reduce reliance on imported oil and gas, contributing to energy independence and national security. This can help stabilize energy prices and reduce the country’s vulnerability to global energy market fluctuations.
4. Lower Energy Costs: Increased domestic production from fracking can lead to lower energy prices for consumers, reducing energy costs for households and businesses. This can stimulate economic growth and enhance consumer purchasing power.
5. Technological Advancements: The development of fracking technology has driven innovation in various sectors, including drilling, hydraulic fracturing, and waste management. These advancements can lead to improved efficiency, reduced environmental impacts, and increased safety in the energy industry.
Addressing Environmental Concerns: A Balancing Act
While fracking offers significant economic benefits, it has also raised concerns about its environmental impact. These concerns center around:
1. Water Contamination: Fracking operations involve the injection of large volumes of water mixed with chemicals into the ground. There are concerns about potential contamination of groundwater sources, particularly in regions with limited water resources.
2. Air Pollution: Fracking activities can release methane, a potent greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere. Additionally, the burning of natural gas extracted through fracking can contribute to air pollution, particularly in areas with high concentrations of fracking operations.
3. Seismic Activity: The injection of fluids into the ground during fracking can induce seismic activity, particularly in areas with pre-existing fault lines. This has led to concerns about potential earthquakes and their impact on infrastructure and public safety.
4. Land Use: Fracking operations require significant land use for drilling, storage facilities, and infrastructure development. This can lead to habitat fragmentation, disruption of natural ecosystems, and potential conflicts with land management practices.
5. Waste Management: Fracking operations generate significant amounts of wastewater and solid waste. The disposal of these materials poses challenges for environmental protection, requiring careful management to minimize potential contamination and environmental risks.
Navigating the Regulatory Landscape: Balancing Environmental Protection and Economic Development
Recognizing the potential environmental impacts of fracking, California has implemented a comprehensive regulatory framework to mitigate risks and ensure responsible development. Key aspects of this framework include:
1. The California Department of Conservation (DOC): The DOC plays a crucial role in regulating oil and gas activities, including fracking. It sets standards for well construction, waste disposal, and environmental monitoring, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
2. The California Environmental Protection Agency (CalEPA): CalEPA oversees environmental protection efforts in the state, ensuring that fracking operations meet environmental standards and minimize potential impacts on air, water, and land.
3. The California Air Resources Board (CARB): CARB regulates air quality in the state, setting emission standards for fracking operations and working to minimize greenhouse gas emissions associated with natural gas production.
4. The California Water Resources Control Board (State Water Board): The State Water Board regulates water quality in California, ensuring that fracking operations do not contaminate groundwater sources and comply with water quality standards.
5. The California Geologic Survey (CGS): The CGS monitors seismic activity in the state, working to assess the potential risks associated with fracking and provide guidance for mitigating seismic hazards.
FAQs: Addressing Key Questions about Fracking in California
1. Is fracking legal in California?
Yes, fracking is legal in California, but it is subject to stringent regulations designed to minimize environmental impacts.
2. What are the environmental risks associated with fracking?
The primary environmental risks associated with fracking include water contamination, air pollution, seismic activity, land use changes, and waste management challenges.
3. How does California regulate fracking?
California has a comprehensive regulatory framework for fracking, overseen by various state agencies, including the Department of Conservation, the Environmental Protection Agency, the Air Resources Board, the Water Resources Control Board, and the Geologic Survey.
4. What are the economic benefits of fracking in California?
Fracking can generate economic benefits, including job creation, tax revenue, energy independence, lower energy costs, and technological advancements.
5. What are the arguments against fracking in California?
Opponents of fracking argue that it poses significant environmental risks, including water contamination, air pollution, seismic activity, and habitat disruption. They also argue that the economic benefits are overstated and that the risks outweigh the potential rewards.
6. Is fracking safe?
The safety of fracking is a subject of ongoing debate. Proponents argue that it is safe when conducted responsibly and under strict regulations. Opponents argue that the potential risks are too great and that the industry cannot be adequately regulated to ensure safety.
7. What are the future prospects for fracking in California?
The future of fracking in California remains uncertain. The state’s regulatory framework is evolving, and public opinion on fracking is divided. The industry is facing challenges related to environmental concerns, regulatory scrutiny, and the growing popularity of renewable energy sources.
Tips for Understanding Fracking in California
1. Consult official sources: Seek information from reputable sources, such as government agencies, scientific organizations, and independent research institutions.
2. Consider multiple perspectives: Explore different viewpoints on fracking, including those of environmental groups, industry representatives, and local communities.
3. Analyze data and research: Review scientific studies, data reports, and regulatory documents to gain a deeper understanding of the environmental and economic implications of fracking.
4. Engage in informed discussions: Participate in public forums, community meetings, and online discussions to share information and engage in constructive dialogue about fracking.
5. Stay informed about regulatory updates: Monitor changes in state regulations and policies related to fracking to stay abreast of the latest developments.
Conclusion
The debate surrounding fracking in California is complex, reflecting the intricate interplay of economic, environmental, and social considerations. While fracking offers the potential for economic benefits, it also raises significant concerns about environmental impacts. The state’s regulatory framework aims to balance these competing interests, ensuring responsible development while protecting public health and the environment. As the energy landscape continues to evolve, the future of fracking in California will depend on the ability to navigate these challenges and find solutions that meet both economic and environmental objectives. By engaging in informed discussions, seeking reliable information, and actively participating in the decision-making process, Californians can contribute to shaping a sustainable energy future for the state.



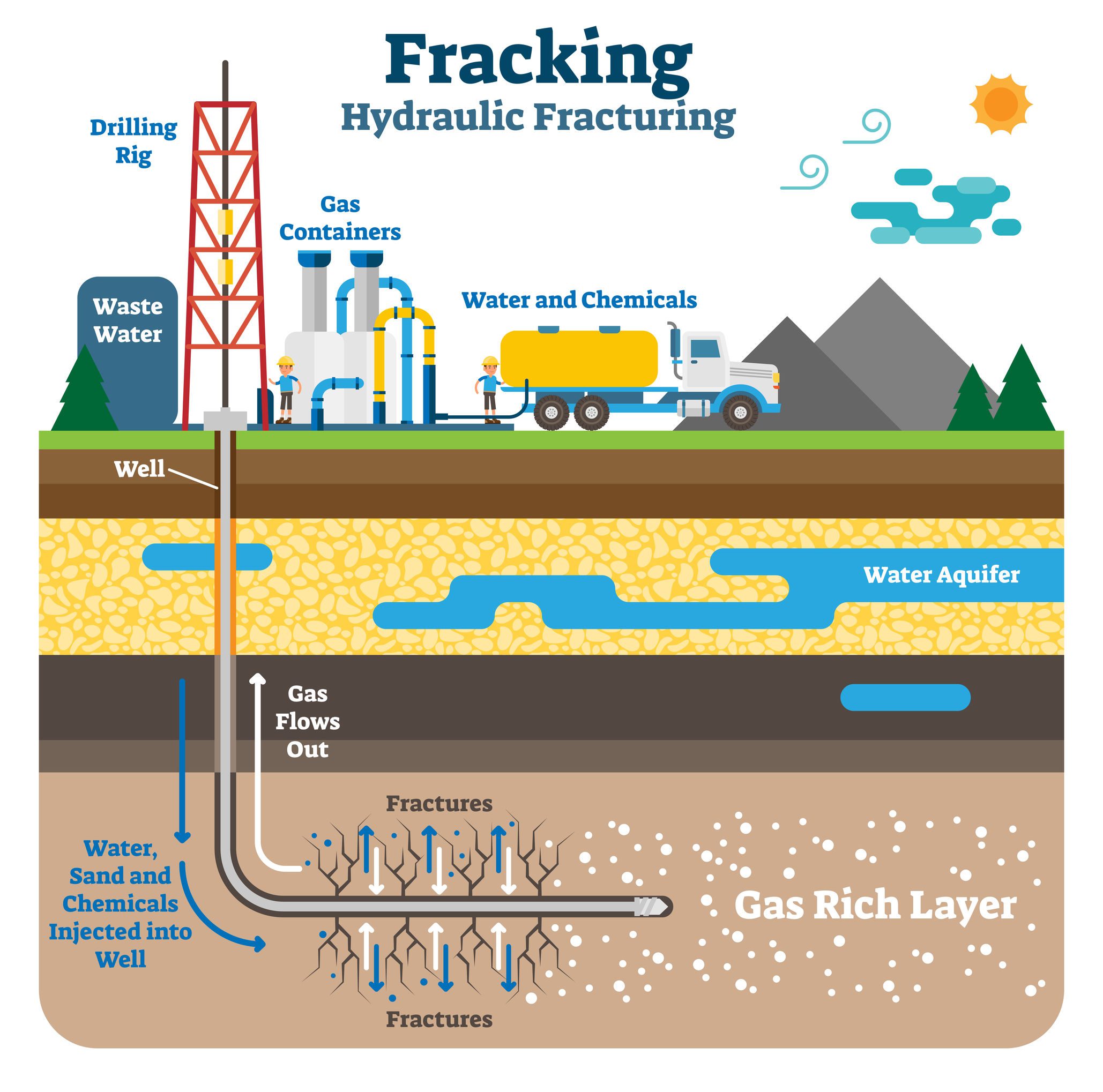


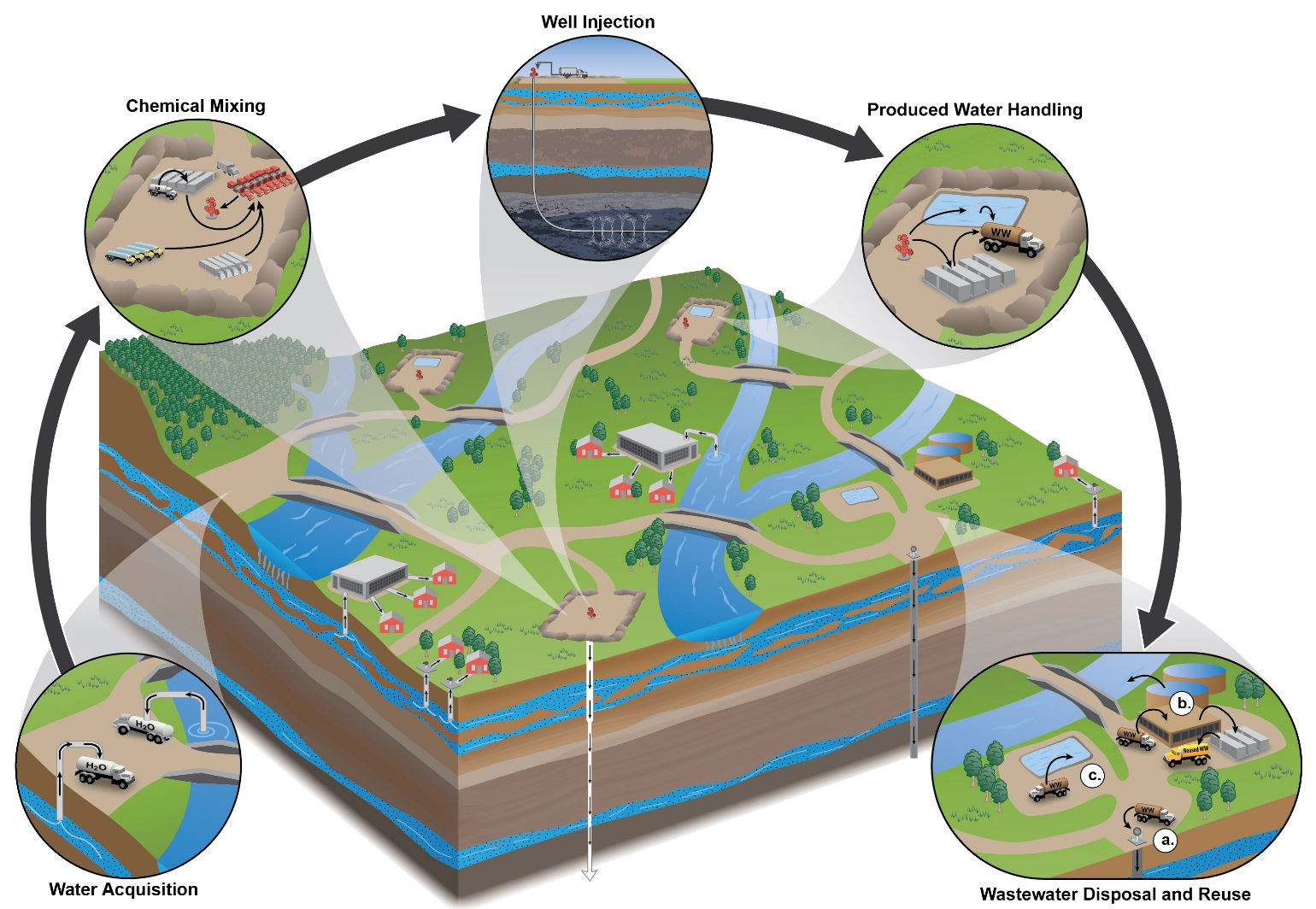

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking California’s Energy Potential: A Comprehensive Look at Hydraulic Fracturing. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!