Unraveling The Tapestry Of Time: A Journey Through Historical Maps Of The Middle East
Unraveling the Tapestry of Time: A Journey Through Historical Maps of the Middle East
Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of Time: A Journey Through Historical Maps of the Middle East
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Tapestry of Time: A Journey Through Historical Maps of the Middle East. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Tapestry of Time: A Journey Through Historical Maps of the Middle East
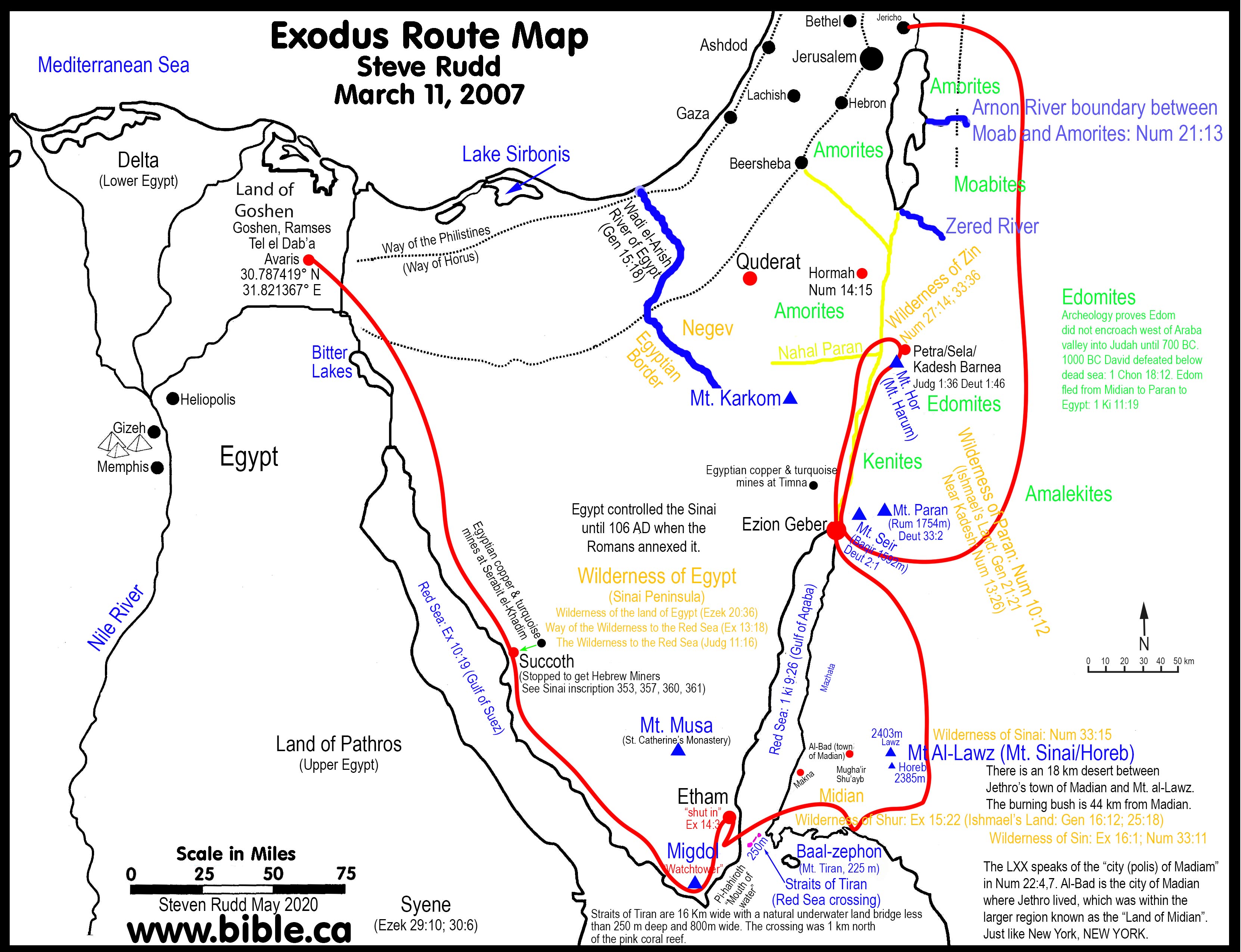
The Middle East, a region steeped in history and cultural significance, has witnessed a kaleidoscope of empires, dynasties, and civilizations rise and fall over millennia. Understanding the intricate tapestry of its past requires navigating the complex and ever-changing landscape of its geography. Historical maps, invaluable tools for navigating both physical and temporal dimensions, provide a window into the evolution of this pivotal region.
A Journey Through Time: Unveiling the Shifting Sands of History
From the dawn of civilization to the present day, the Middle East has been a crucible of cultural exchange, a crossroads where empires clashed and trade routes flourished. Historical maps, meticulously crafted by cartographers, serve as a visual chronicle of this dynamic history, revealing the ebb and flow of power and the shifting boundaries of empires.
The Ancient World: Empires and Trade Routes
The ancient Middle East was a mosaic of powerful civilizations, each leaving an indelible mark on the region’s history. The Sumerian civilization, renowned for its cuneiform script and sophisticated city-states, flourished in Mesopotamia, a fertile crescent between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. The Akkadian Empire, under the leadership of Sargon the Great, united Mesopotamia, laying the foundation for a period of unprecedented expansion and cultural influence.
Historical maps from this era depict these early empires, showcasing the vastness of their territories and the strategic importance of their trade routes. The map of the Akkadian Empire, for instance, reveals the extent of its dominion, stretching from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea, highlighting the significance of the Euphrates River as a vital artery for trade and communication.
The Rise of Persia and the Hellenistic Age
The Persian Empire, under the Achaemenid dynasty, emerged as a formidable power in the 6th century BCE, uniting a vast territory encompassing Persia, Mesopotamia, and parts of Egypt. The Achaemenids established a sophisticated administrative system and built a network of roads that facilitated trade and communication across their empire.
Historical maps of the Persian Empire vividly illustrate its vastness and the strategic importance of its major cities, such as Persepolis, the ceremonial capital, and Susa, a major administrative center. The map also highlights the importance of the Royal Road, a paved highway that connected Sardis in Anatolia to Susa, facilitating communication and trade between the eastern and western parts of the empire.
The conquests of Alexander the Great in the 4th century BCE marked a turning point in the history of the Middle East. His empire, which stretched from Greece to India, encompassed much of the region, ushering in the Hellenistic period, characterized by the fusion of Greek and Eastern cultures.
Historical maps of the Hellenistic period illustrate the spread of Greek influence, showcasing the establishment of new cities and the adoption of Greek language and culture in regions previously dominated by other civilizations. The map of the Seleucid Empire, founded by one of Alexander’s generals, reveals the extent of its territory, encompassing parts of Mesopotamia, Syria, and Persia, highlighting the spread of Hellenistic culture in the region.
The Roman Empire and the Rise of Islam
The Roman Empire, at its peak, extended its influence into the Middle East, conquering Egypt, Syria, and parts of Mesopotamia. The Romans established a sophisticated administrative system and built a network of roads that connected the eastern and western parts of their empire.
Historical maps of the Roman Empire in the Middle East depict the Roman provinces, showcasing the strategic importance of key cities such as Antioch, Alexandria, and Damascus. The map also highlights the Roman road network, which facilitated trade and communication across the region, contributing to the spread of Roman culture and influence.
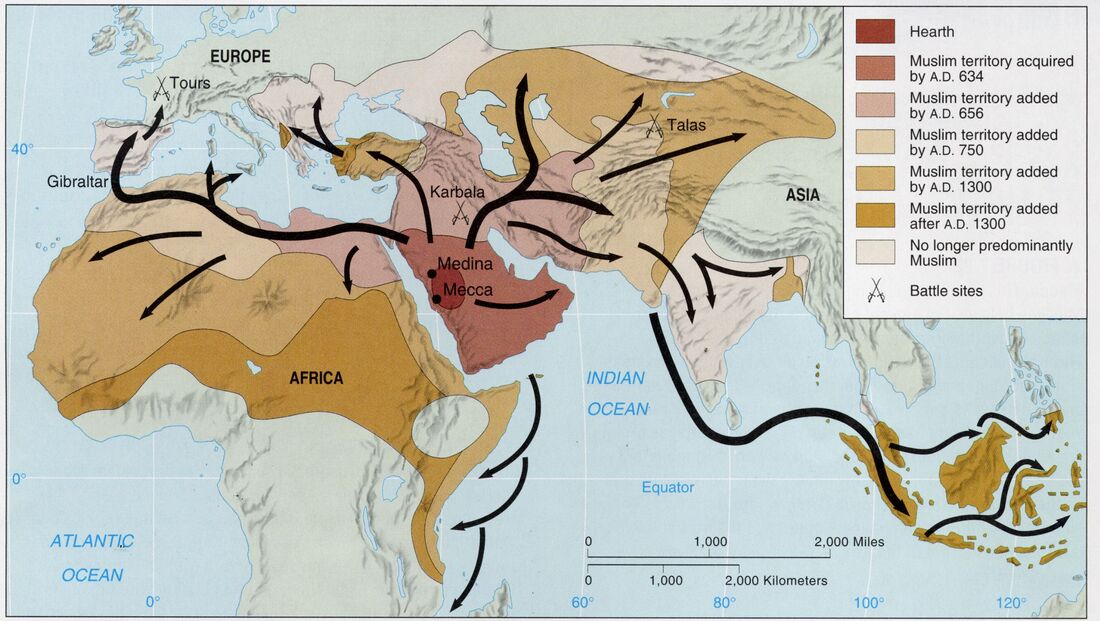
The rise of Islam in the 7th century CE marked a significant turning point in the history of the Middle East. The rapid expansion of the Islamic Caliphate, starting from the Arabian Peninsula, resulted in the conquest of vast territories, including Syria, Egypt, North Africa, Persia, and parts of Spain.
Historical maps of the Islamic Caliphate showcase the vastness of its territory, highlighting the strategic importance of key cities such as Mecca, Medina, Damascus, and Baghdad. The map also reveals the importance of trade routes, connecting the Islamic world with the rest of the world, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and knowledge.
The Crusades and the Ottoman Empire
The Crusades, a series of religious wars launched by European Christians to recapture Jerusalem from the Muslims, had a profound impact on the Middle East. These wars, spanning centuries, resulted in the establishment of Crusader states in the Levant, highlighting the clash of civilizations and the struggle for control over strategically important territories.
Historical maps of the Crusader states, such as the Kingdom of Jerusalem, illustrate their geographical locations and the extent of their territories, showcasing the complex political landscape of the region during the Crusades.
The Ottoman Empire, a powerful Islamic empire that emerged in the 13th century, eventually came to dominate much of the Middle East, North Africa, and parts of Europe. The Ottoman Empire’s vast territory, encompassing diverse cultures and religions, was a testament to its military prowess and administrative capabilities.
Historical maps of the Ottoman Empire reveal the extent of its territories, highlighting the strategic importance of key cities such as Istanbul, Constantinople, Damascus, and Cairo. The map also showcases the complex network of trade routes that connected the Ottoman Empire with the rest of the world, contributing to its economic and cultural influence.
The Modern Middle East: A Legacy of Conflict and Transformation
The 20th century witnessed a period of significant political and social upheaval in the Middle East, marked by the decline of the Ottoman Empire, the rise of nationalism, and the creation of new nation-states. The region has been plagued by conflicts, including the Arab-Israeli wars, the Iran-Iraq War, and the ongoing conflicts in Syria and Yemen.
Historical maps of the modern Middle East illustrate the political boundaries of contemporary nation-states, highlighting the complex geopolitical landscape of the region. The map also reveals the legacy of colonialism and the impact of international interventions on the region’s political and social landscape.
The Importance of Historical Maps in Understanding the Middle East
Historical maps are invaluable tools for understanding the complex history of the Middle East. They provide a visual representation of the region’s evolving geography, showcasing the rise and fall of empires, the shifting boundaries of nations, and the strategic importance of key cities and trade routes.
By studying these maps, we gain insights into the interconnectedness of the region’s history, the impact of cultural exchange, and the role of geography in shaping the region’s political and social landscape. They serve as a reminder of the enduring legacy of the Middle East, a region that has played a pivotal role in shaping the course of human history.
FAQs about Historical Maps of the Middle East
1. What are the different types of historical maps of the Middle East?
Historical maps of the Middle East can be categorized based on their historical period, geographic focus, and purpose. For example, there are maps depicting ancient empires, medieval Islamic caliphates, Crusader states, Ottoman territories, and modern nation-states. They can also be categorized based on their purpose, such as military maps, trade route maps, or maps depicting cultural and religious landscapes.
2. What are some of the key features to look for when examining historical maps of the Middle East?
When examining historical maps of the Middle East, it is crucial to consider the following key features:
- Scale and Projection: The scale of the map determines the level of detail and the size of the area depicted. The projection used to create the map can influence the accuracy of distances and shapes.
- Legends and Symbols: The legend explains the symbols used on the map, representing different geographical features, cities, empires, or cultural groups.
- Historical Context: It is essential to consider the historical context in which the map was created. The mapmaker’s perspective, biases, and the purpose of the map can influence its content and interpretation.
3. How can historical maps be used in research and education?
Historical maps are invaluable tools for research and education, providing a visual representation of historical events, geographical relationships, and cultural influences. They can be used to:
- Illustrate the geographical context of historical events: Maps can help visualize the locations of battles, trade routes, or the spread of empires.
- Compare and contrast different historical periods: Maps can be used to show how the boundaries of empires, the locations of cities, or the distribution of populations have changed over time.
- Explore the relationship between geography and history: Maps can help understand how geographical features, such as mountains, rivers, or deserts, have influenced historical events and cultural development.
4. What are some of the challenges of interpreting historical maps of the Middle East?
Interpreting historical maps of the Middle East can be challenging due to:
- Inaccuracies and Biases: Maps are often based on limited information and can reflect the mapmaker’s biases.
- Changing Political Boundaries: The boundaries of empires and nation-states have changed frequently throughout history, making it difficult to compare maps from different periods.
- Limited Availability of Maps: Not all historical periods are well-documented with maps, making it challenging to reconstruct the geographical landscape of certain eras.
Tips for Using Historical Maps of the Middle East
- Consult multiple sources: Compare maps from different periods and mapmakers to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the region’s history.
- Consider the historical context: Understand the mapmaker’s perspective, biases, and the purpose of the map to interpret its content accurately.
- Utilize online resources: Online databases and digital libraries provide access to a wide range of historical maps, allowing for detailed examination and analysis.
- Engage in critical thinking: Approach historical maps with a critical eye, considering their limitations and potential inaccuracies.
Conclusion
Historical maps of the Middle East are invaluable tools for understanding the region’s complex and dynamic history. They provide a visual representation of the evolving geography, showcasing the rise and fall of empires, the shifting boundaries of nations, and the strategic importance of key cities and trade routes. By studying these maps, we gain insights into the interconnectedness of the region’s past, the impact of cultural exchange, and the role of geography in shaping the Middle East’s political and social landscape. As we navigate the complexities of the present, understanding the region’s historical tapestry is essential for fostering informed dialogue, promoting peaceful coexistence, and building a more stable and prosperous future for the Middle East.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Tapestry of Time: A Journey Through Historical Maps of the Middle East. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!