Unveiling the Diverse Climates of Latin America: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unveiling the Diverse Climates of Latin America: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Diverse Climates of Latin America: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Diverse Climates of Latin America: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Diverse Climates of Latin America: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 A Mosaic of Climates: Unveiling the Diversity
- 3.2 Influencing Factors: Shaping the Climate Tapestry
- 3.3 The Importance of Understanding Latin American Climates
- 3.4 FAQs: Exploring the Nuances of Latin American Climates
- 3.5 Tips for Navigating the Climate Landscape of Latin America
- 3.6 Conclusion: Embracing the Climate Challenge
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Diverse Climates of Latin America: A Comprehensive Guide

Latin America, a vast and geographically diverse region spanning from the Caribbean to the southern tip of South America, exhibits a remarkable array of climates. Understanding these climatic variations is crucial for various fields, including agriculture, resource management, infrastructure development, and even public health. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate tapestry of Latin American climates, exploring their characteristics, influencing factors, and implications for the region’s diverse populations.
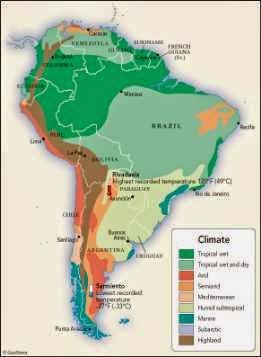
A Mosaic of Climates: Unveiling the Diversity
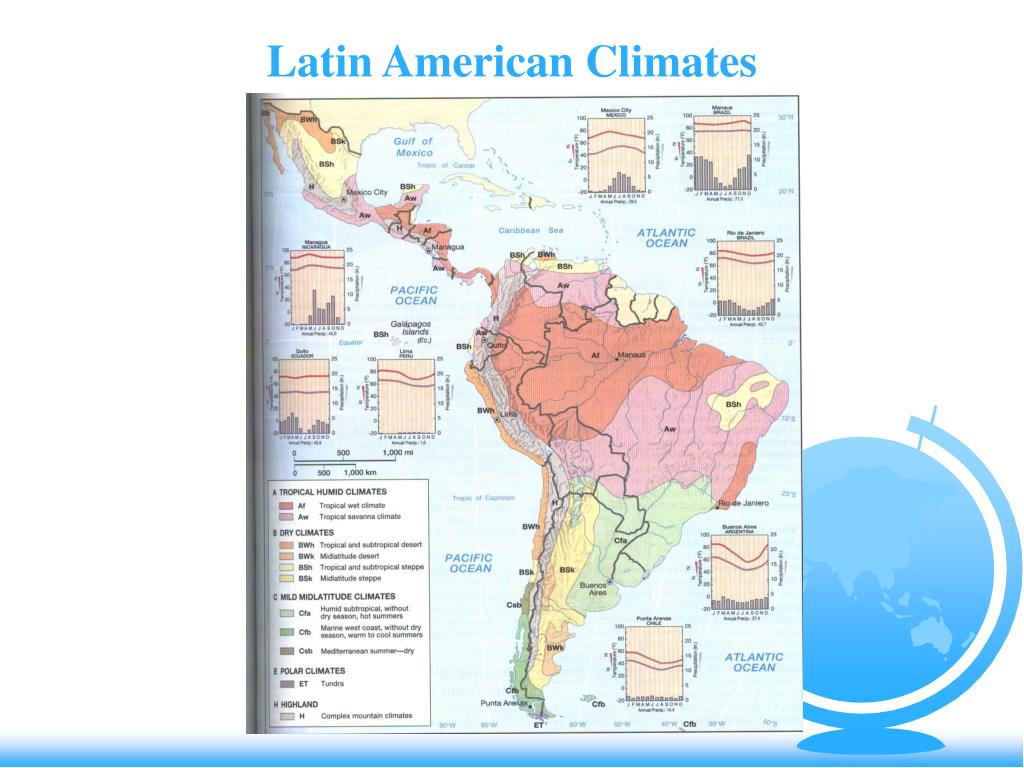
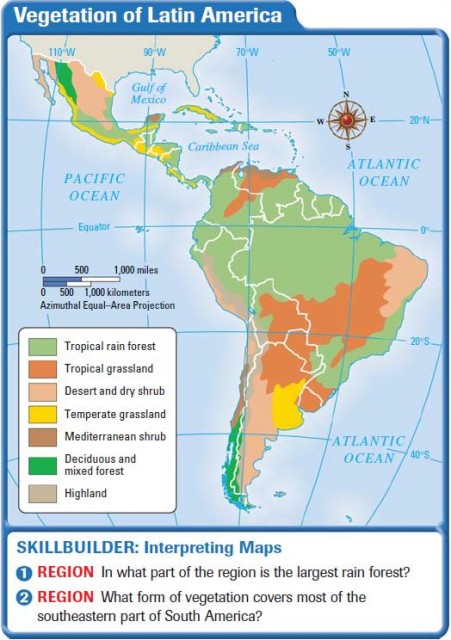
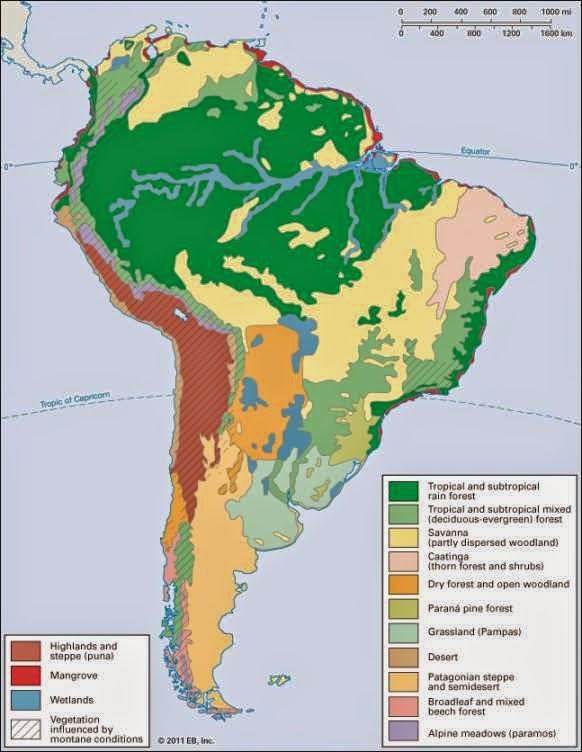
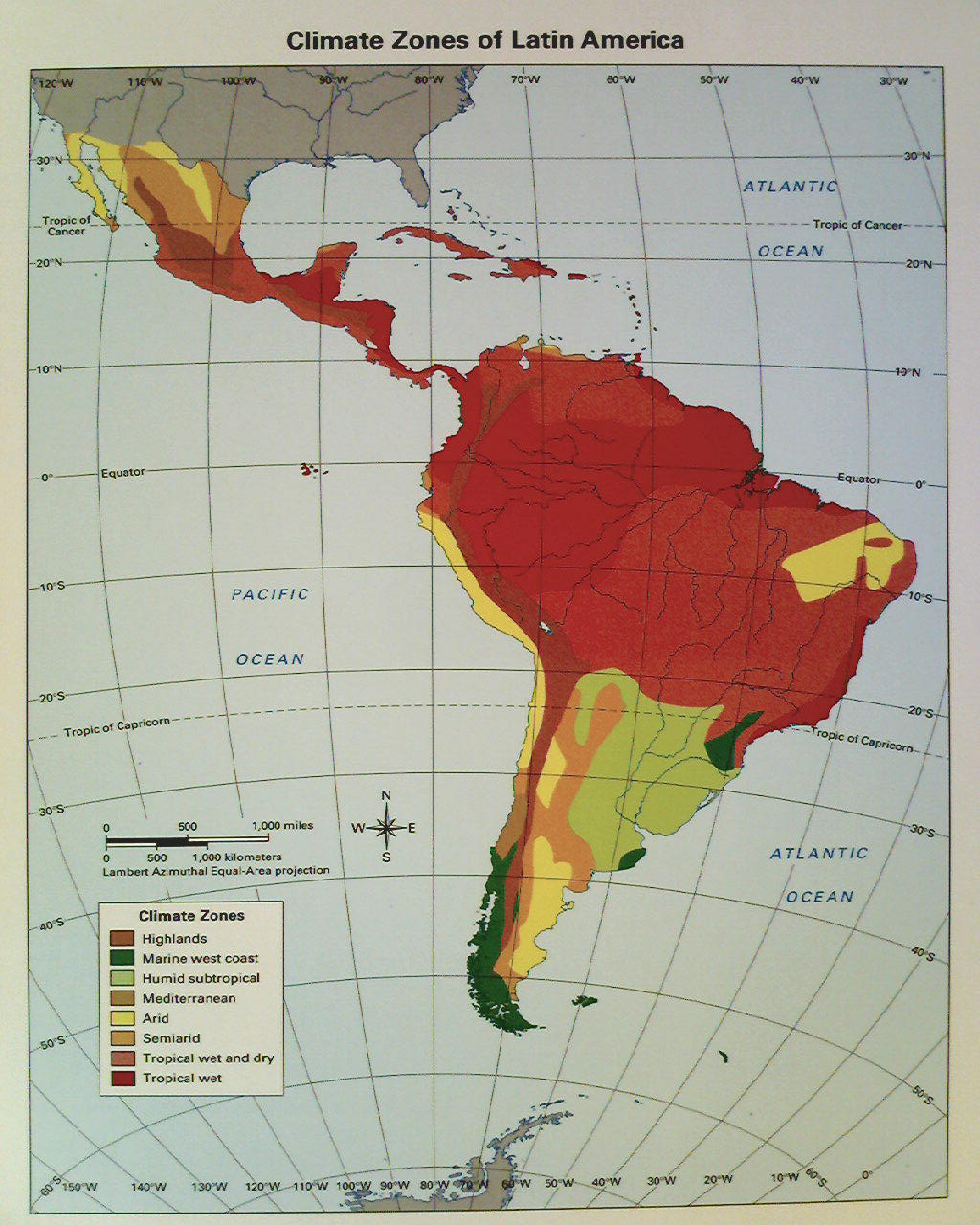
Latin America’s climate map is a testament to the region’s complex geographical features, encompassing a range of ecosystems from towering mountains to lush rainforests, arid deserts, and vast grasslands. The interplay of latitude, altitude, ocean currents, and prevailing winds shapes the unique climatic patterns that define different regions.
Tropical Climates: Dominating much of Central America, the Caribbean, and northern South America, tropical climates are characterized by consistently high temperatures and abundant rainfall throughout the year. These regions experience high humidity, fostering lush vegetation and biodiversity. The Amazon rainforest, the largest tropical rainforest on Earth, thrives under this climate, playing a crucial role in global carbon cycling and biodiversity conservation.
Subtropical Climates: Transitioning from the tropics, subtropical climates exhibit distinct wet and dry seasons, with warmer temperatures than tropical regions. These climates are found in coastal areas of Brazil, Argentina, and Chile, supporting a wide range of agricultural activities and diverse ecosystems, including grasslands and savannas.
Temperate Climates: Moving further south, Latin America embraces temperate climates with four distinct seasons, including warm summers and cold winters. These climates are prevalent in southern South America, encompassing regions like Patagonia and the Andes Mountains. They support a diverse range of vegetation, from deciduous forests to grasslands, and are home to a wide array of endemic species.
Arid and Semi-Arid Climates: Characterized by low rainfall and high temperatures, arid and semi-arid climates dominate parts of Chile, Argentina, and Mexico. These regions often feature deserts and semi-deserts, with limited vegetation and unique adaptations to survive harsh conditions.
Mountain Climates: The towering Andes Mountains, stretching the length of western South America, experience a wide range of climates influenced by altitude. From snow-capped peaks to verdant valleys, the Andes exhibit a diverse array of microclimates, impacting local ecosystems and human settlements.
Influencing Factors: Shaping the Climate Tapestry
Latitude: The position of a region relative to the equator significantly influences its climate. Regions closer to the equator experience higher temperatures and more consistent rainfall due to the direct angle of the sun’s rays.
Altitude: As altitude increases, temperatures generally decrease. This phenomenon, known as the lapse rate, creates a variety of microclimates within mountainous regions, influencing vegetation patterns and agricultural practices.
Ocean Currents: Warm and cold ocean currents play a significant role in shaping regional climates. The warm El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) current, for example, can cause increased rainfall and warmer temperatures across much of Latin America, while the cold Humboldt Current off the coast of Chile contributes to the aridity of the Atacama Desert.
Prevailing Winds: The direction and intensity of prevailing winds influence rainfall patterns and temperature distribution. The trade winds, for instance, bring moisture from the Atlantic Ocean to the Caribbean and parts of Central America, contributing to their high rainfall.
The Importance of Understanding Latin American Climates
Comprehending the diverse climates of Latin America is essential for sustainable development and adaptation to the challenges posed by climate change.
Agriculture and Food Security: Understanding climate patterns is crucial for optimizing agricultural practices and ensuring food security. Climate maps help farmers select appropriate crops, manage water resources, and adapt to changing weather conditions.
Water Resource Management: Climate data informs water management strategies, enabling efficient allocation of scarce resources, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions where water scarcity is a major concern.
Infrastructure Development: Understanding climate patterns is crucial for designing and constructing infrastructure projects that are resilient to extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts.
Public Health: Climate change can exacerbate health risks, such as heat waves, vector-borne diseases, and respiratory illnesses. Climate maps help public health officials identify vulnerable populations and implement preventive measures.
Biodiversity Conservation: Climate change poses a significant threat to Latin America’s rich biodiversity. Understanding climate patterns is essential for identifying vulnerable ecosystems and developing conservation strategies.
FAQs: Exploring the Nuances of Latin American Climates
Q1: What is the driest region in Latin America?
A: The Atacama Desert in northern Chile is considered the driest desert in the world, receiving minimal rainfall annually. Its aridity is attributed to the rain shadow effect of the Andes Mountains and the cold Humboldt Current.
Q2: How does El Niño affect Latin American climates?
A: El Niño, a warming of the central and eastern Pacific Ocean, can significantly impact rainfall patterns and temperatures across Latin America. During El Niño events, many regions experience increased rainfall, leading to floods, while other areas experience drought.
Q3: What are the main challenges posed by climate change to Latin America?
A: Climate change poses significant challenges to Latin America, including increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, sea-level rise, glacier retreat, and changes in agricultural productivity. These challenges threaten ecosystems, human health, and socioeconomic stability.
Q4: What are some of the adaptations being implemented to address climate change in Latin America?
A: Latin American countries are implementing various adaptation measures, such as developing drought-resistant crops, improving water management systems, strengthening infrastructure against extreme weather events, and promoting sustainable land use practices.
Q5: What are the key research areas related to Latin American climates?
A: Research on Latin American climates focuses on understanding the impacts of climate change, developing climate models for regional predictions, assessing the vulnerability of ecosystems and human populations, and exploring adaptation and mitigation strategies.
Tips for Navigating the Climate Landscape of Latin America
1. Utilize Climate Data and Resources: Access reliable climate data and resources from reputable organizations such as the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
2. Embrace Sustainable Practices: Promote sustainable land management practices, water conservation, and renewable energy sources to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
3. Enhance Climate Literacy: Foster climate literacy among communities, particularly in vulnerable areas, to empower them to understand climate risks and adapt accordingly.
4. Collaborate for Climate Action: Encourage collaboration between governments, research institutions, and civil society organizations to address climate change challenges collectively.
5. Support Climate Research: Invest in research and innovation to improve understanding of climate dynamics, develop adaptation strategies, and enhance climate resilience.
Conclusion: Embracing the Climate Challenge
Latin America’s diverse climates are a testament to the region’s rich geographical tapestry. Understanding these climates is crucial for addressing challenges posed by climate change, ensuring sustainable development, and fostering resilience among its diverse populations. By embracing knowledge, promoting sustainable practices, and fostering collaborative action, Latin America can navigate the complexities of climate change and build a brighter future for its people and its environment.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Diverse Climates of Latin America: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!