Unveiling The Diverse Landscape Of Mexico: A Comprehensive Look At Its Relief Map
Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Mexico: A Comprehensive Look at its Relief Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Mexico: A Comprehensive Look at its Relief Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Mexico: A Comprehensive Look at its Relief Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Mexico: A Comprehensive Look at its Relief Map
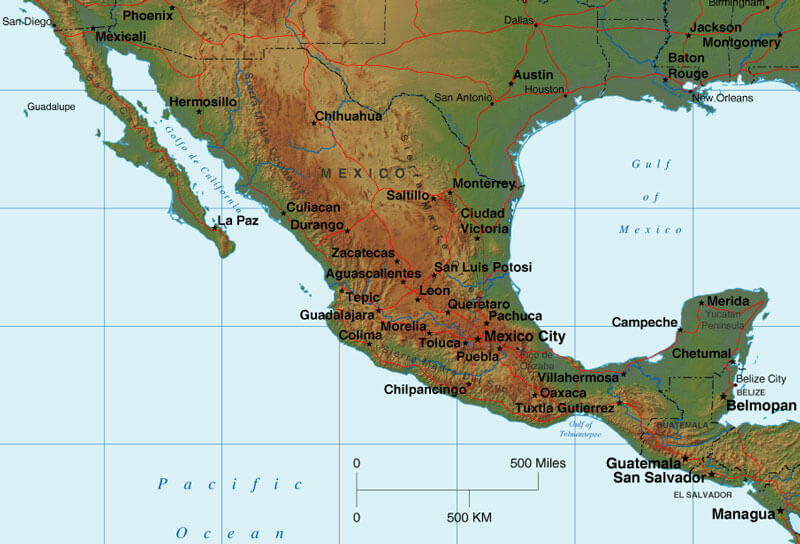
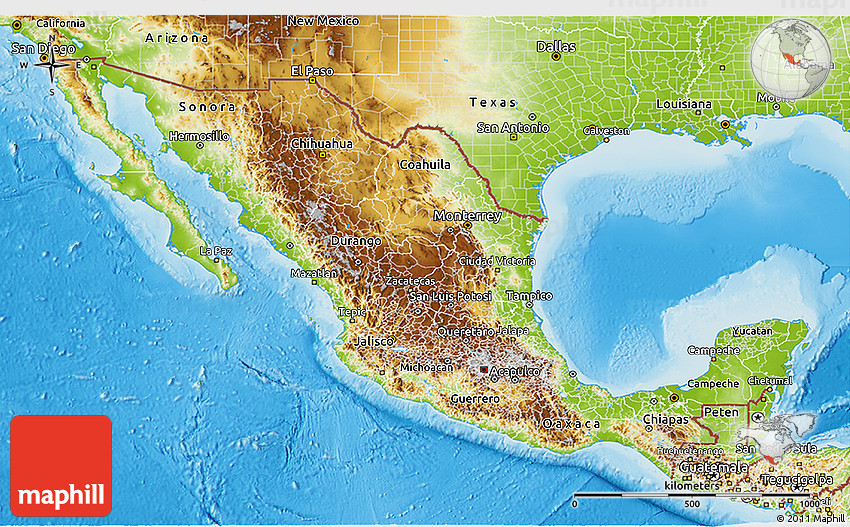
Mexico, a vibrant tapestry of cultures, traditions, and landscapes, boasts a remarkable geographical diversity. The country’s physical features, ranging from towering mountains to expansive deserts, are intricately woven into its history, economy, and cultural identity. Understanding these physical attributes requires a deeper dive into the nation’s relief map, a visual representation of its terrain and elevation. This article delves into the intricacies of Mexico’s relief map, exploring its key features, regional variations, and the profound impact it has on the country’s environment, resources, and human activities.
A Tapestry of Terrain: Key Features of Mexico’s Relief Map
Mexico’s relief map reveals a fascinating interplay of contrasting features, each contributing to the country’s unique character:
-
The Sierra Madre: A Spine of Mountains
The Sierra Madre mountain ranges, stretching across the country like a colossal backbone, dominate Mexico’s landscape. These towering peaks, a testament to the nation’s tectonic history, are further subdivided into three distinct ranges:
-
Sierra Madre Occidental: Located in western Mexico, this range boasts rugged peaks, deep canyons, and extensive forests. The Sierra Madre Occidental is home to the Copper Canyon, a network of canyons even more impressive than the Grand Canyon in the United States.
-
Sierra Madre Oriental: Rising in the east, the Sierra Madre Oriental is characterized by its steep slopes, rugged cliffs, and limestone formations. This range is particularly important for its rich biodiversity, housing numerous endemic species.
-
Sierra Madre del Sur: Stretching along the southern Pacific coast, the Sierra Madre del Sur is marked by its volcanic peaks, fertile valleys, and coastal lowlands. This range is known for its diverse flora and fauna, including the iconic Monarch Butterfly Biosphere Reserve.
-
-
The Mexican Plateau: A Vast Heart of Land
Nestled between the Sierra Madre Occidental and Oriental, the Mexican Plateau is a vast, elevated region known as the "Altiplano." This plateau is characterized by its high altitude, dry climate, and fertile soils, making it a crucial agricultural area for Mexico.
-
The Gulf Coastal Plain: A Fertile Ribbon
Along the Gulf of Mexico, a low-lying plain stretches from the north to the south, forming a fertile region ideal for agriculture. This coastal plain is also home to a vast network of rivers and lagoons, supporting a rich ecosystem.
-
The Pacific Coastal Plain: A Diverse Coastline
The Pacific Coast of Mexico features a more varied landscape, encompassing both coastal plains and rugged mountains. The Pacific Coastal Plain is known for its diverse ecosystems, including beaches, estuaries, and mangrove forests.
-
The Baja California Peninsula: A Desert Oasis
The Baja California Peninsula, a long, narrow strip of land extending southward from the United States, is a unique geographical feature. This peninsula is characterized by its arid climate, diverse desert landscapes, and rich marine life.
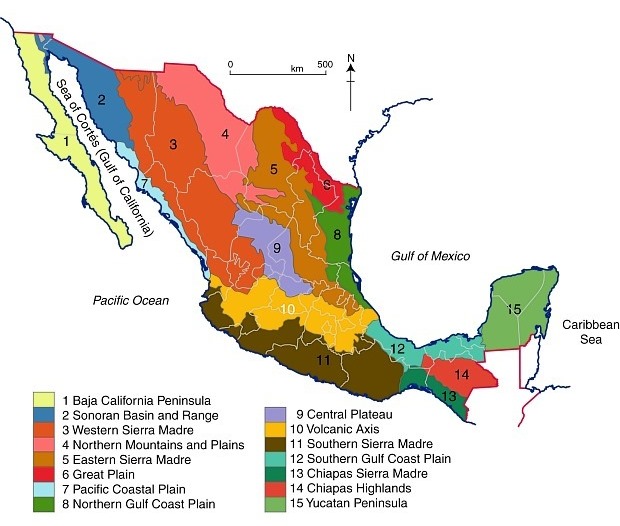
Regional Variations: A Diverse Mosaic of Landscapes
Mexico’s relief map is not a uniform canvas; it reveals a fascinating mosaic of regional variations, each with its unique characteristics and influences:
-
Northern Mexico: A Land of Deserts and Mountains
Northern Mexico is dominated by the arid landscapes of the Chihuahuan Desert and the rugged peaks of the Sierra Madre Occidental. This region is characterized by its sparse vegetation, harsh climate, and significant mineral resources.
-
Central Mexico: A Cradle of Civilization
Central Mexico is home to the Mexican Plateau, a fertile region that has been the cradle of civilization for centuries. The region’s fertile soils, moderate climate, and abundant water resources have supported a thriving agricultural sector and dense populations.
-
Southern Mexico: A Tapestry of Landscapes
Southern Mexico is a diverse region, encompassing the Sierra Madre del Sur, the Gulf Coastal Plain, and the Yucatan Peninsula. This region boasts a rich biodiversity, with lush rainforests, volcanic landscapes, and ancient Mayan ruins.
-
The Yucatan Peninsula: A Land of Limestone and Cenotes
The Yucatan Peninsula is a unique geographical feature, characterized by its flat, limestone terrain and a network of sinkholes known as cenotes. These cenotes, formed by the collapse of limestone, provide access to underground water sources and are a vital part of the region’s ecosystem.
The Impact of Relief on Mexico’s Environment and Resources
Mexico’s relief map plays a critical role in shaping its environment and resources, influencing factors such as:
-
Climate: The country’s diverse relief map contributes to a wide range of climates, from the arid deserts of the north to the tropical rainforests of the south. The Sierra Madre mountain ranges act as barriers, influencing rainfall patterns and creating distinct microclimates.
-
Water Resources: Mexico’s relief map influences the distribution and availability of water resources. The Sierra Madre mountains are the source of numerous rivers and streams, providing water for agriculture, industry, and human consumption.
-
Biodiversity: The country’s diverse relief map supports a rich biodiversity, with different ecosystems harboring unique flora and fauna. The Sierra Madre mountains, for instance, are home to a wide range of endemic species, while the coastal plains support a diverse marine ecosystem.
-
Natural Hazards: Mexico’s relief map also exposes the country to various natural hazards, such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and landslides. The Sierra Madre mountains, along with the Pacific Coast, are particularly prone to seismic activity.
Human Activities and the Relief Map
Mexico’s relief map has a profound impact on human activities, shaping:
-
Agriculture: The fertile soils of the Mexican Plateau and the Gulf Coastal Plain make them ideal for agriculture. The country’s diverse climate zones also support a wide range of crops, from corn and beans to coffee and citrus fruits.
-
Mining: The Sierra Madre mountains are rich in mineral resources, including silver, gold, copper, and lead. Mining is a significant industry in Mexico, contributing to the country’s economy.
-
Tourism: Mexico’s diverse landscapes, from the beaches of the Pacific Coast to the ancient Mayan ruins of the Yucatan Peninsula, attract millions of tourists annually. The country’s unique geological features, such as the Copper Canyon and the Cenotes, are also major tourist attractions.
-
Transportation: Mexico’s relief map presents both challenges and opportunities for transportation. The Sierra Madre mountains pose a barrier to road and rail construction, while the coastal plains offer relatively flat terrain for transportation infrastructure.
FAQs: Understanding Mexico’s Relief Map
Q: What is the highest mountain in Mexico?
A: The highest mountain in Mexico is Pico de Orizaba, also known as Citlaltépetl, with an elevation of 5,636 meters (18,491 feet).
Q: What is the driest region in Mexico?
A: The driest region in Mexico is the Baja California Peninsula, characterized by its arid climate and sparse vegetation.
Q: What is the most important agricultural region in Mexico?
A: The most important agricultural region in Mexico is the Mexican Plateau, known for its fertile soils and moderate climate.
Q: What are the main natural hazards in Mexico?
A: The main natural hazards in Mexico include earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, landslides, and hurricanes.
Q: How does the relief map influence Mexico’s cultural diversity?
A: Mexico’s diverse relief map has contributed to the development of distinct regional cultures, influenced by factors such as climate, resources, and historical interactions.
Tips for Understanding Mexico’s Relief Map
-
Use a physical map: A physical map of Mexico is essential for visualizing the country’s terrain and elevation.
-
Identify key features: Focus on the major features of the relief map, such as the Sierra Madre mountain ranges, the Mexican Plateau, and the coastal plains.
-
Explore regional variations: Pay attention to the distinct characteristics of each region, such as the arid landscapes of the north and the lush rainforests of the south.
-
Consider the impact on human activities: Analyze how the relief map influences agriculture, mining, tourism, and transportation in different regions.
Conclusion: A Tapestry of Landscapes and Opportunities
Mexico’s relief map is a captivating tapestry of diverse landscapes, shaping the country’s environment, resources, and human activities. From the towering peaks of the Sierra Madre mountains to the fertile plains of the Mexican Plateau, each feature contributes to the nation’s unique character and potential. Understanding this intricate relief map is crucial for appreciating the complexity and beauty of Mexico, a country where nature and culture are intertwined in a vibrant and enduring embrace.
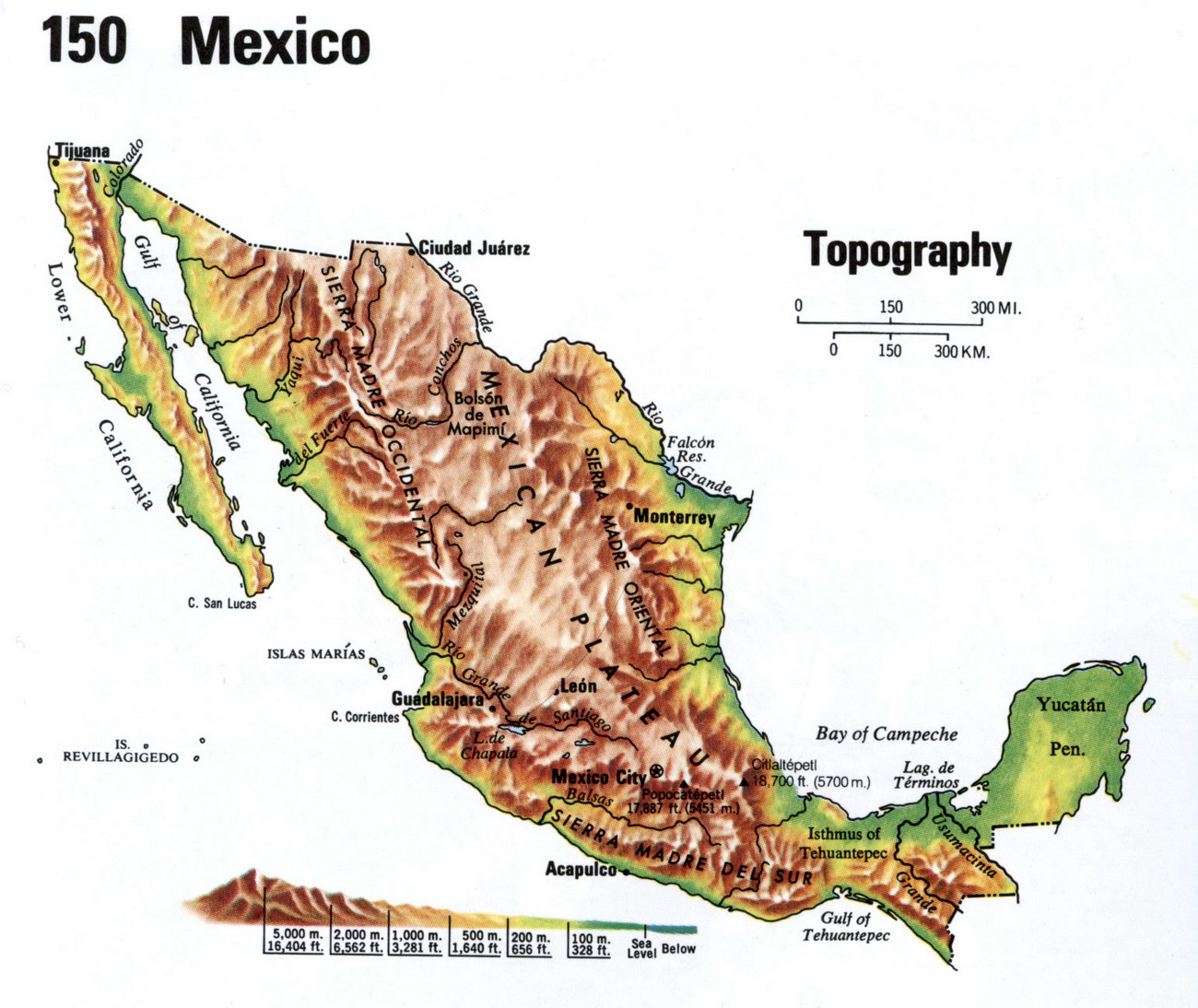
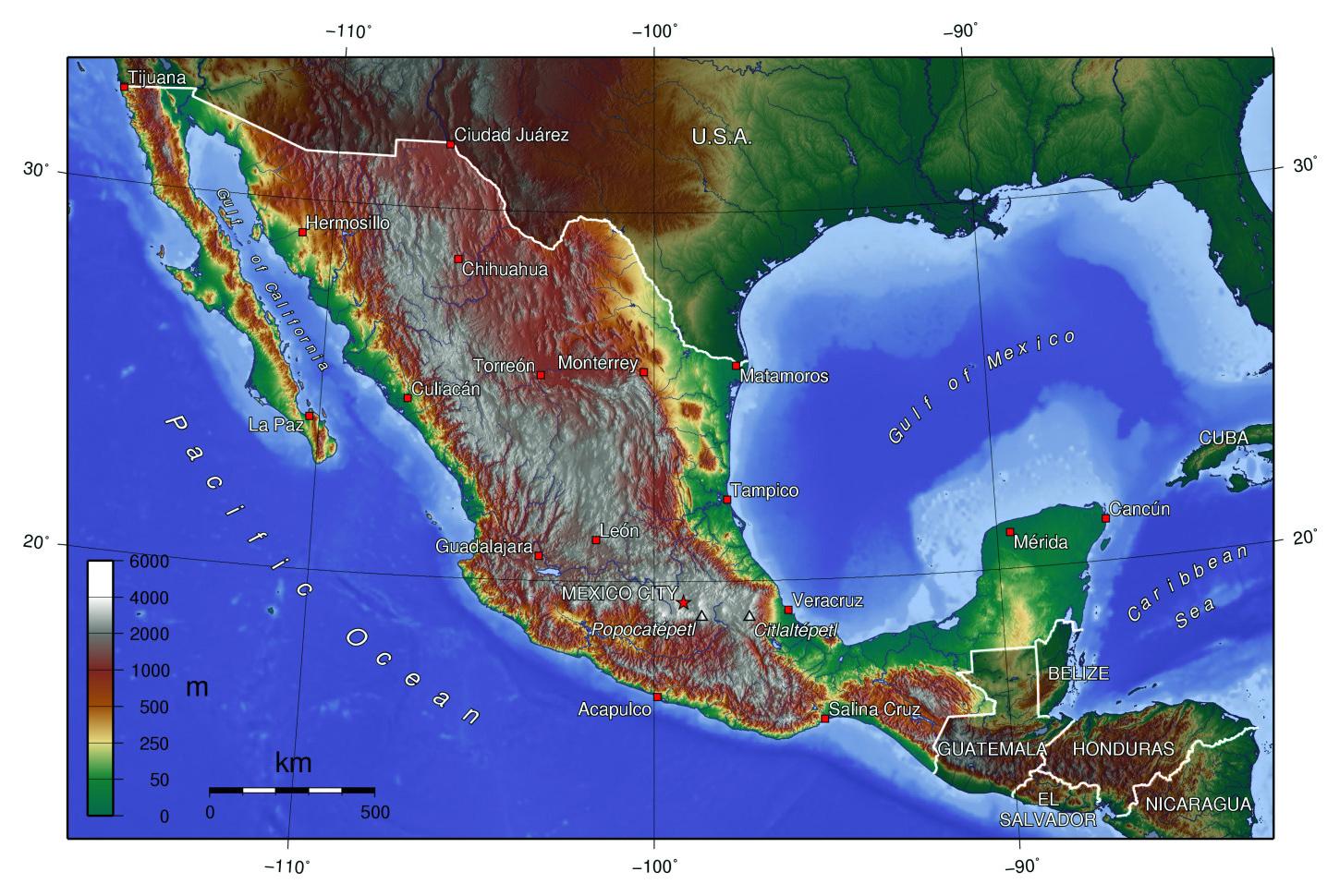


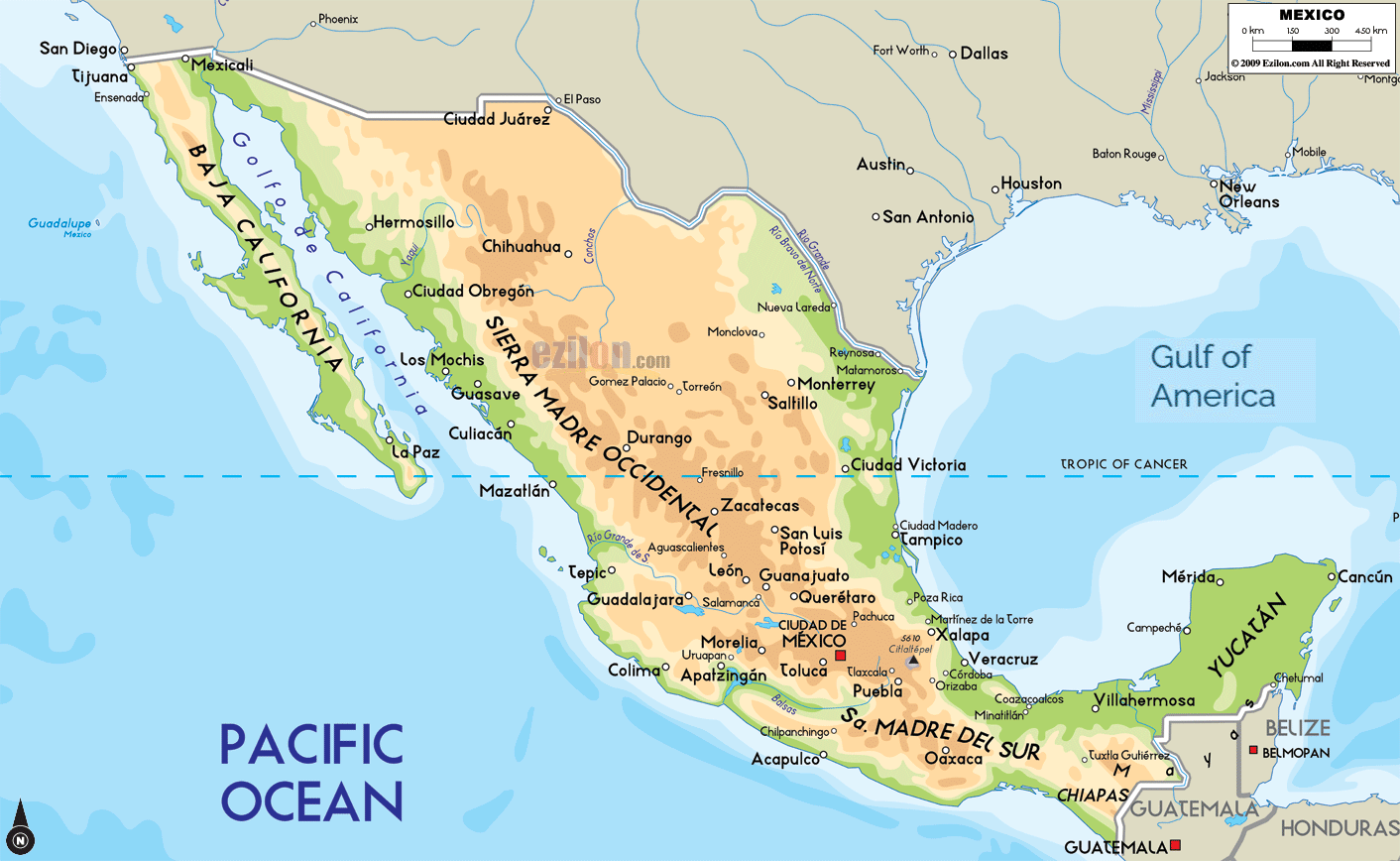

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Diverse Landscape of Mexico: A Comprehensive Look at its Relief Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!