Unveiling the Global Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Carbon Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Global Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Carbon Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Global Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Carbon Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Global Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Carbon Maps
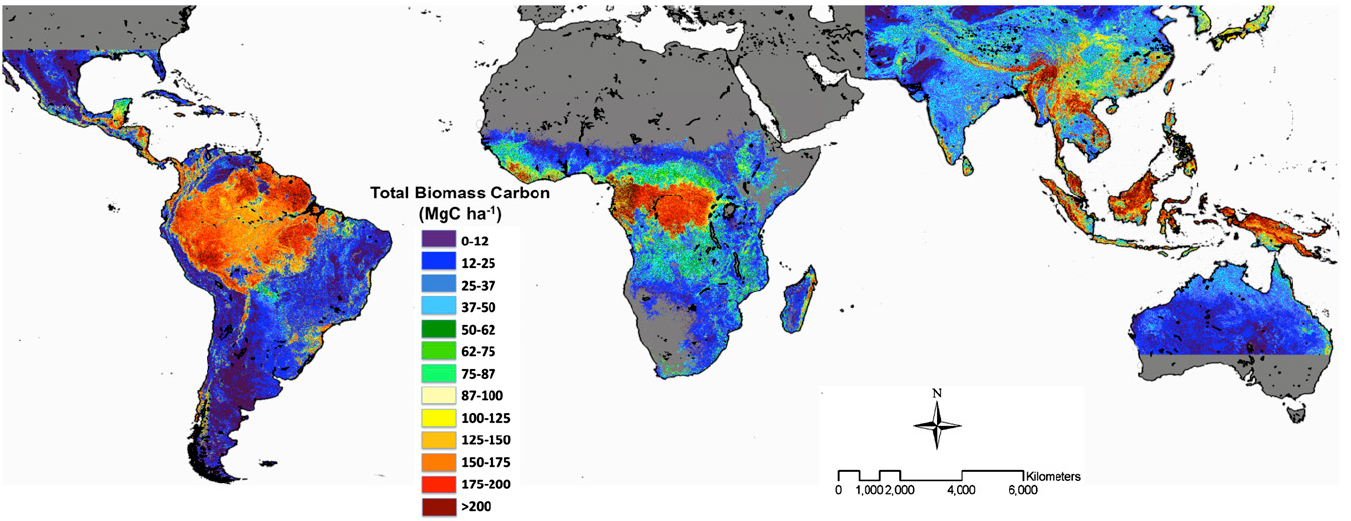
In the face of an increasingly urgent climate crisis, understanding the distribution and sources of greenhouse gas emissions has become paramount. Enter the carbon map, a powerful tool that visualizes and analyzes global carbon footprints, offering invaluable insights for policymakers, businesses, and individuals alike.
Defining the Carbon Map: A Visual Representation of Our Emissions
A carbon map is essentially a graphical representation of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, often displayed on a global or regional scale. It combines data from various sources, including satellite imagery, ground-based monitoring stations, and emission inventories, to create a comprehensive picture of where emissions originate and how they disperse across the globe.
The Significance of Carbon Maps: Illuminating the Path to Sustainability
Carbon maps serve as critical tools for addressing climate change, offering a range of benefits:
1. Enhanced Understanding of Emission Sources: Carbon maps provide a detailed breakdown of emission sources, revealing the sectors and activities responsible for the largest contributions to global warming. This granular level of information empowers policymakers and businesses to implement targeted interventions and mitigation strategies.
2. Identifying Emission Hotspots: By highlighting regions with high concentrations of emissions, carbon maps help prioritize areas for focused climate action. This knowledge allows for the deployment of resources and technologies where they are most needed, maximizing their impact.
3. Tracking Emission Trends: Carbon maps enable the monitoring of emission levels over time, revealing trends and patterns in global carbon footprints. This data is crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of climate policies, identifying emerging emission sources, and adapting strategies as needed.
4. Supporting Sustainable Development: By informing decision-making processes, carbon maps promote sustainable development practices. They help businesses make informed choices about their operations, encouraging the adoption of cleaner technologies and emission reduction strategies.
5. Empowering Individuals: Carbon maps provide individuals with a clearer understanding of their own carbon footprint and the impact of their daily choices. This knowledge empowers them to adopt sustainable practices, reduce their environmental impact, and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Types of Carbon Maps: A Diverse Landscape of Data Visualization
Carbon maps come in various forms, each offering unique perspectives and insights:
1. Global Carbon Maps: These maps depict the distribution of CO2 emissions across the entire planet, providing a comprehensive overview of global carbon footprints.
2. Regional Carbon Maps: Focusing on specific geographic areas, these maps provide localized insights into emission patterns and trends. They are particularly useful for understanding regional variations in emissions and identifying areas with high emission concentrations.
3. Sector-Specific Carbon Maps: These maps focus on specific industries or sectors, revealing their contributions to overall emissions. They are valuable for understanding the carbon footprints of individual sectors and identifying opportunities for targeted emission reductions.
4. Temporal Carbon Maps: These maps visualize changes in emissions over time, revealing trends and patterns in carbon footprints. They are essential for tracking the effectiveness of climate policies and identifying emerging emission sources.
5. Interactive Carbon Maps: Offering dynamic visualizations and data exploration capabilities, these maps allow users to interact with the data, customize views, and gain deeper insights into emission patterns.
Building a Carbon Map: A Multifaceted Process
Creating a comprehensive carbon map requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing:
1. Data Acquisition: This involves gathering data from various sources, including satellite imagery, ground-based monitoring stations, emission inventories, and climate models.
2. Data Processing: The collected data needs to be processed, cleaned, and standardized to ensure consistency and accuracy.
3. Data Visualization: The processed data is then visualized using various mapping techniques, creating graphical representations of emission patterns.
4. Data Analysis: The visualized data is analyzed to identify trends, patterns, and hotspots, providing valuable insights into emission sources and distributions.
5. Data Dissemination: The findings from the carbon map are disseminated to policymakers, businesses, and individuals, informing decision-making processes and promoting climate action.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Carbon Maps
1. What are the limitations of carbon maps?
While carbon maps offer valuable insights, they have certain limitations:
- Data Availability: Data availability and accuracy can vary depending on the region and source.
- Spatial Resolution: Some maps may have limited spatial resolution, making it difficult to pinpoint precise emission sources.
- Temporal Resolution: Data collection frequency can affect the temporal resolution of the map, limiting its ability to capture short-term emission fluctuations.
- Emission Quantification: Carbon maps often focus on CO2 emissions, neglecting other greenhouse gases, which can impact the overall accuracy of the picture.
2. How can carbon maps be used to promote climate action?
Carbon maps serve as powerful tools for promoting climate action by:
- Informing Policymaking: Providing data-driven insights to policymakers, enabling them to develop effective climate policies.
- Encouraging Business Action: Motivating businesses to adopt sustainable practices and reduce their carbon footprints.
- Empowering Individuals: Providing individuals with the knowledge and tools to make informed choices and reduce their own emissions.
3. What are the future directions for carbon mapping?
Future developments in carbon mapping include:
- Improved Data Quality: Continued advancements in data collection and processing techniques will enhance the accuracy and resolution of carbon maps.
- Expanded Coverage: Efforts are underway to expand carbon map coverage to include more regions and greenhouse gases.
- Integration with Other Data: Carbon maps will be increasingly integrated with other data sources, such as climate models and socioeconomic data, providing a more comprehensive understanding of the climate system.
- Interactive Platforms: The development of user-friendly interactive platforms will enhance accessibility and engagement with carbon map data.
Tips for Utilizing Carbon Maps Effectively
To maximize the benefits of carbon maps, consider the following:
- Choose the Right Map: Select a carbon map that aligns with your specific needs and objectives.
- Understand Data Limitations: Be aware of the data limitations and potential biases inherent in carbon maps.
- Interpret Data Carefully: Analyze data carefully and consider contextual factors that may influence emission patterns.
- Engage with Stakeholders: Share carbon map data with relevant stakeholders, promoting collaborative action.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of advancements in carbon mapping technology and data availability.
Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for a Sustainable Future
Carbon maps are essential tools for understanding the global carbon footprint and promoting climate action. They provide valuable insights into emission sources, trends, and hotspots, empowering policymakers, businesses, and individuals to make informed decisions and contribute to a more sustainable future. By harnessing the power of data visualization and analysis, carbon maps are playing a crucial role in shaping a cleaner and more sustainable world.

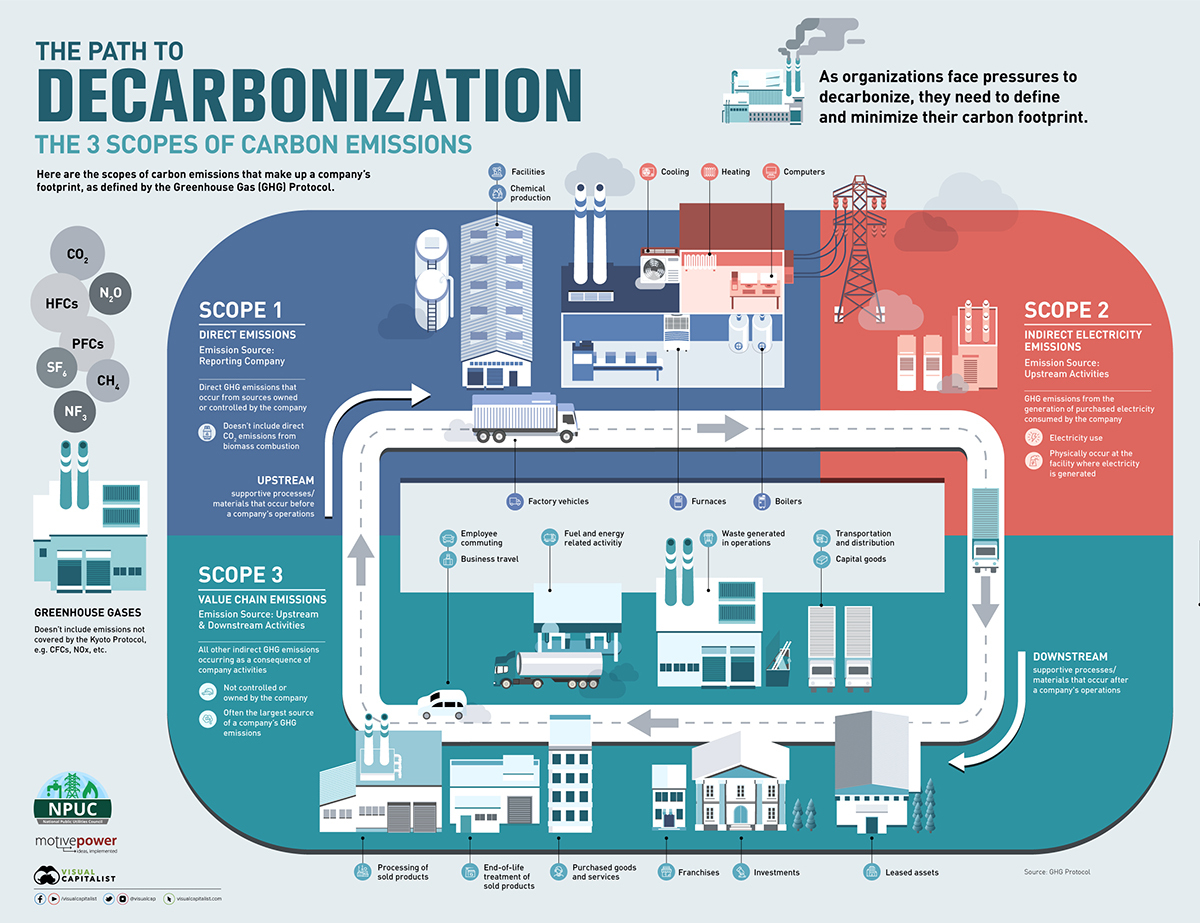
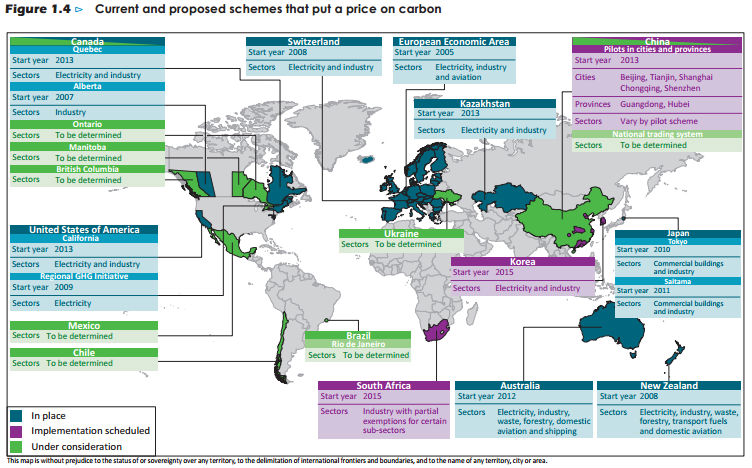
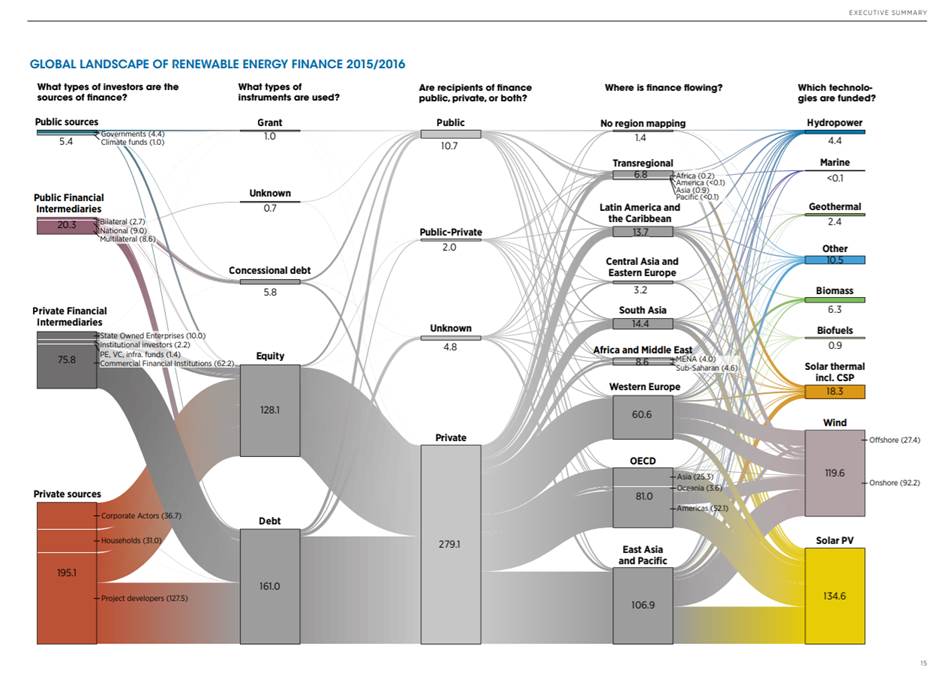

/https://blog.ofbusiness.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/Screenshot-2023-10-12-100908.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Global Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Carbon Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!