Unveiling the Heat: Understanding the Current Heat Index Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Heat: Understanding the Current Heat Index Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Heat: Understanding the Current Heat Index Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Heat: Understanding the Current Heat Index Map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Heat: Understanding the Current Heat Index Map
- 3.1 Deciphering the Heat Index Map: A Guide to Understanding the Data
- 3.2 The Importance of the Heat Index Map: A Beacon of Safety and Awareness
- 3.3 FAQs Regarding the Heat Index Map
- 3.4 Tips for Utilizing the Heat Index Map Effectively
- 3.5 Conclusion: The Heat Index Map – A Tool for Informed Action
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Heat: Understanding the Current Heat Index Map

The summer sun blazes, temperatures soar, and the air feels heavier than usual. This is the time when the heat index, a measure of how hot it feels to the human body, becomes a crucial factor in our daily lives. The heat index map, a visual representation of this perceived temperature across a geographic area, provides invaluable information for individuals, communities, and authorities alike.
Deciphering the Heat Index Map: A Guide to Understanding the Data
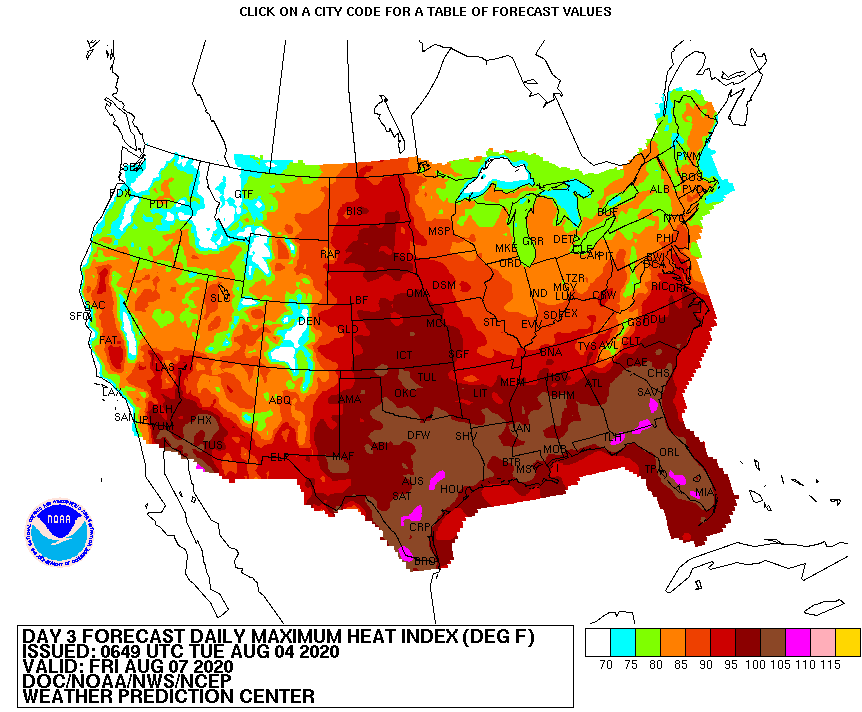
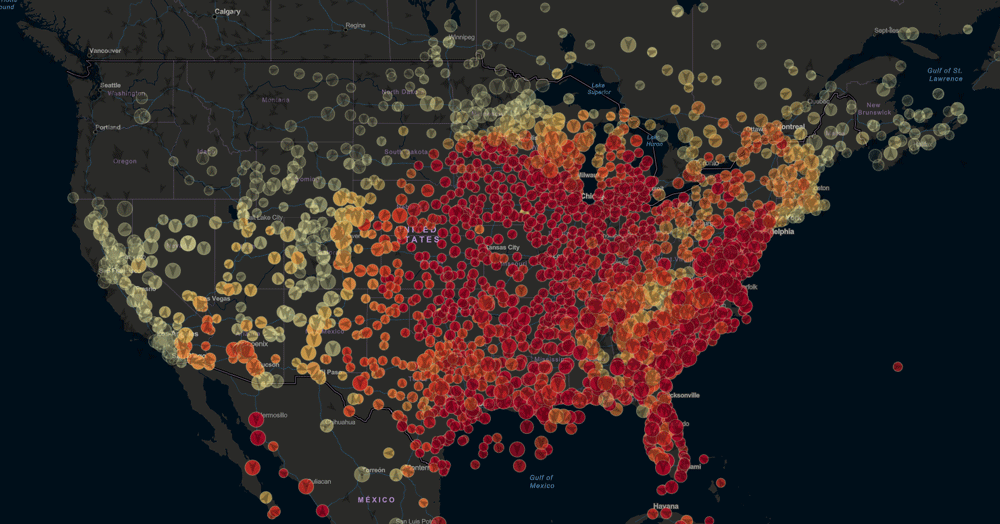
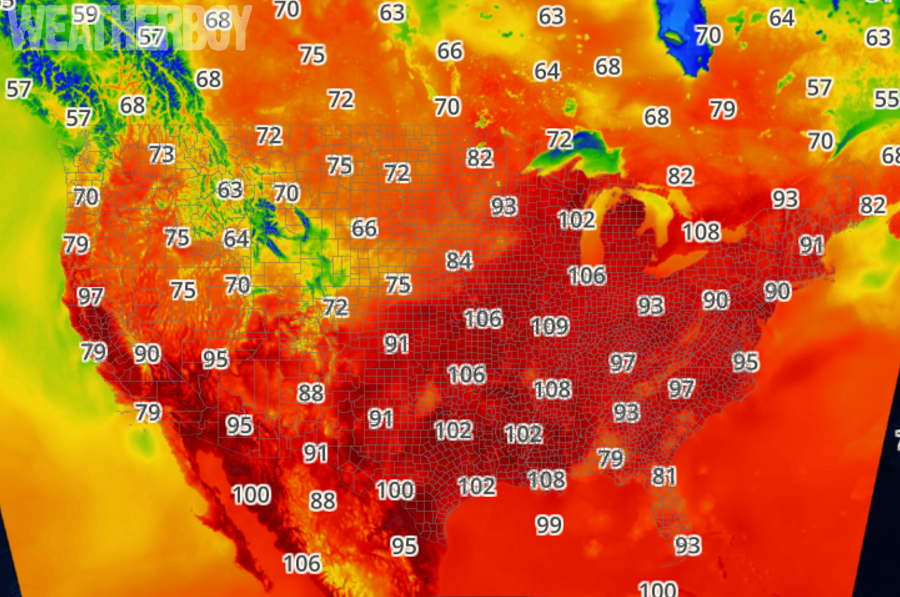
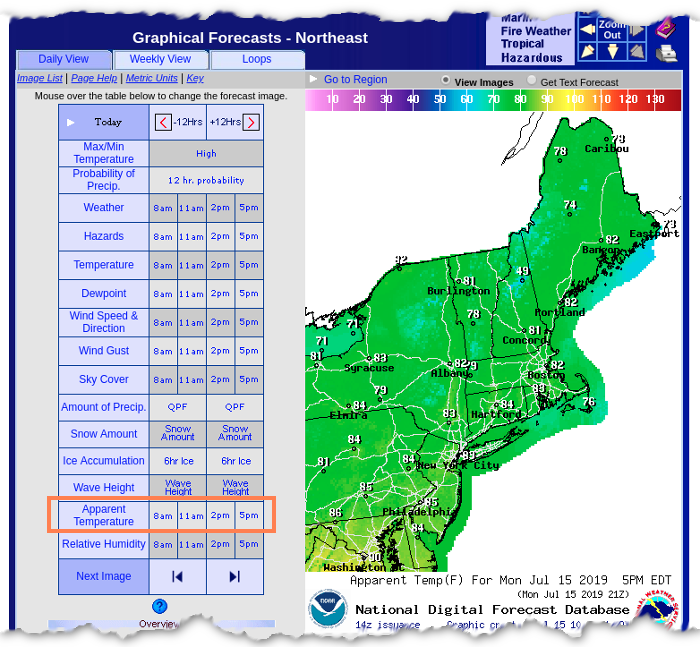
The heat index map, often displayed on weather websites and apps, uses a color-coded system to represent the perceived temperature. Each color corresponds to a specific heat index range, with darker colors indicating higher perceived temperatures. This visual representation allows users to quickly assess the severity of the heat in different locations.
Key Components of the Heat Index Map:
- Geographic Coverage: The map usually covers a specific region, ranging from a local area to a national or even global scale.
- Color Scale: The color scale is standardized, typically employing a gradient from green (low heat index) to red (extreme heat index).
- Numerical Values: Alongside the color scale, numerical values for the heat index are often provided, offering a more precise understanding of the perceived temperature.
- Time Stamp: The heat index map is dynamic, reflecting real-time data. Therefore, a time stamp is crucial to understand the relevance of the information.
Understanding the Heat Index:
The heat index is calculated by considering both the air temperature and the relative humidity. When humidity is high, the air’s ability to evaporate sweat is reduced, making it feel hotter than the actual air temperature. This is because sweat evaporation is our body’s primary mechanism for cooling down.
Interpreting the Heat Index Values:
- Low Heat Index (Green): Temperatures feel comfortable and pose no significant heat-related risks.
- Moderate Heat Index (Yellow): Temperatures are warm, but individuals may experience discomfort and fatigue.
- High Heat Index (Orange): Temperatures are hot, and prolonged exposure can lead to heat exhaustion.
- Very High Heat Index (Red): Temperatures are extremely hot, posing a significant risk of heat stroke and other heat-related illnesses.
The Importance of the Heat Index Map: A Beacon of Safety and Awareness
The heat index map serves as a vital tool for various stakeholders, playing a crucial role in:
Public Safety:
- Heatwave Alerts: Authorities use the heat index map to issue heatwave warnings and advisories, informing the public about potential health risks.
- Emergency Response: First responders can utilize the map to anticipate areas with extreme heat and prioritize resources accordingly.
- Community Outreach: Local organizations can leverage the heat index map to target vulnerable populations with heat-related safety information and support services.
Individual Health and Well-being:
- Informed Decision-Making: Individuals can use the heat index map to plan outdoor activities, choose appropriate clothing, and stay hydrated.
- Heat-Related Illness Prevention: By understanding the perceived temperature, individuals can take preventive measures to avoid heat exhaustion and heat stroke.
- Personal Health Management: Individuals with pre-existing health conditions can use the map to adjust their activities and medication schedules based on the heat index.
Environmental Monitoring:
- Climate Change Impacts: The heat index map provides valuable data for monitoring the impact of climate change on extreme heat events.
- Urban Heat Island Effect: The map can help identify areas with high heat concentrations, aiding in urban planning initiatives to mitigate the urban heat island effect.
- Heat Vulnerability Assessment: The heat index map can be used to assess the vulnerability of communities to extreme heat, informing public health and infrastructure planning.
FAQs Regarding the Heat Index Map
Q: How accurate are heat index maps?
A: The accuracy of heat index maps depends on the quality of the data used in their creation. Reliable maps utilize real-time data from weather stations and other monitoring systems. However, localized variations in temperature and humidity can affect the accuracy of the map.
Q: What are the limitations of the heat index map?
A: The heat index map does not account for individual factors that can influence heat perception, such as age, health conditions, and physical activity levels. It also does not provide information about other environmental factors that can exacerbate heat stress, such as wind speed and solar radiation.
Q: Can I rely on the heat index map for outdoor activities?
A: While the heat index map provides a valuable indication of the perceived temperature, it is crucial to consider individual factors and take appropriate precautions during outdoor activities. Seek shade, stay hydrated, and take breaks to avoid overheating.
Q: How can I stay safe during extreme heat events?
A: Consult the heat index map for your area, stay hydrated, avoid strenuous activities during the hottest part of the day, wear light-colored clothing, and seek air-conditioned environments when possible.
Q: Is there a difference between the heat index and the actual temperature?
A: Yes, the heat index is a measure of how hot it feels to the human body, taking into account both air temperature and humidity. The actual temperature refers to the air temperature measured by a thermometer.
Q: How often are heat index maps updated?
A: The frequency of updates varies depending on the source of the data. Many weather websites and apps update their heat index maps every few minutes, ensuring real-time information.
Tips for Utilizing the Heat Index Map Effectively
- Check the Time Stamp: Ensure the heat index map you are using is current, as the data can change rapidly.
- Consider Local Variations: The heat index can vary significantly even within a small geographic area. Consider factors such as proximity to bodies of water, urban heat islands, and vegetation cover.
- Pay Attention to Color Coding: Understand the color scale and the corresponding heat index ranges to effectively interpret the map.
- Use the Heat Index as a Guide: The heat index map should be used as a guide to inform your decisions, not as a definitive measure of safety.
- Take Individual Factors into Account: Remember that the heat index is a general measure and does not account for individual differences in heat tolerance.
Conclusion: The Heat Index Map – A Tool for Informed Action
The heat index map is a valuable tool for understanding and responding to extreme heat events. By providing a visual representation of the perceived temperature, it empowers individuals, communities, and authorities to make informed decisions regarding health, safety, and environmental management. As climate change continues to drive increases in extreme heat, the heat index map will become increasingly crucial for mitigating the impacts of rising temperatures and protecting public well-being.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Heat: Understanding the Current Heat Index Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!