Unveiling The Secrets Of Africa’s Rainfall: A Comprehensive Guide To The Africa Rain Map
Unveiling the Secrets of Africa’s Rainfall: A Comprehensive Guide to the Africa Rain Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of Africa’s Rainfall: A Comprehensive Guide to the Africa Rain Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets of Africa’s Rainfall: A Comprehensive Guide to the Africa Rain Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Secrets of Africa’s Rainfall: A Comprehensive Guide to the Africa Rain Map

Africa, a continent of vast and diverse landscapes, experiences a complex and dynamic rainfall pattern. Understanding this pattern is crucial for various sectors, from agriculture and water resource management to public health and disaster preparedness. The Africa Rain Map, a visual representation of rainfall distribution across the continent, provides valuable insights into the intricacies of precipitation patterns and their impact on the African landscape and its inhabitants.
The Importance of Rainfall in Africa
Rainfall is a fundamental lifeblood for Africa, playing a pivotal role in shaping its ecosystems, supporting its population, and driving its economy.
- Agriculture: Africa is home to a significant agricultural sector, with a large portion of its population relying on rain-fed agriculture. Consistent rainfall is essential for crop production, ensuring food security and economic stability.
- Water Resources: Rainfall replenishes rivers, lakes, and groundwater, providing vital water resources for drinking, irrigation, and industrial use. Water scarcity, often linked to unpredictable rainfall patterns, poses a significant challenge to development in many parts of Africa.
- Biodiversity: Rainfall patterns influence the distribution and diversity of flora and fauna across the continent. Different rainfall zones support unique ecosystems, from lush rainforests to arid deserts.
- Public Health: Rainfall can impact public health through the spread of waterborne diseases like malaria and cholera. Understanding rainfall patterns is crucial for disease prevention and control.
- Disaster Preparedness: Extreme rainfall events, including droughts and floods, can lead to natural disasters with devastating consequences. Rainfall data helps predict and prepare for these events, minimizing their impact.
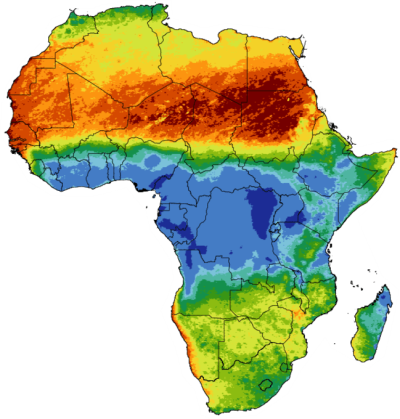
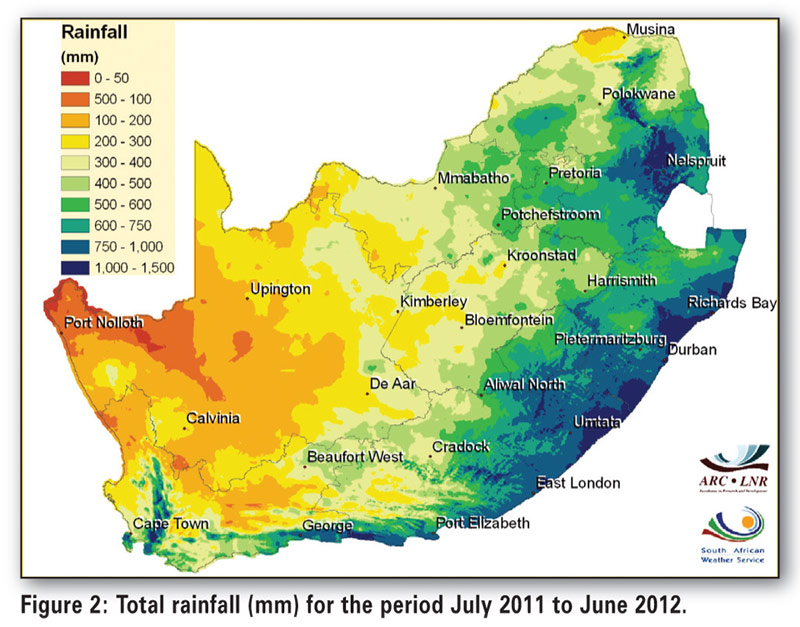
Understanding the Africa Rain Map
The Africa Rain Map is a powerful tool for visualizing rainfall patterns across the continent. It typically depicts rainfall distribution by:
- Spatial Variations: The map highlights regional differences in rainfall, showing areas that receive high, moderate, and low precipitation.
- Temporal Variations: The map can display rainfall patterns over time, such as seasonal variations, annual trends, and long-term changes.
- Data Sources: The map draws data from various sources, including weather stations, satellite observations, and climate models.
Interpreting the Africa Rain Map
The Africa Rain Map reveals a complex and diverse rainfall pattern across the continent, influenced by several factors:
- Latitude: The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), a band of low pressure and high rainfall, shifts north and south seasonally, impacting rainfall across equatorial Africa.
- Altitude: Higher altitudes generally experience higher rainfall due to orographic lift, where air is forced upwards by mountains, leading to condensation and precipitation.
- Oceanic Influences: The Atlantic and Indian Oceans influence rainfall patterns through trade winds and monsoon systems.
- Vegetation: Forests and other vegetation types can influence rainfall patterns through evapotranspiration, the process of water moving from the ground to the atmosphere.
Key Features of the Africa Rain Map
- The Equatorial Rain Belt: This zone, located around the equator, experiences consistent rainfall throughout the year, supporting lush rainforests and diverse ecosystems.
- The Sahel: This semi-arid region bordering the Sahara Desert experiences a distinct dry season and a short, intense rainy season.
- The Horn of Africa: This region experiences a bimodal rainfall pattern with two rainy seasons, typically associated with the monsoon winds.
- Southern Africa: The southern part of the continent experiences a more seasonal rainfall pattern, with a wet season during summer months and a dry season during winter.
Benefits of the Africa Rain Map
The Africa Rain Map provides numerous benefits for various stakeholders:
- Farmers: The map helps farmers understand local rainfall patterns, allowing them to optimize planting schedules and irrigation strategies, improving crop yields and ensuring food security.
- Water Resource Managers: The map provides valuable data for water resource management, helping to identify areas prone to drought or flooding and plan for water conservation and distribution.
- Government Agencies: The map supports disaster preparedness and response efforts, enabling authorities to anticipate and mitigate the impacts of extreme weather events.
- Scientists: The map serves as a valuable tool for research, allowing scientists to study rainfall patterns, climate change impacts, and the dynamics of African ecosystems.
FAQs on the Africa Rain Map
Q: What are the main sources of rainfall data for the Africa Rain Map?
A: The Africa Rain Map utilizes data from various sources, including:
- Weather Stations: Networks of ground-based weather stations provide real-time rainfall measurements.
- Satellite Observations: Satellites equipped with rain-detecting sensors provide comprehensive coverage of rainfall patterns across the continent.
- Climate Models: Numerical models simulate rainfall patterns based on atmospheric conditions, providing insights into future trends.
Q: How accurate is the Africa Rain Map?
A: The accuracy of the Africa Rain Map depends on the quality and availability of data sources. While weather stations provide precise local data, satellite observations can be less accurate in areas with dense vegetation or cloud cover. Climate models provide estimates of rainfall patterns but are subject to uncertainties.
Q: How does climate change affect rainfall patterns in Africa?
A: Climate change is expected to alter rainfall patterns in Africa, leading to:
- Increased Variability: Rainfall patterns are becoming more unpredictable, with more frequent and intense droughts and floods.
- Shifting Rainfall Zones: The ITCZ is predicted to shift northward, potentially leading to increased rainfall in some regions and decreased rainfall in others.
- Changes in Seasonality: The timing and duration of rainy seasons are expected to change, impacting agricultural practices and water resources.
Q: What are the implications of changing rainfall patterns in Africa?
A: Changing rainfall patterns have significant implications for Africa, including:
- Food Security: Increased drought and flood events threaten agricultural productivity, leading to food insecurity and potential famine.
- Water Scarcity: Changing rainfall patterns can exacerbate water scarcity in already water-stressed regions, impacting drinking water supply and agricultural production.
- Migration and Conflict: Climate-induced migration and resource scarcity can lead to social unrest and conflict.
- Biodiversity Loss: Altered rainfall patterns can disrupt ecosystems, leading to habitat loss and biodiversity decline.
Tips for Utilizing the Africa Rain Map
- Consult Multiple Sources: Compare data from different sources to obtain a more comprehensive understanding of rainfall patterns.
- Consider Time Scales: Analyze rainfall data over different time scales, such as seasonal, annual, and decadal, to identify long-term trends.
- Factor in Local Conditions: Understand the influence of local factors, such as altitude, vegetation, and proximity to water bodies, on rainfall patterns.
- Collaborate with Experts: Engage with experts in meteorology, climatology, and agriculture to interpret rainfall data and develop effective strategies for adaptation and mitigation.
Conclusion
The Africa Rain Map serves as a vital tool for understanding the complex and dynamic rainfall patterns across the continent. By visualizing rainfall distribution and its variations, the map provides valuable insights for various sectors, from agriculture and water management to public health and disaster preparedness. As climate change continues to influence rainfall patterns, the Africa Rain Map becomes even more crucial for informed decision-making and sustainable development in Africa.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets of Africa’s Rainfall: A Comprehensive Guide to the Africa Rain Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!