Unveiling Value: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating a Value Stream Map
Related Articles: Unveiling Value: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating a Value Stream Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Value: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating a Value Stream Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Value: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating a Value Stream Map
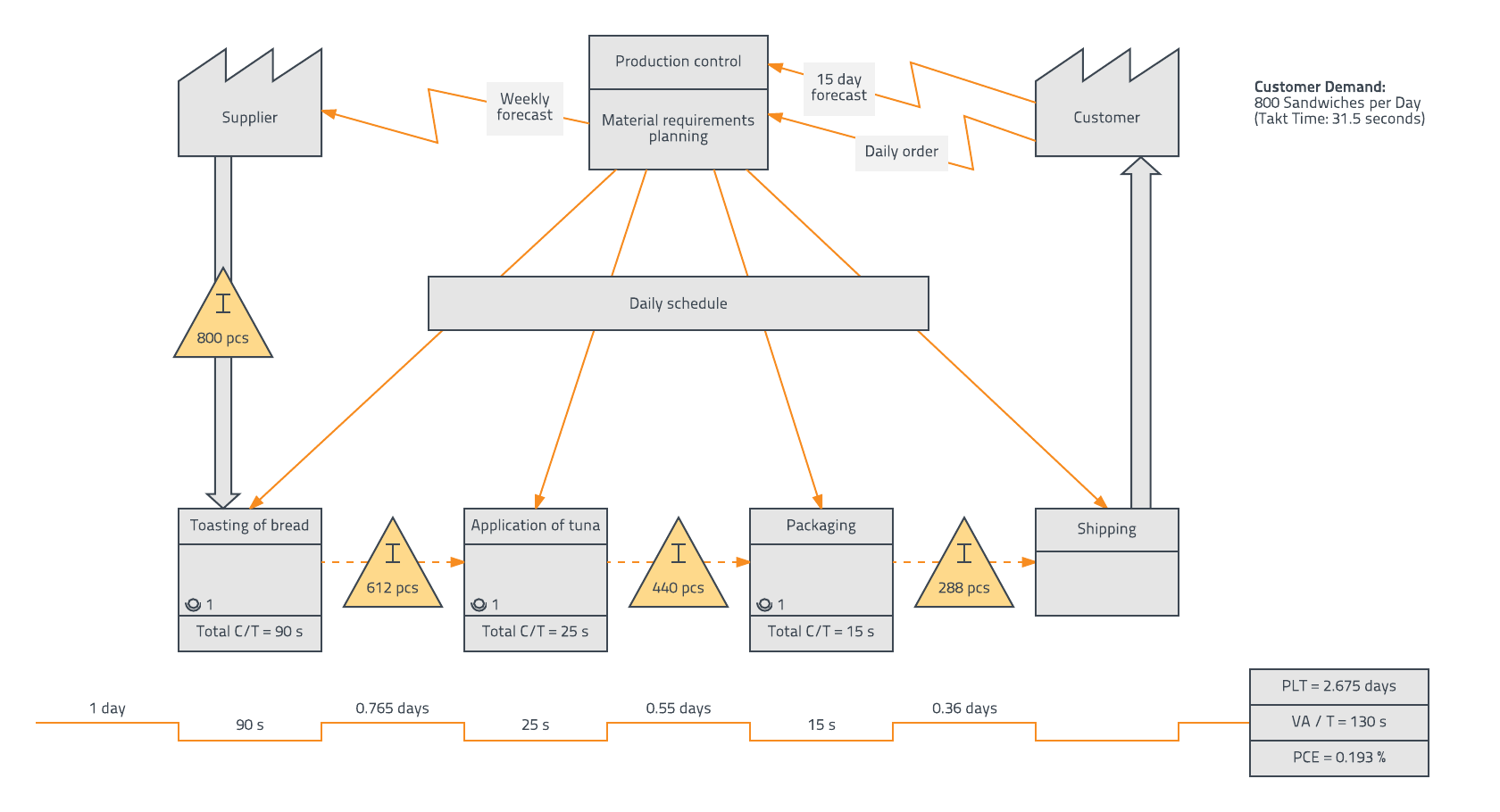
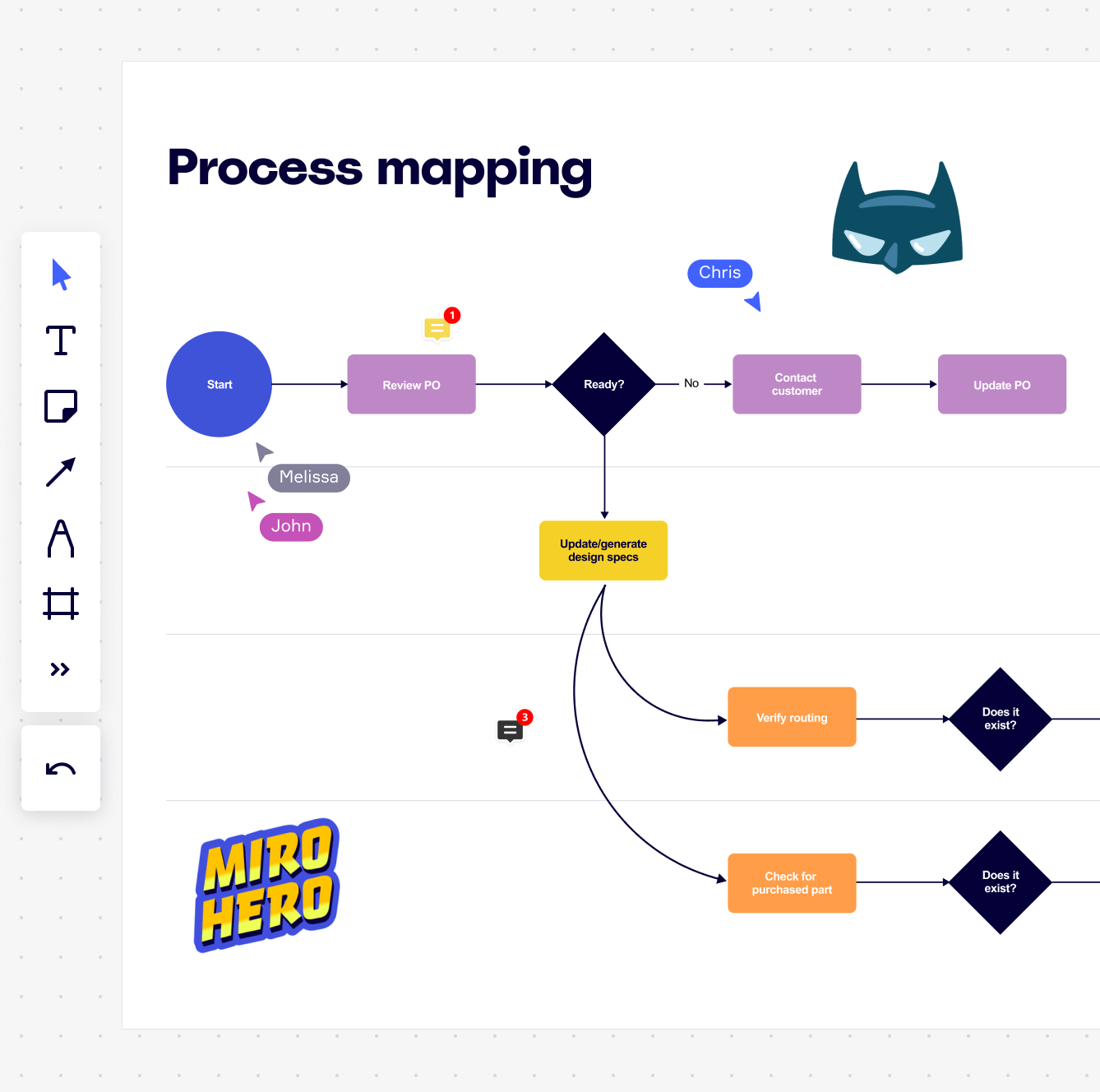
In the realm of process improvement and operational efficiency, the value stream map stands as a powerful tool for visualizing and understanding the flow of value creation within an organization. This visual representation, often depicted as a flowchart, provides a comprehensive view of all activities involved in delivering a product or service to the customer, from the initial raw materials to the final delivery.
Understanding the Importance of Value Stream Mapping
The value stream map serves as a roadmap for identifying inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement within a process. By revealing the intricate dance of activities, resources, and information, it offers a clear picture of how value is created and delivered, highlighting both the essential and the non-essential steps. This understanding empowers organizations to:
- Identify and Eliminate Waste: By visualizing the entire value stream, organizations can identify and eliminate activities that do not add value for the customer, such as unnecessary delays, rework, or excessive inventory. This streamlining process optimizes resource allocation and enhances efficiency.
- Reduce Lead Time: By pinpointing bottlenecks and areas of inefficiency, organizations can identify opportunities to shorten the time it takes to deliver a product or service to the customer. This reduction in lead time improves responsiveness and enhances customer satisfaction.
- Improve Communication and Collaboration: The value stream map fosters a shared understanding of the process among all stakeholders, including employees, managers, and customers. This transparency promotes better communication, collaboration, and alignment across departments.
- Drive Continuous Improvement: The value stream map serves as a living document, reflecting the ongoing efforts to optimize the process. As improvements are implemented, the map is updated to reflect the changes, creating a cycle of continuous improvement and innovation.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Value Stream Map
Creating a value stream map is a systematic process that involves careful observation, data collection, and collaborative analysis. The following steps provide a comprehensive framework for developing a valuable and insightful map:
1. Define the Value Stream:
- Choose a specific product or service: The value stream map should focus on a single product or service, allowing for a detailed analysis of its journey through the organization.
- Identify the customer: Clearly define the end customer who receives the value from the product or service. This helps to ensure that the map reflects the customer’s perspective and needs.
- Set the scope: Determine the starting and ending points of the value stream. This might include the sourcing of raw materials, the manufacturing process, the distribution network, and the final delivery to the customer.
2. Map the Current State:
- Identify the key activities: Document all activities involved in the value stream, from the initial procurement of materials to the final delivery of the product or service. This includes both physical and information-based activities.
- Determine the process flow: Trace the path of the product or service through the value stream, noting the sequence of activities and the flow of information.
- Collect data: Gather data on the time, cost, and resources associated with each activity. This data will be used to identify potential areas for improvement.
- Identify waste: Analyze the activities and data to identify any non-value-adding activities, such as delays, rework, or excessive inventory.
3. Analyze the Current State:
- Identify bottlenecks: Analyze the data to identify the activities that are the slowest or most expensive in the value stream. These bottlenecks represent areas where improvement efforts can have the greatest impact.
- Identify opportunities for improvement: Analyze the map to identify potential areas where the process could be streamlined, simplified, or automated.
- Prioritize improvement opportunities: Based on the analysis, prioritize the improvement opportunities based on their potential impact and feasibility.
4. Map the Future State:
- Develop a vision for improvement: Based on the analysis of the current state, define a vision for the future state of the value stream. This vision should outline the desired improvements in terms of lead time, cost, quality, and customer satisfaction.
- Develop improvement actions: Identify specific actions that can be taken to achieve the desired future state. These actions might involve eliminating waste, streamlining processes, automating activities, or improving communication.
- Map the future state: Create a new value stream map that reflects the proposed improvements. This map should show the new process flow, the elimination of waste, and the anticipated benefits of the changes.
5. Implement and Monitor:
- Implement the improvements: Put the identified improvement actions into practice. This may involve changes to processes, technology, or employee training.
- Monitor the results: Track the impact of the changes on the value stream. Measure the improvements in lead time, cost, quality, and customer satisfaction.
- Continuously improve: Use the data collected to identify further opportunities for improvement. The value stream map should be a living document that is updated regularly to reflect the ongoing efforts to optimize the process.
Tips for Creating an Effective Value Stream Map
- Engage the right people: Involve all relevant stakeholders in the process, including employees, managers, and customers. This ensures that the map reflects the perspectives and needs of everyone involved.
- Use a standardized template: Utilize a standardized template to ensure consistency and clarity in the map. This makes it easier to compare different value streams and track progress over time.
- Keep it simple and visual: The value stream map should be easy to understand and interpret. Use clear and concise language, and employ visual elements such as symbols, arrows, and colors to enhance clarity.
- Focus on value: Remember that the goal of the value stream map is to identify and eliminate waste. Focus on activities that add value for the customer and eliminate those that do not.
- Use technology: Leverage digital tools and software to create and manage value stream maps. These tools can facilitate collaboration, data collection, and analysis.
FAQs About Value Stream Mapping
1. What are the different types of value stream maps?
There are several types of value stream maps, each designed to focus on different aspects of the process. Some common types include:
- Current State Map: Depicts the existing process flow, including all activities, resources, and delays.
- Future State Map: Visualizes the proposed improvements to the process, showing the elimination of waste and the anticipated benefits.
- Material and Information Flow Map: Focuses on the flow of materials and information within the value stream.
- Lean Value Stream Map: Emphasizes the elimination of waste and the creation of a leaner, more efficient process.
2. What are the benefits of using a value stream map?
Value stream mapping offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved efficiency: Identifying and eliminating waste leads to a more efficient and streamlined process.
- Reduced lead time: Shortening the time it takes to deliver a product or service enhances customer satisfaction.
- Enhanced communication: The map promotes better communication and collaboration among stakeholders.
- Increased profitability: Streamlining the process and reducing waste can lead to significant cost savings and increased profitability.
- Improved customer satisfaction: Delivering products or services faster and more efficiently leads to a better customer experience.
3. How often should value stream maps be updated?
The frequency of updates depends on the nature of the process and the rate of change within the organization. However, it is generally recommended to update the map at least once a year to reflect any changes in the process or the business environment.
4. What are some common mistakes to avoid when creating a value stream map?
- Overcomplicating the map: Avoid including too much detail or unnecessary information. Keep the map simple and focused on the key activities.
- Failing to involve all stakeholders: Ensure that all relevant stakeholders are involved in the process to ensure a comprehensive and accurate map.
- Ignoring data: Collect and analyze data to support the map and identify areas for improvement.
- Not updating the map: Regularly update the map to reflect changes in the process and the business environment.
Conclusion
The value stream map is a powerful tool for understanding and improving the flow of value within an organization. By visualizing the entire process, identifying waste, and implementing improvements, organizations can achieve significant gains in efficiency, lead time, and customer satisfaction. This comprehensive guide provides a step-by-step framework for creating a valuable and insightful value stream map, empowering organizations to unlock their full potential for operational excellence.
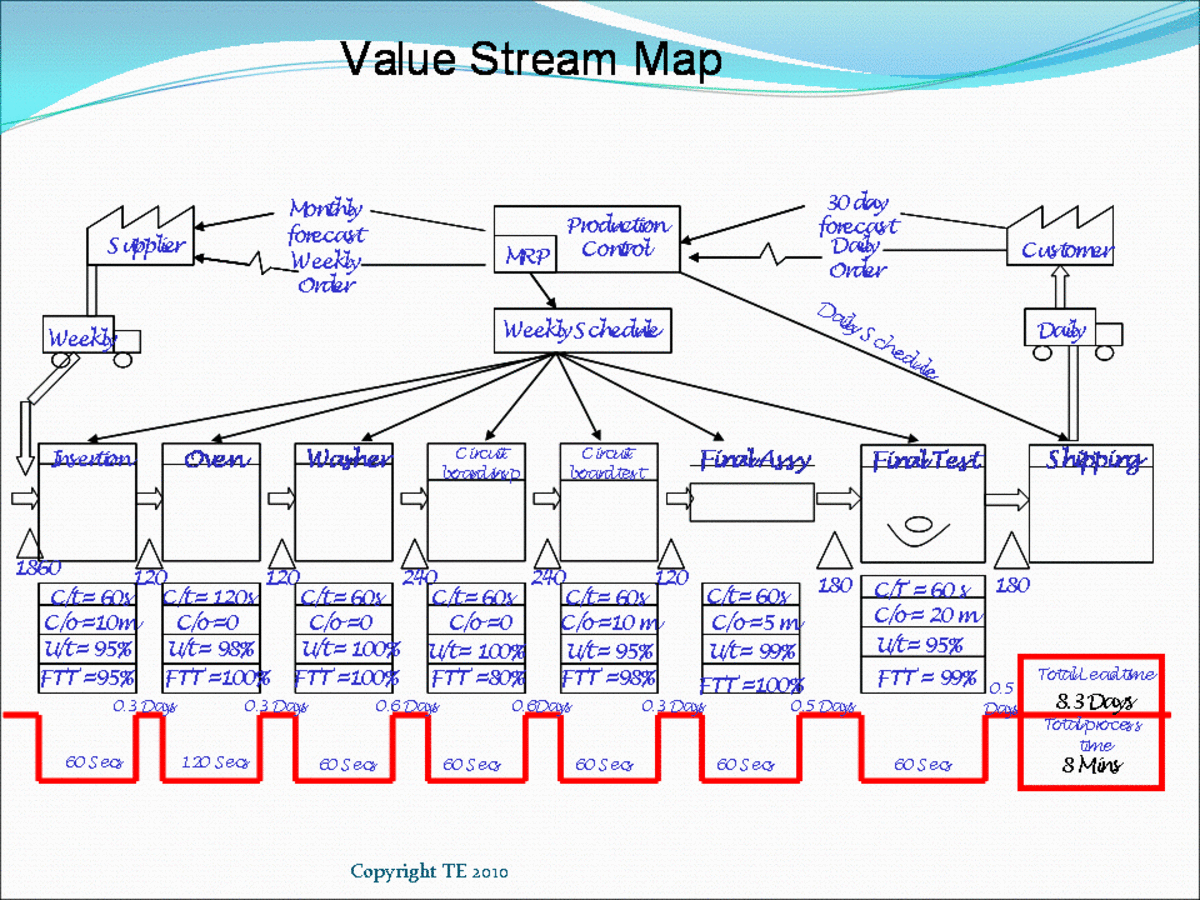
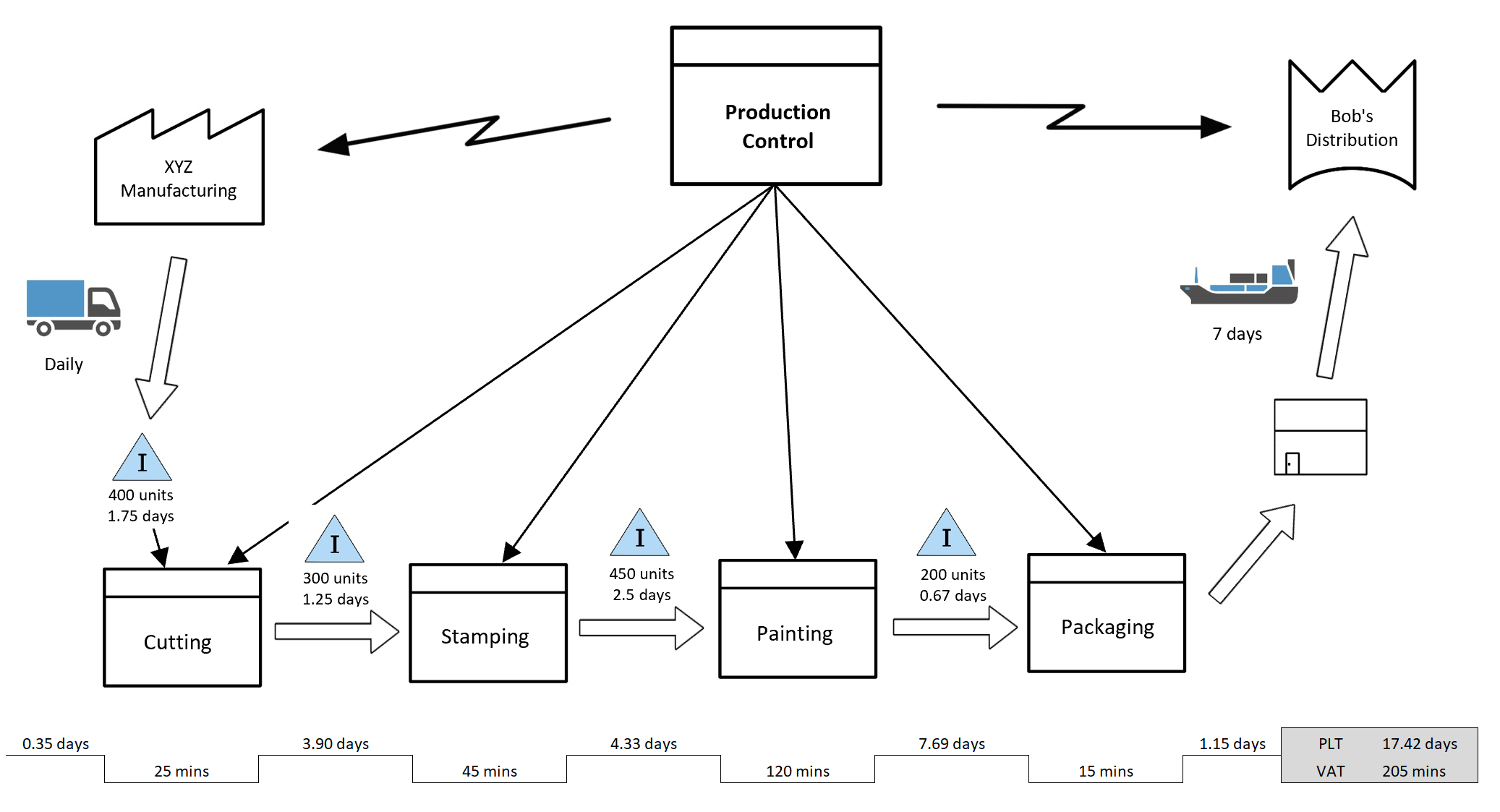
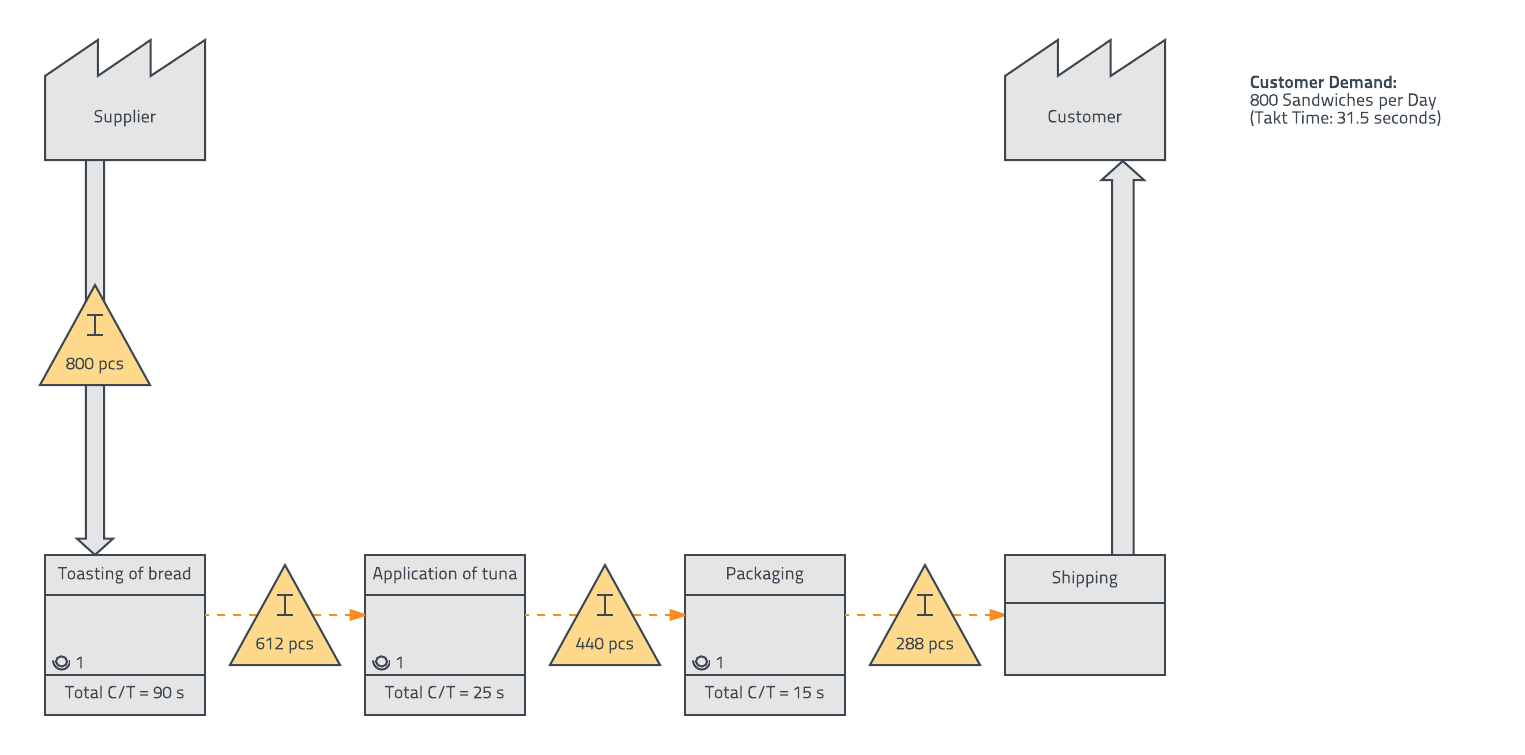

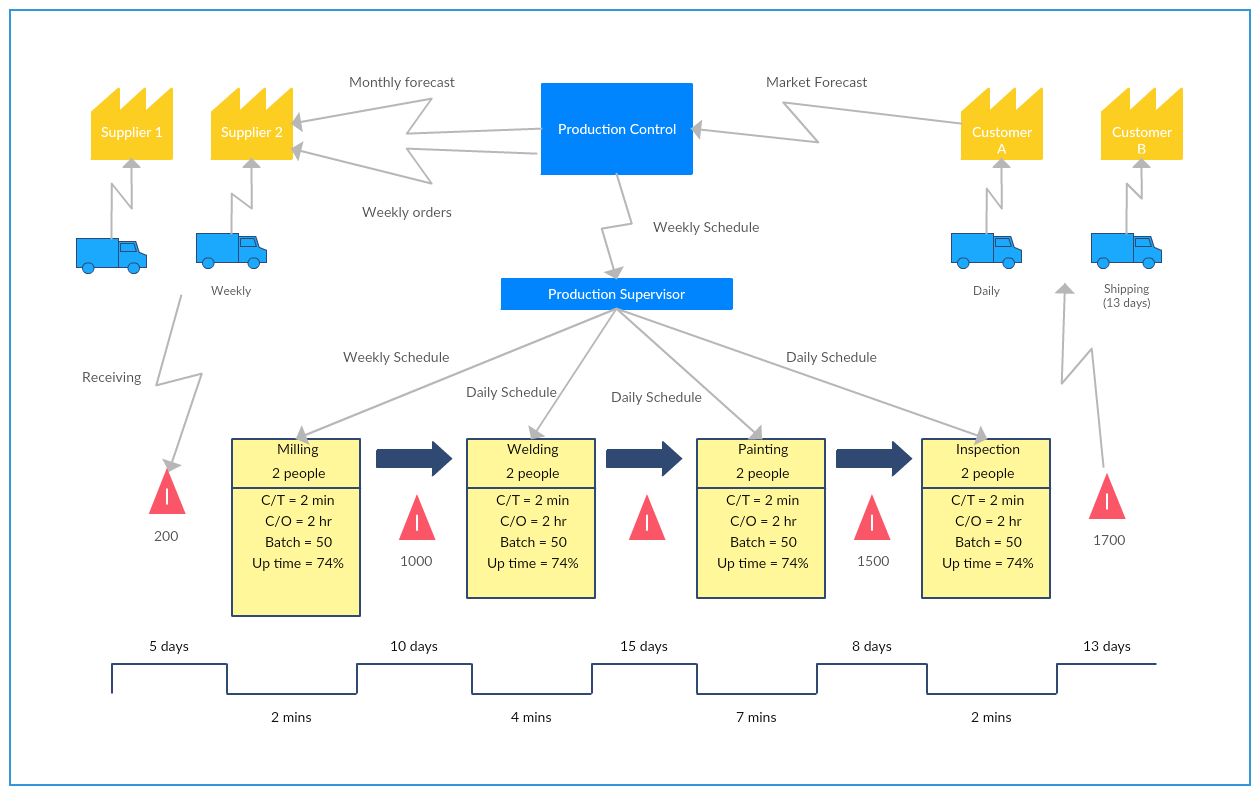
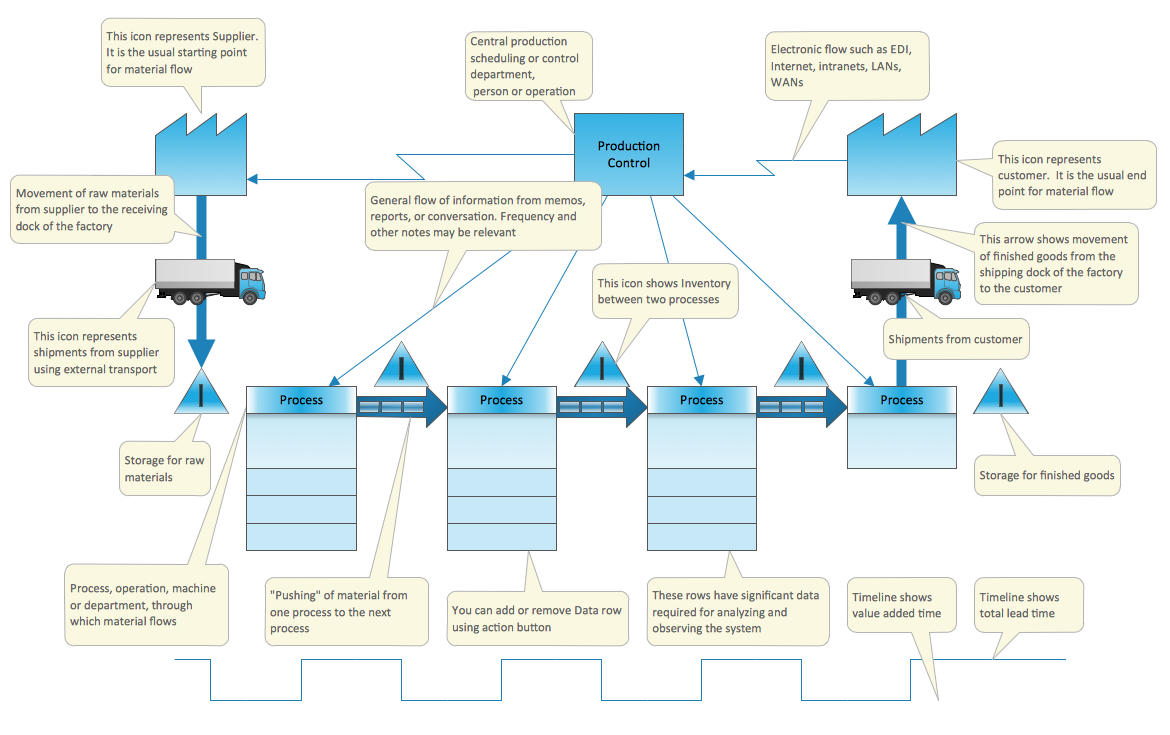

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Value: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating a Value Stream Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!